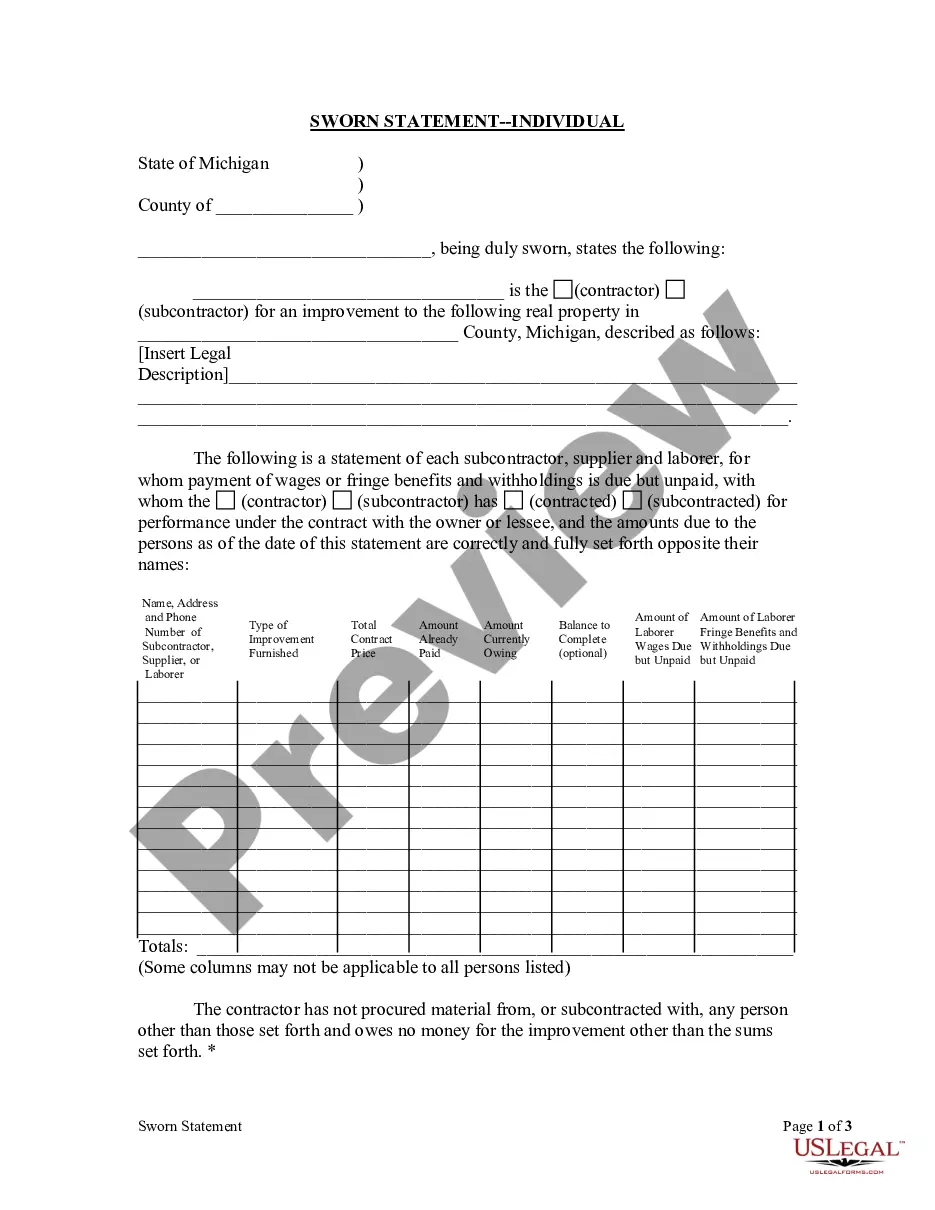
A security interest in an aircraft engine can be perfected only in the manner required by federal law. Federal law excludes by preemption the recording of title to or liens against aircraft, so that a transfer that is not recorded under the federal system is not effective. Security Interests in Engines less than 550 horsepower are not eligible for recording. A security interest in an aircraft is perfected by filing with the Aircraft Registration Branch of the Federal Aviation Administration.
Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine
Description
How to fill out Security Agreement Granting Security Interest In Aircraft Engine?
US Legal Forms - one of the most extensive collections of legal documents in the United States - provides a broad selection of legal form templates available for download or printing.
By using the website, you will access a vast number of forms for both business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can quickly find the most recent versions of documents such as the Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine.
If you already have a monthly subscription, Log In to download the Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine from the US Legal Forms library. The Acquire button will appear on every form you review.
If you are satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking the Buy now button. Then, choose your preferred payment plan and provide your details to register an account.
Process the payment. Use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction. Select the format and download the form to your device. Make modifications. Fill out, edit, print, and sign the downloaded Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine.
Every template you added to your account has no expiration date and is yours permanently. Therefore, if you need to download or print another copy, simply visit the My documents section and click on the desired form.
Access the Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine with US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive library of legal document templates. Utilize a plethora of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal requirements.
- You have access to all previously downloaded forms in the My documents section of your account.
- To use US Legal Forms for the first time, here are simple steps to assist you.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/state.
- Click the Review button to examine the contents of the form.
- Check the form description to make sure you have selected the right one.
- If the form does not meet your needs, use the Lookup field at the top of the screen to find a suitable one.
Form popularity
FAQ
Yes, a security agreement can be filed to perfect a security interest in an aircraft engine. This process involves registering the security agreement with the relevant authorities, which solidifies your claim. By doing so, you ensure that your interest is legally recognized, making it enforceable against third parties. Using the Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine via the uslegalforms platform can streamline this process and provide the necessary documentation.
To identify all outstanding security interests in an aircraft, you should conduct a thorough search of the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) records. This search reveals any registered security interests and liens against the aircraft. Additionally, utilizing resources such as the Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine can help you understand the implications of any existing interests. For comprehensive results, consider using ulegalforms platform, where you can access legal forms and guidance specific to aircraft interests.
Yes, the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) does apply to aircraft, specifically under Article 9, which governs secured transactions. This includes the process for perfecting a security interest in aircraft through the filing of UCC-1 statements. By utilizing a Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine, you can seamlessly navigate UCC regulations to secure your interests.
The three main ways of perfecting a security interest include filing a UCC financing statement, possession of the collateral, and automatic perfection in specific situations. Each method has distinct circumstances where it is most effective. When dealing with a Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine, filing remains the most reliable method to ensure your rights are protected.
To perfect a security interest in a fixture, you should file a UCC-1 statement and ensure it accurately describes the fixture. This action gives legal notice to other creditors about your claim. If the fixture in question relates to aircraft operations, a Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine can play a pivotal role in securing your investment.
An aircraft security agreement is a legal document that outlines the terms under which a security interest is granted in an aircraft. This agreement details the obligations of the borrower and the rights of the lender regarding the aircraft. If you are looking for a structured approach, consider using a Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine to simplify this process.
To perfect a security interest in an aircraft, follow a similar procedure as with other types of collateral. You should file a UCC-1 financing statement and reference your Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine. This process enables you to inform other parties of your interest in the aircraft, protecting your rights.
The most common way to perfect a security interest is by filing a UCC-1 financing statement with the appropriate state authority. This action gives notice to other creditors and establishes your claim. In the context of a Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine, this filing is crucial for securing your position.
To perfect a security interest in an airplane, you typically need to file a UCC financing statement. This statement must include essential details about the aircraft and the security interest. Utilizing a Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine, you can establish your rights effectively, ensuring your interests are legally recognized.
You file a security agreement, such as the Utah Security Agreement Granting Security Interest in Aircraft Engine, with the appropriate authority. In Utah, this usually means filing with the Utah Secretary of State's office or other relevant local agencies. Proper filing ensures legal recognition of your security interest, protecting your investment. If you need guidance, consider using US Legal Forms for a streamlined process.