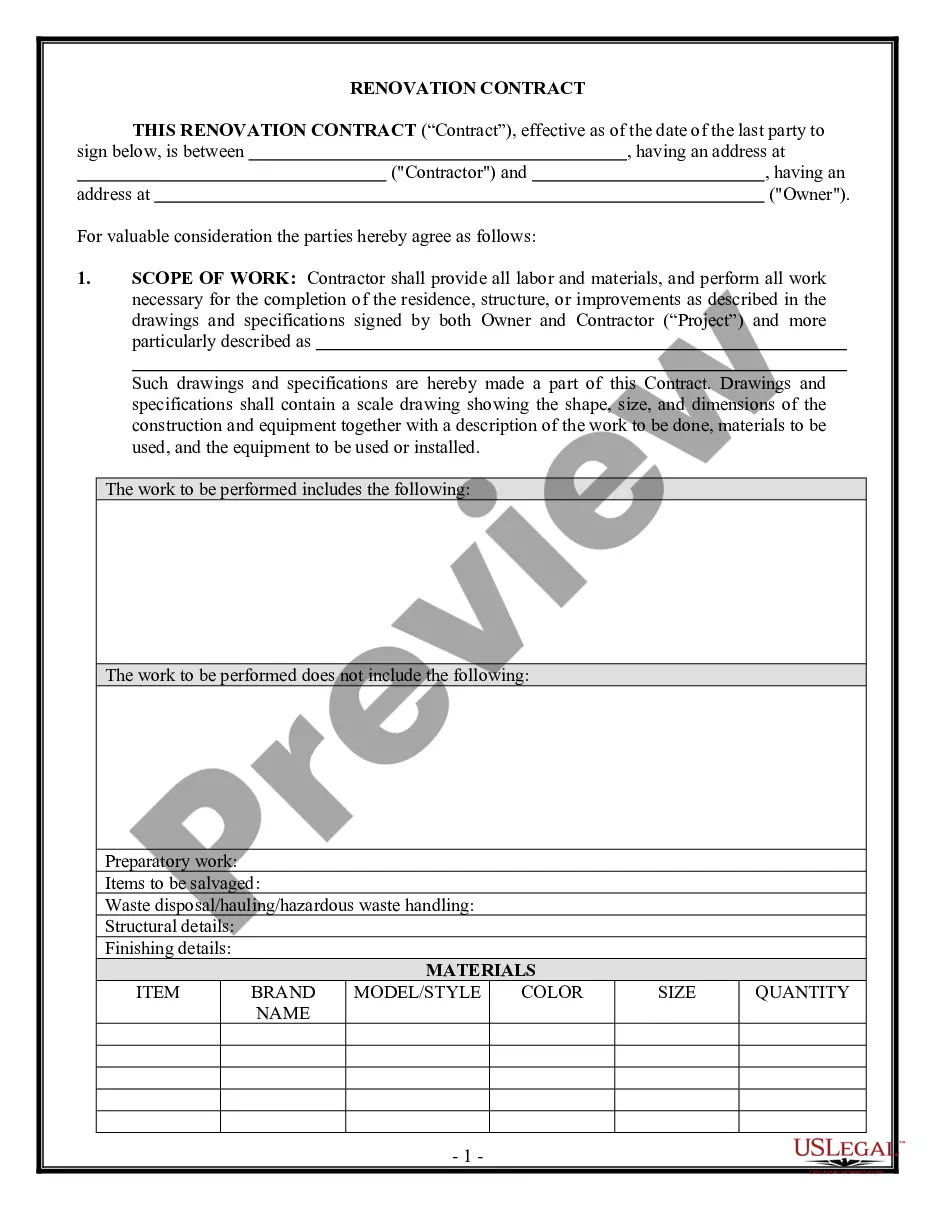
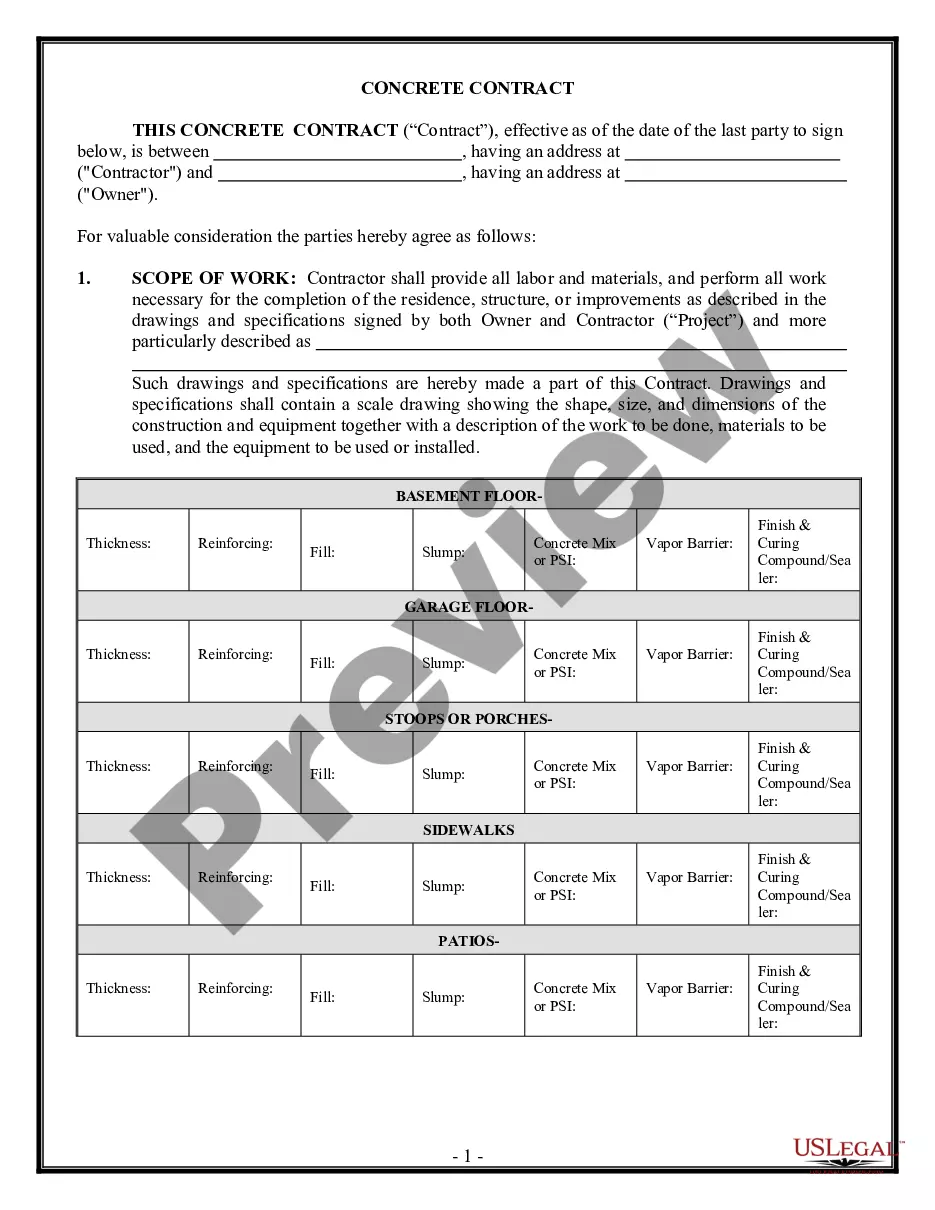
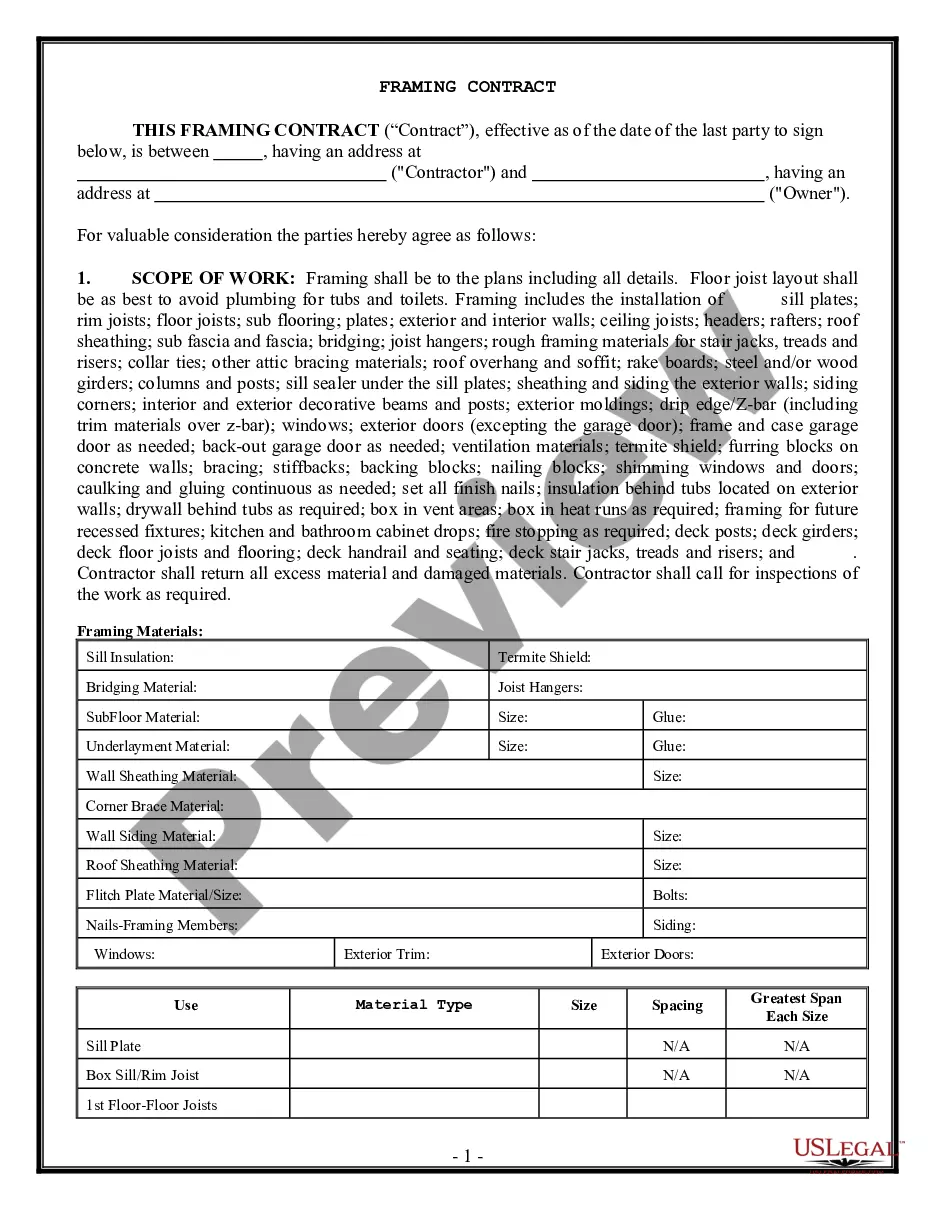
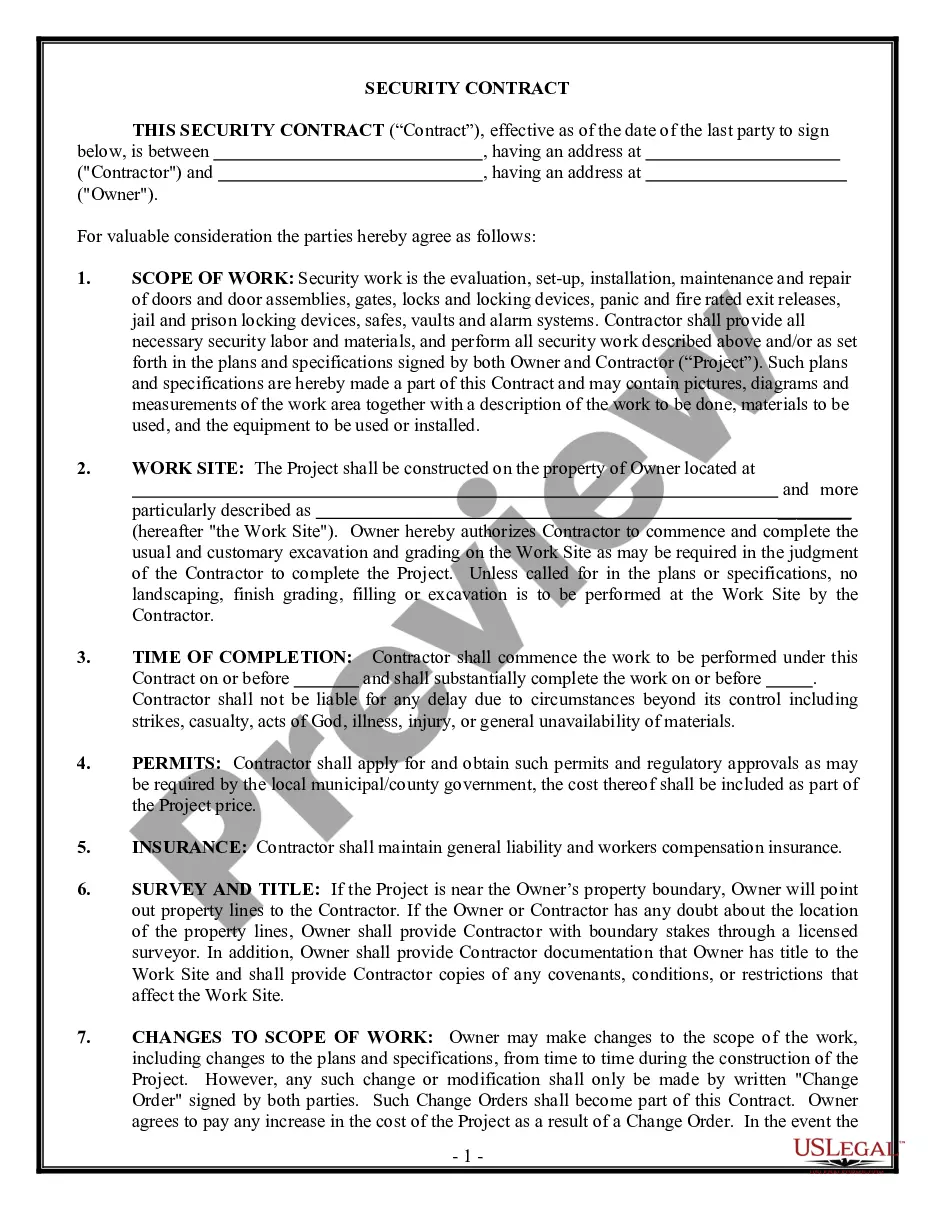
Aggravating and mitigating factors generally refer to considerations that can influence the severity of a sentence handed down in a criminal case. Aggravating factors are elements of a crime or circumstances of the crime that would make the sentence more severe, while mitigating factors would make the sentence less severe. Types of Aggravating Factors Generally: — The severity of the injury or harm caused by the criminal act — The presence of any prior criminal history — The use of a weapon or violence during the criminal act — Participation of a minor or vulnerable person in the criminal act — The planning or premeditation of the criminal act — Whether the crime was motivated by financial gain, hatred, revenge, or other malicious intent Types of Mitigating Factors Generally: — The lack of prior criminahistoryor— - Any remorse or contrition for the criminal act — The willingness of the perpetrator to cooperate with law enforcement — The age of the perpetrator at the time of the criminal act — The level of mental impairment of the perpetrator at the time of the criminal act — The presence of duress or coercion on the part of the perpetrator.
Aggravating and mitigating factors generally refer to considerations that can influence the severity of a sentence handed down in a criminal case. Aggravating factors are elements of a crime or circumstances of the crime that would make the sentence more severe, while mitigating factors would make the sentence less severe. Types of Aggravating Factors Generally: — The severity of the injury or harm caused by the criminal act — The presence of any prior criminal history — The use of a weapon or violence during the criminal act — Participation of a minor or vulnerable person in the criminal act — The planning or premeditation of the criminal act — Whether the crime was motivated by financial gain, hatred, revenge, or other malicious intent Types of Mitigating Factors Generally: — The lack of prior criminahistoryor— - Any remorse or contrition for the criminal act — The willingness of the perpetrator to cooperate with law enforcement — The age of the perpetrator at the time of the criminal act — The level of mental impairment of the perpetrator at the time of the criminal act — The presence of duress or coercion on the part of the perpetrator.