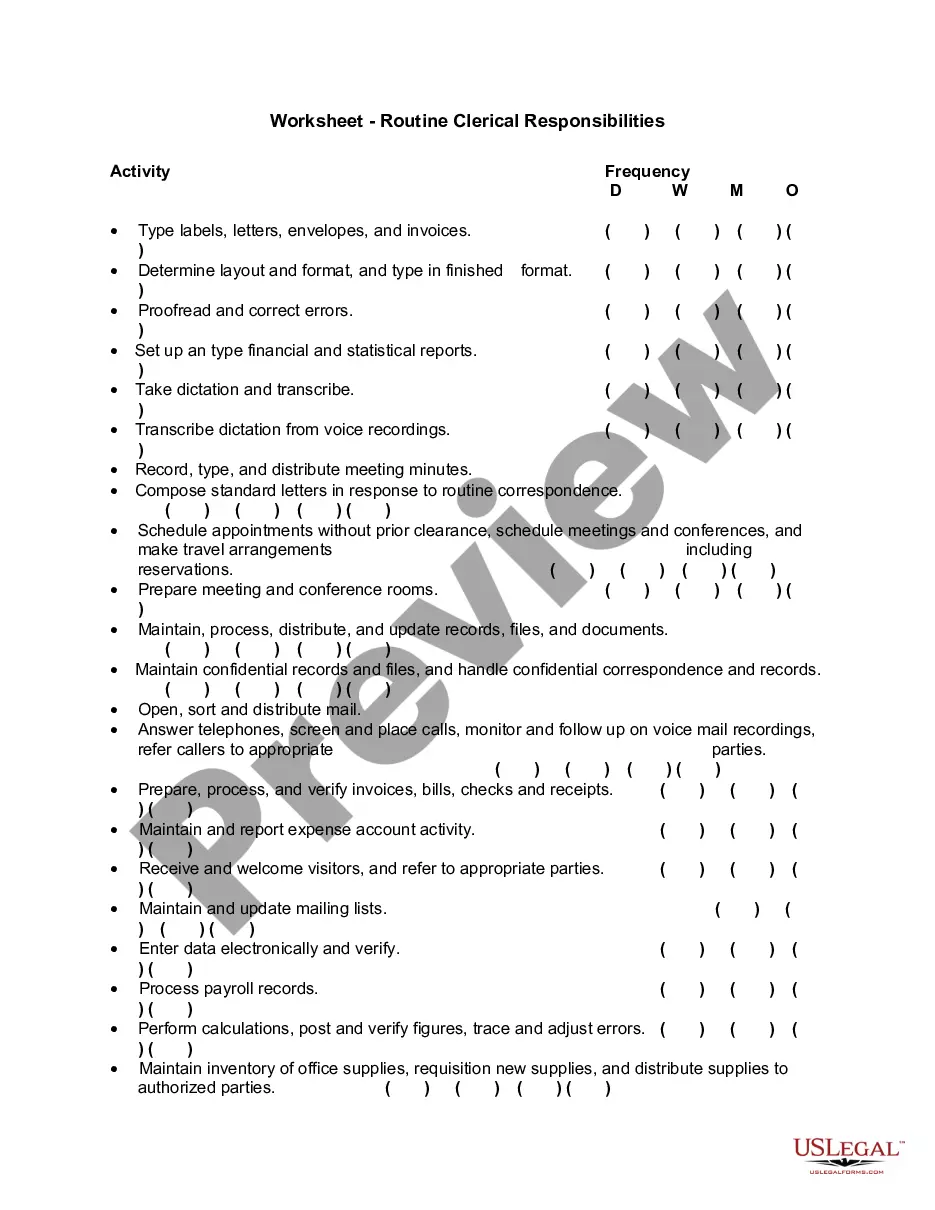
Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees
Description
How to fill out Classification Of Employees For Personnel Manual Or Employee Handbook Regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, And Nonexempt Employees?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal templates in the United States - offers a variety of legal document formats that you can download or print.
By using the website, you can find thousands of templates for commercial and personal use, organized by categories, states, or keywords.
You can access the latest templates such as the Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook concerning Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees in just a few seconds.
If the form does not suit your needs, use the Search field located at the top of the page to find the one that does.
When you are satisfied with the form, confirm your selection by clicking the Purchase now button. Then, select your preferred payment plan and provide your details to register for an account.
- If you already possess a membership, Log In to download the Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook regarding Full Time, Part Time, Temporary, Leased, Exempt, and Nonexempt Employees from your US Legal Forms library.
- The Download button will appear on every form you view.
- You can access all previously downloaded templates in the My documents section of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, here are simple steps to assist you in getting started.
- Ensure you have chosen the correct form for your state/region.
- Click the Review button to examine the form's content.
Form popularity
FAQ
Describing full-time employees as permanent can create misconceptions about job stability. It is important to clarify the status of full-time workers in the Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook, particularly concerning at-will employment. Clear definitions help set proper expectations for employment continuity and security.
Employee handbooks can be considered legally binding if they contain specific commitments and clear language. Courts may enforce the policies within the Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook if an employee relies on them to their detriment. Therefore, it's important for employers to craft these documents with care and precision.
An employee handbook does not automatically create a binding contract. However, certain statements and policies may be interpreted as contractual terms if they are clear and definitive. It is advisable to consult legal counsel when drafting the Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook to ensure compliance and clarity.
Yes, statements made in an employee handbook can potentially be regarded as terms in an employment contract. Therefore, it is crucial for employers to ensure that the language used in the Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook aligns with their intentions. Any unclear or vague statements may lead to misunderstandings regarding employee rights and obligations.
In Utah, a standard full-time work schedule typically consists of 40 hours per week. However, this can vary depending on the employer's policies as specified in the Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook. Employers should communicate these expectations clearly to avoid any confusion regarding full-time status.
A handbook serves as a vital resource for employees, outlining workplace policies and procedures. In the context of the Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook, it helps clarify the distinctions among full-time, part-time, temporary, leased, exempt, and nonexempt employees. This document fosters transparency and ensures that employees understand their rights and responsibilities.
Formatting an employee handbook involves creating a clear structure that outlines policies, procedures, and classifications of employees. Start with a table of contents, followed by sections on employment classifications, benefits, and company policies. For assistance, consider using platforms like USLegalForms to access templates that guide you through proper formatting.
Part-time employment in Utah generally requires working fewer than 30 hours per week, although this can vary by employer. This classification should be clearly defined within your employee handbook. By establishing clear guidelines for part-time work, you can promote understanding among your employees.
An employment at will statement indicates that either the employer or the employee can terminate the employment relationship at any time, for any lawful reason. This clause provides flexibility for both parties and is crucial in your Utah Classification of Employees for Personnel Manual or Employee Handbook. Ensure that this statement is clearly articulated to set mutual expectations.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) defines full-time employees as those working 30 hours or more per week. This rule is significant for employer compliance regarding health insurance offerings. Understanding the ACA's implications helps you properly classify employees in your Utah employee handbook or personnel manual.