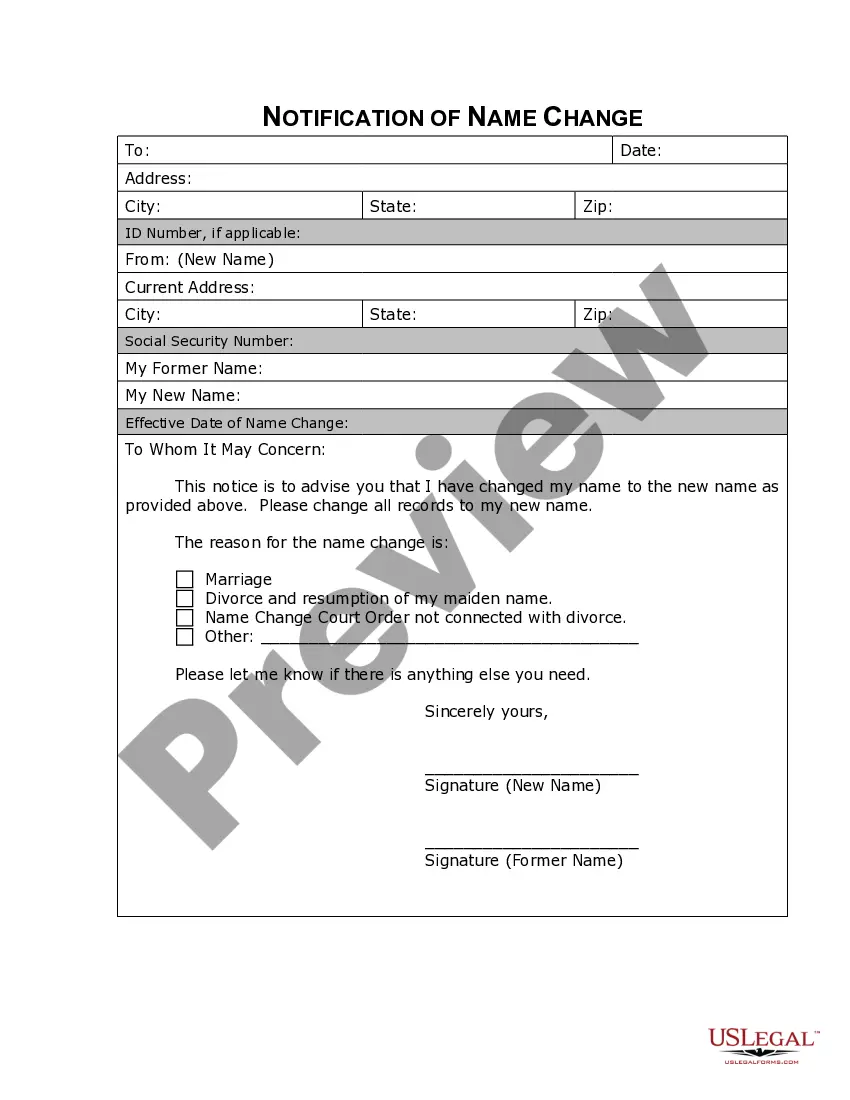
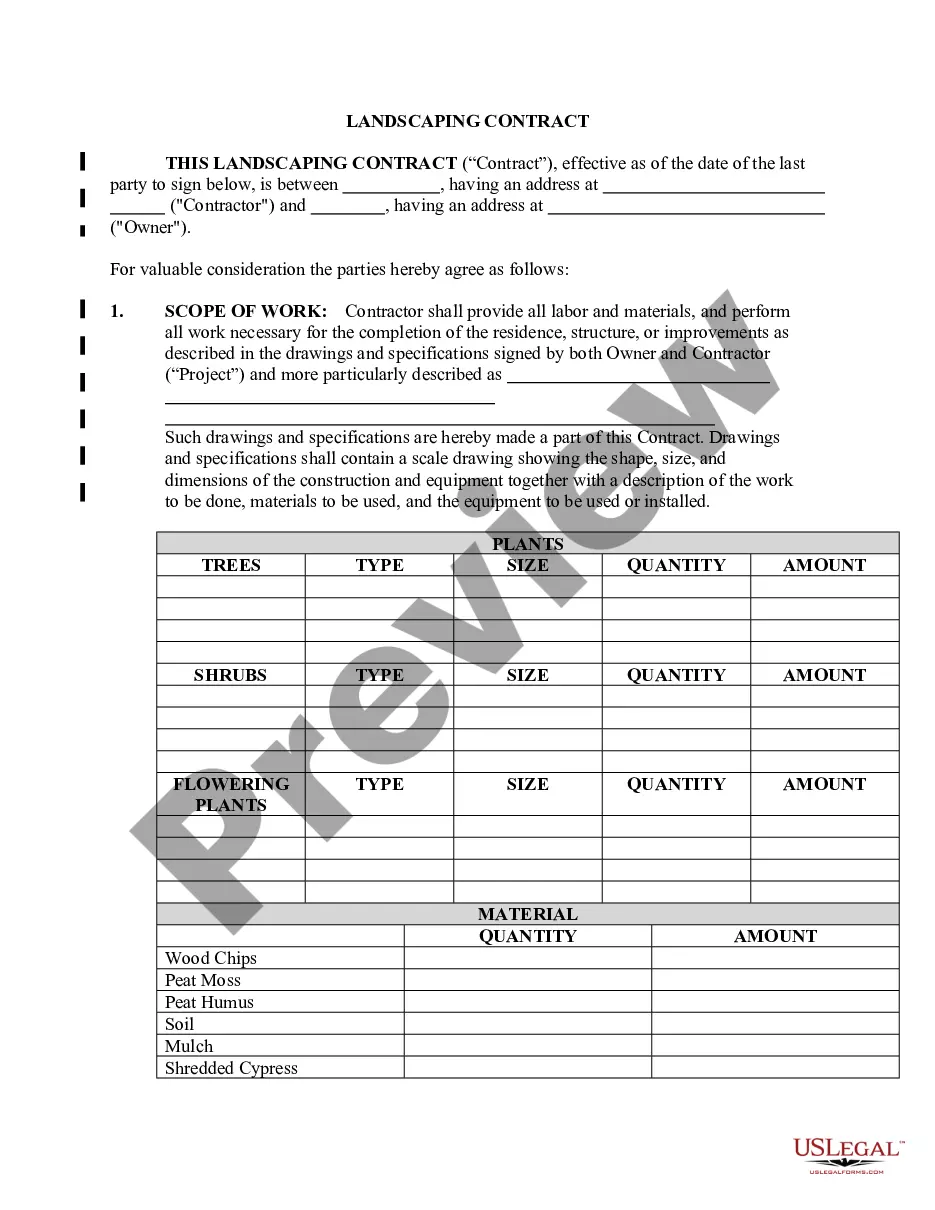
Credibility of Witnesses is a measure of the reliability and believability of witness testimony in a legal setting. It is a fundamental principle of the law that testimony given by a witness must be credible in order for it to be considered as evidence in a trial. Credibility of Witnesses is evaluated by a judge or jury in a court of law, and there are several factors that are taken into account when evaluating the credibility of a witness. These include the witness’s character, past behavior, and demeanor, as well as the consistency between the witness’s words and other evidence presented in the case. There are two primary types of Credibility of Witnesses: direct and circumstantial. Direct Credibility of Witnesses refers to the direct testimony of a witness, which is based on what the witness has seen, heard, or experienced. Circumstantial Credibility of Witnesses refers to evidence that is used to infer the credibility of a witness, such as the behavior of the witness or the consistency between the witness’s words and other evidence. In addition, Credibility of Witnesses can also be evaluated based on the witness’s qualifications and experience, as well as how the witness was prepared for the trial. The court also takes into account any bias or interest that the witness may have in the outcome of the trial.
Credibility of Witnesses is a measure of the reliability and believability of witness testimony in a legal setting. It is a fundamental principle of the law that testimony given by a witness must be credible in order for it to be considered as evidence in a trial. Credibility of Witnesses is evaluated by a judge or jury in a court of law, and there are several factors that are taken into account when evaluating the credibility of a witness. These include the witness’s character, past behavior, and demeanor, as well as the consistency between the witness’s words and other evidence presented in the case. There are two primary types of Credibility of Witnesses: direct and circumstantial. Direct Credibility of Witnesses refers to the direct testimony of a witness, which is based on what the witness has seen, heard, or experienced. Circumstantial Credibility of Witnesses refers to evidence that is used to infer the credibility of a witness, such as the behavior of the witness or the consistency between the witness’s words and other evidence. In addition, Credibility of Witnesses can also be evaluated based on the witness’s qualifications and experience, as well as how the witness was prepared for the trial. The court also takes into account any bias or interest that the witness may have in the outcome of the trial.