6.09 Voluntary Intoxication is the intentional ingestion of a substance (alcohol or drugs) that results in intoxication or impairment of the individual’s mental or physical faculties. It is a form of self-harming behavior and can lead to a variety of negative consequences, including accidents, violence, and death. There are two types of voluntary intoxication: acute intoxication and chronic intoxication. Acute intoxication occurs when an individual takes a large amount of a substance in a short period of time and experiences an immediate, intense effect. Chronic intoxication occurs when an individual continuously takes a smaller amount of a substance over a longer period of time and experiences a gradual, less intense effect. In either case, the individual's judgment and decision-making abilities are impaired, which can lead to dangerous situations and potential harm.
6.09 VOLUNTARY INTOXICATION
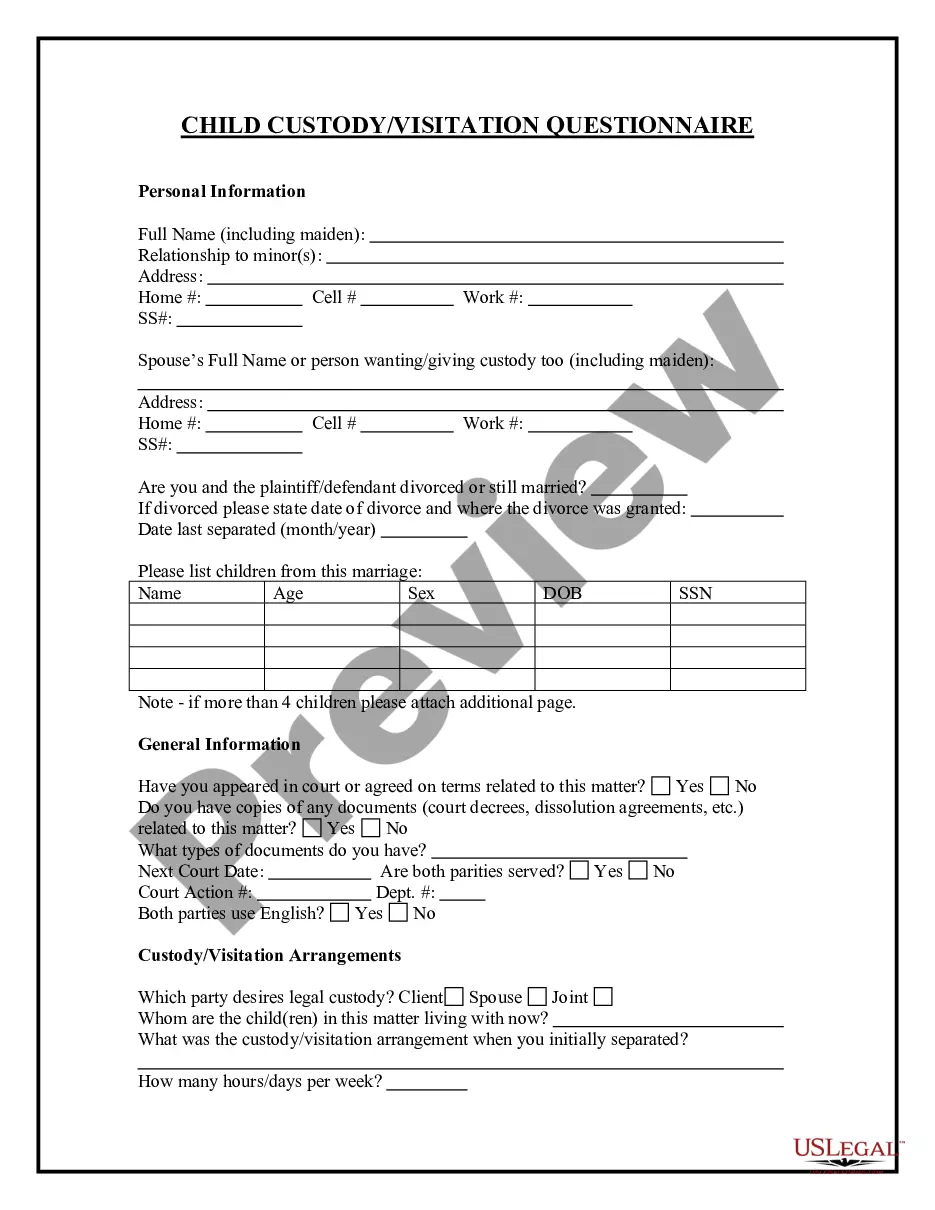
Description
How to fill out 6.09 VOLUNTARY INTOXICATION?
How much time and resources do you often spend on drafting formal paperwork? There’s a greater opportunity to get such forms than hiring legal specialists or spending hours searching the web for an appropriate template. US Legal Forms is the top online library that provides professionally designed and verified state-specific legal documents for any purpose, including the 6.09 VOLUNTARY INTOXICATION.
To acquire and complete an appropriate 6.09 VOLUNTARY INTOXICATION template, adhere to these simple instructions:
- Look through the form content to make sure it complies with your state requirements. To do so, check the form description or use the Preview option.
- In case your legal template doesn’t satisfy your needs, locate another one using the search bar at the top of the page.
- If you already have an account with us, log in and download the 6.09 VOLUNTARY INTOXICATION. If not, proceed to the next steps.
- Click Buy now once you find the correct blank. Select the subscription plan that suits you best to access our library’s full opportunities.
- Create an account and pay for your subscription. You can make a transaction with your credit card or through PayPal - our service is totally safe for that.
- Download your 6.09 VOLUNTARY INTOXICATION on your device and complete it on a printed-out hard copy or electronically.
Another advantage of our service is that you can access previously downloaded documents that you securely keep in your profile in the My Forms tab. Pick them up anytime and re-complete your paperwork as often as you need.
Save time and effort completing formal paperwork with US Legal Forms, one of the most trustworthy web solutions. Sign up for us now!
Form popularity
FAQ
Voluntary Intoxication This defense is only valid for specific intent crimes. Voluntary intoxication is never a defense for general intent crimes. For specific intent crimes, voluntary intoxication can prevent the defendant from achieving the requisite intent to commit the crime.
Voluntary intoxication means that a person voluntarily decided to get intoxicated. For example, if a person goes into a bar and consumes enough alcohol to be intoxicated, that person can be said to be voluntarily intoxicated. When it comes to criminal law, voluntary intoxication can be a defense to a crime.
Voluntary intoxication is the willing ingestion or injection of any drink, drug, or other intoxicating substance that the defendant knows can produce an intoxicating effect.
Voluntary intoxication is recognized as a defense to all statutory crimes. In American courts, a mistake of fact can be a defense only to negate the defendant's specific intent. The concept of a defendant being allowed to plead the statute of limitations as a defense is derived from the common law.
Voluntary intoxication cannot be used as a defense to general intent crimes. It can, however, be used as a defense to a specific intent crime. For example, burglary generally requires breaking and entering into a dwelling with the intent to commit a crime therein.
The basic precept of criminal law is that voluntary intoxication does not excuse criminal behavior. The most common rationale for this rule is that an intoxication defense can be easily simulated, thus making prosecutions too difficult.
Voluntary intoxication is, therefore, primarily a mitigating defense; i.e., it prevents conviction for certain crimes but does not entirely exculpate the defendant from criminal liability. Insanity, by contrast, is an exculpating defense.