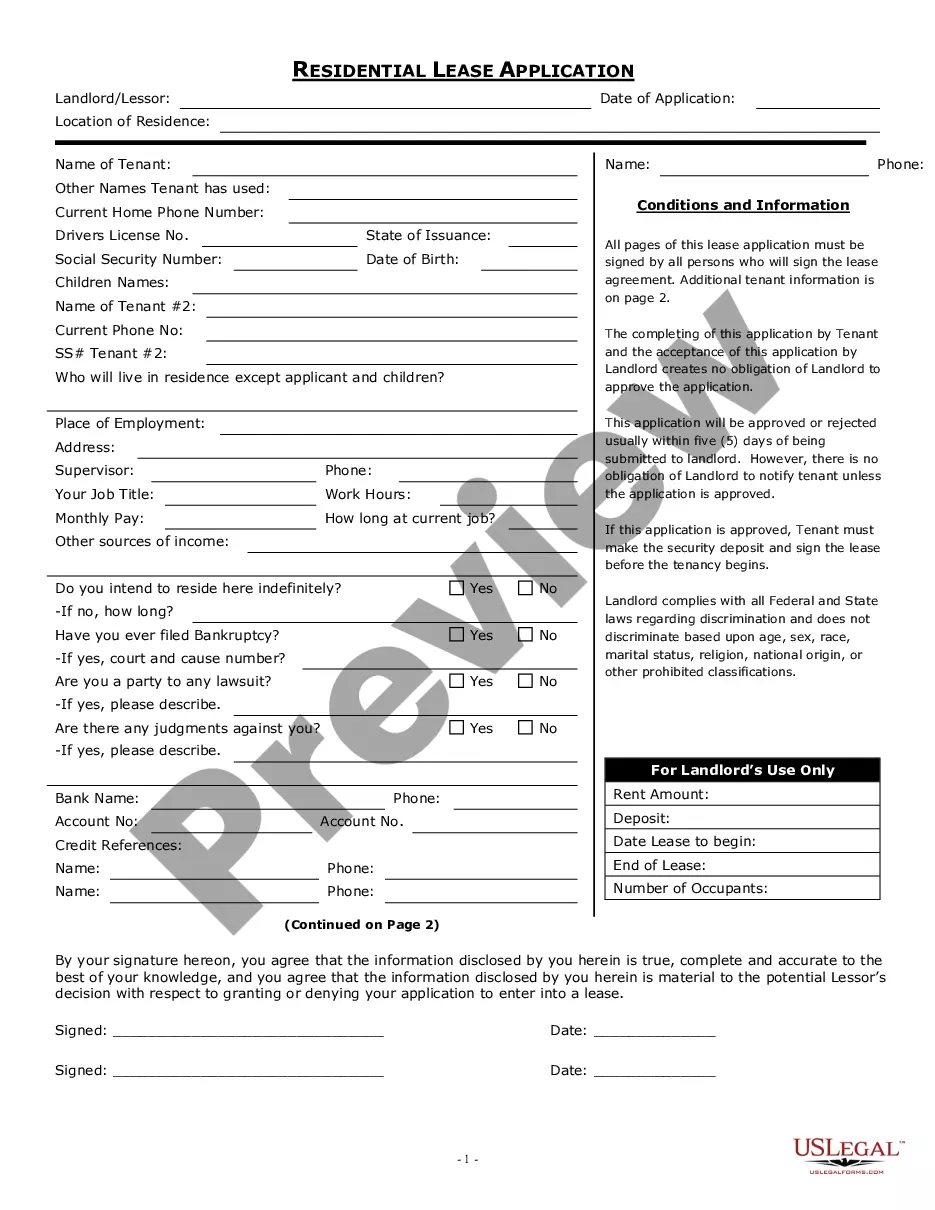
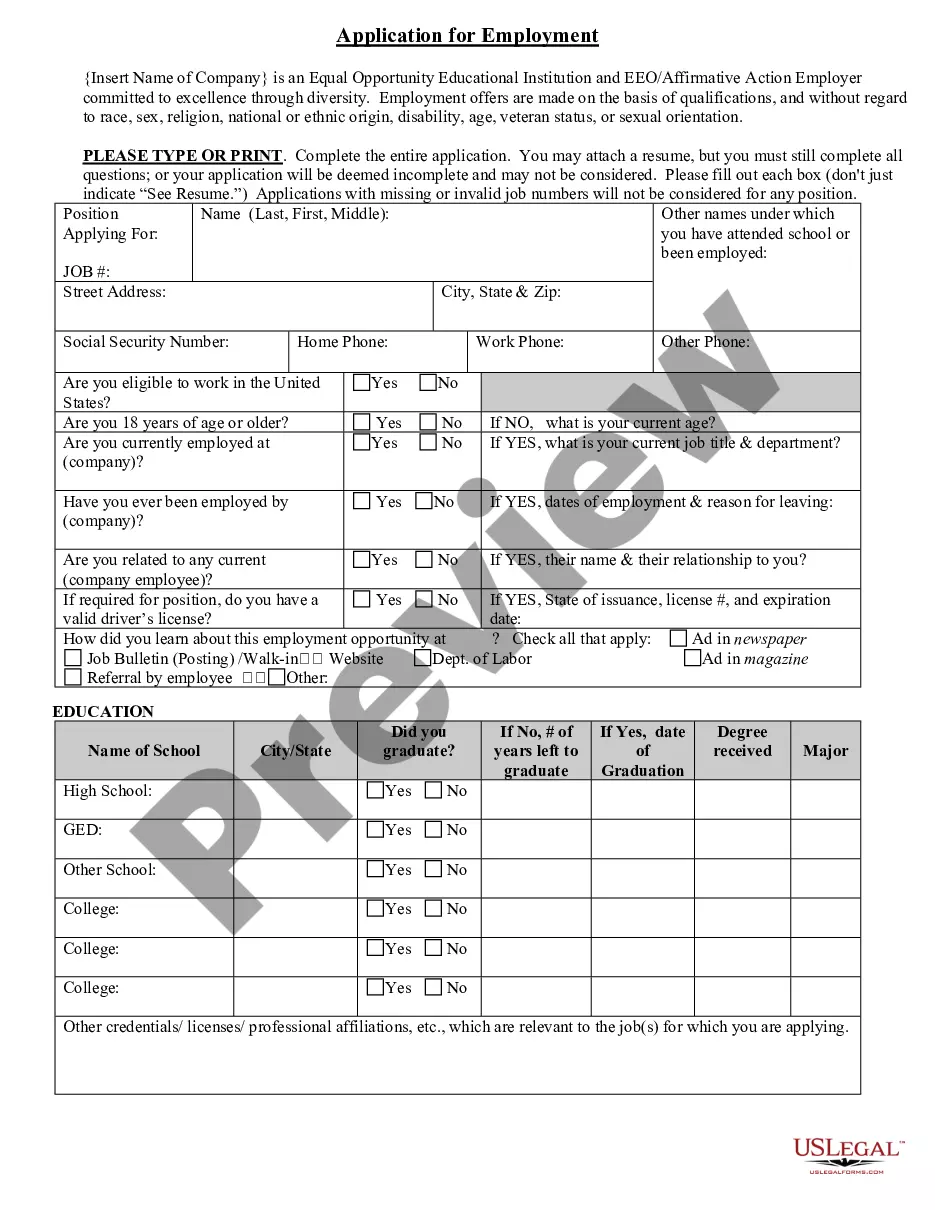
3.6 What Is Evidence? Evidence is any form of proof or support used to substantiate a claim or an argument. It can be physical, such as a document, a photograph, or a piece of audio or video recording. It can also be testimonial, such as an eyewitness account or a statement by an expert. In the legal context, evidence is necessary to prove a case in court. There are three main types of evidence: direct evidence, circumstantial evidence, and documentary evidence. Direct evidence is evidence that directly proves or disproves the claim at hand. Examples of direct evidence are eyewitness accounts, physical evidence, or confessions. Circumstantial evidence is indirect evidence that requires the use of logic and inference to prove or disprove a claim. Examples of circumstantial evidence include circumstantial facts, patterns, and trends. Documentary evidence is written or recorded evidence used to prove or disprove a claim. Examples of documentary evidence are contracts, letters, or diaries.
3.6 What Is Evidence? Evidence is any form of proof or support used to substantiate a claim or an argument. It can be physical, such as a document, a photograph, or a piece of audio or video recording. It can also be testimonial, such as an eyewitness account or a statement by an expert. In the legal context, evidence is necessary to prove a case in court. There are three main types of evidence: direct evidence, circumstantial evidence, and documentary evidence. Direct evidence is evidence that directly proves or disproves the claim at hand. Examples of direct evidence are eyewitness accounts, physical evidence, or confessions. Circumstantial evidence is indirect evidence that requires the use of logic and inference to prove or disprove a claim. Examples of circumstantial evidence include circumstantial facts, patterns, and trends. Documentary evidence is written or recorded evidence used to prove or disprove a claim. Examples of documentary evidence are contracts, letters, or diaries.