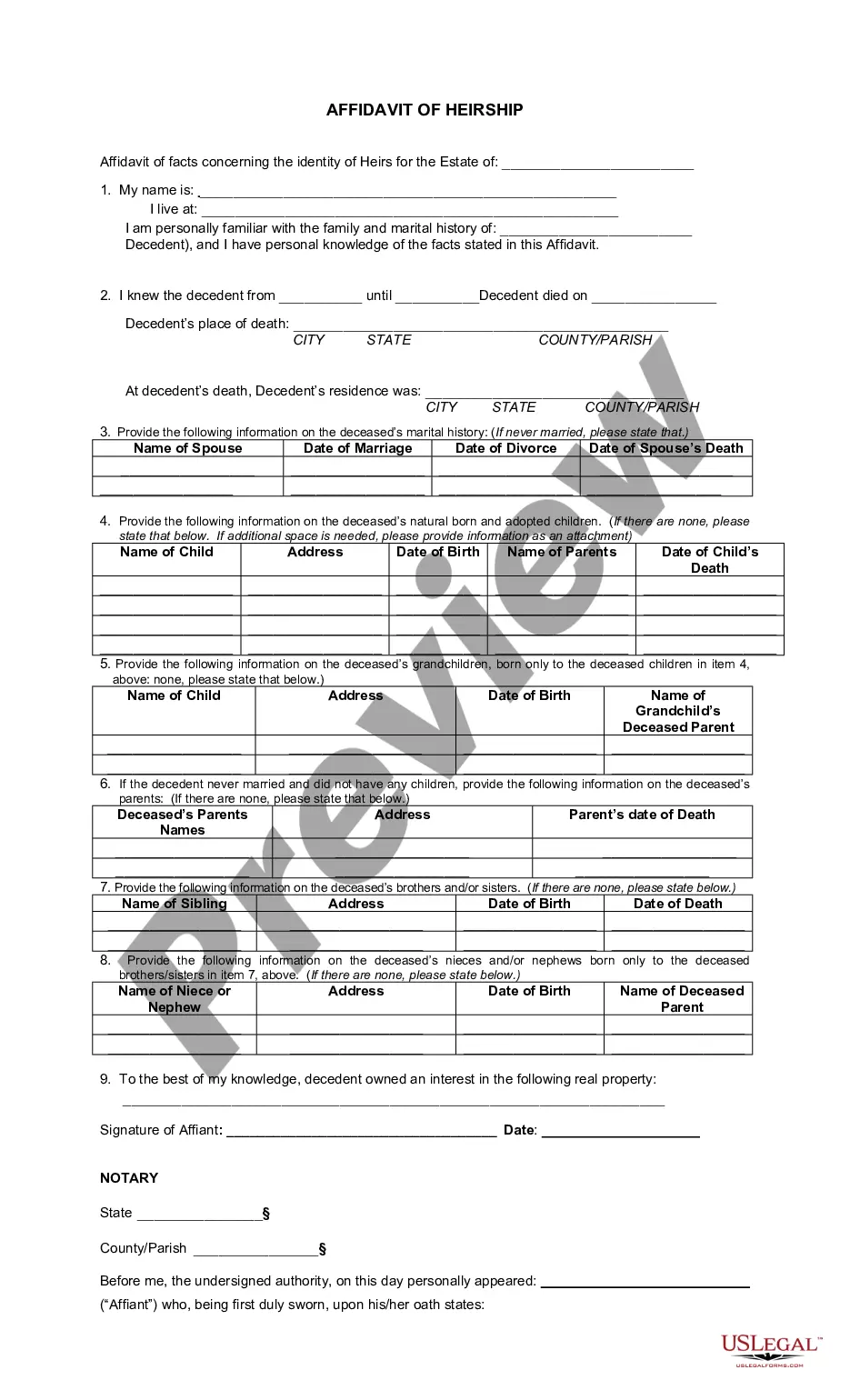
Utah Affidavit of Heirship for Mineral Rights
Description
How to fill out Affidavit Of Heirship For Mineral Rights?
If you have to complete, download, or printing legal record themes, use US Legal Forms, the most important variety of legal kinds, that can be found online. Make use of the site`s easy and convenient search to get the files you want. Different themes for organization and individual purposes are categorized by types and says, or search phrases. Use US Legal Forms to get the Utah Affidavit of Heirship for Mineral Rights in just a number of clicks.
In case you are presently a US Legal Forms client, log in for your profile and then click the Down load key to have the Utah Affidavit of Heirship for Mineral Rights. You can also gain access to kinds you formerly acquired in the My Forms tab of your profile.
If you use US Legal Forms the very first time, follow the instructions under:
- Step 1. Make sure you have chosen the shape for your right town/nation.
- Step 2. Utilize the Review solution to check out the form`s information. Don`t neglect to learn the explanation.
- Step 3. In case you are unsatisfied together with the type, make use of the Search area towards the top of the monitor to locate other types of the legal type template.
- Step 4. After you have found the shape you want, click on the Buy now key. Choose the prices program you prefer and add your qualifications to sign up for an profile.
- Step 5. Approach the purchase. You should use your Мisa or Ьastercard or PayPal profile to finish the purchase.
- Step 6. Find the structure of the legal type and download it on your own product.
- Step 7. Total, revise and printing or sign the Utah Affidavit of Heirship for Mineral Rights.
Every legal record template you buy is yours permanently. You may have acces to every single type you acquired with your acccount. Click on the My Forms area and pick a type to printing or download once again.
Remain competitive and download, and printing the Utah Affidavit of Heirship for Mineral Rights with US Legal Forms. There are many professional and condition-specific kinds you can utilize for your organization or individual demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
An affidavit of heirship must be signed and sworn to before a notary public by a person who knew the decedent and the decedent's family history. This person can be a friend of the decedent, an old friend of the family, or a neighbor, for example.
A ballpark fee for preparation of the affidavit is between $750 for a very simple estate with few heirs to several thousand dollars for a more complicated estate with many heirs. The filing fees to record the affidavit in each county where the real property is located usually run about $50 to $75 in Texas.
The purpose of an Affidavit of Heirship is to put the county records on notice for mineral owners who are deceased that did not have probate proceedings administered to their estate.
Once the affidavit has been recorded, the heirs are identified in the property records as the new owners of the property. Thereafter, the heir or heirs may transfer or sell the property if they choose to do so.
The mailing address is: Harris County Clerk, P.O. Box 1525, Houston, TX 77251-1525.
The affidavit of heirship is a document that provides a statement of facts of the family history, genealogy, marital status, or the identity of the heirs of a decedent. The affidavit of heirship is not an alternative to probate per se. Rather, it is an alternative that may be used when probate is not necessary.
Unlike the affidavit of heirship, the small estate affidavit only transfers the title of the decedent's homestead. Only a surviving spouse or minor child can inherit property through this affidavit type. The other types of the deceased person's real property cannot be transferred by submitting a small estate affidavit.
Upon payment in full, the Release of Lien document will be created and sent to the payee and then should be promptly filed with Harris County Real Property Records Division, providing that it contains no errors. For specific instructions, please call the Harris County office at (713)755-6439.