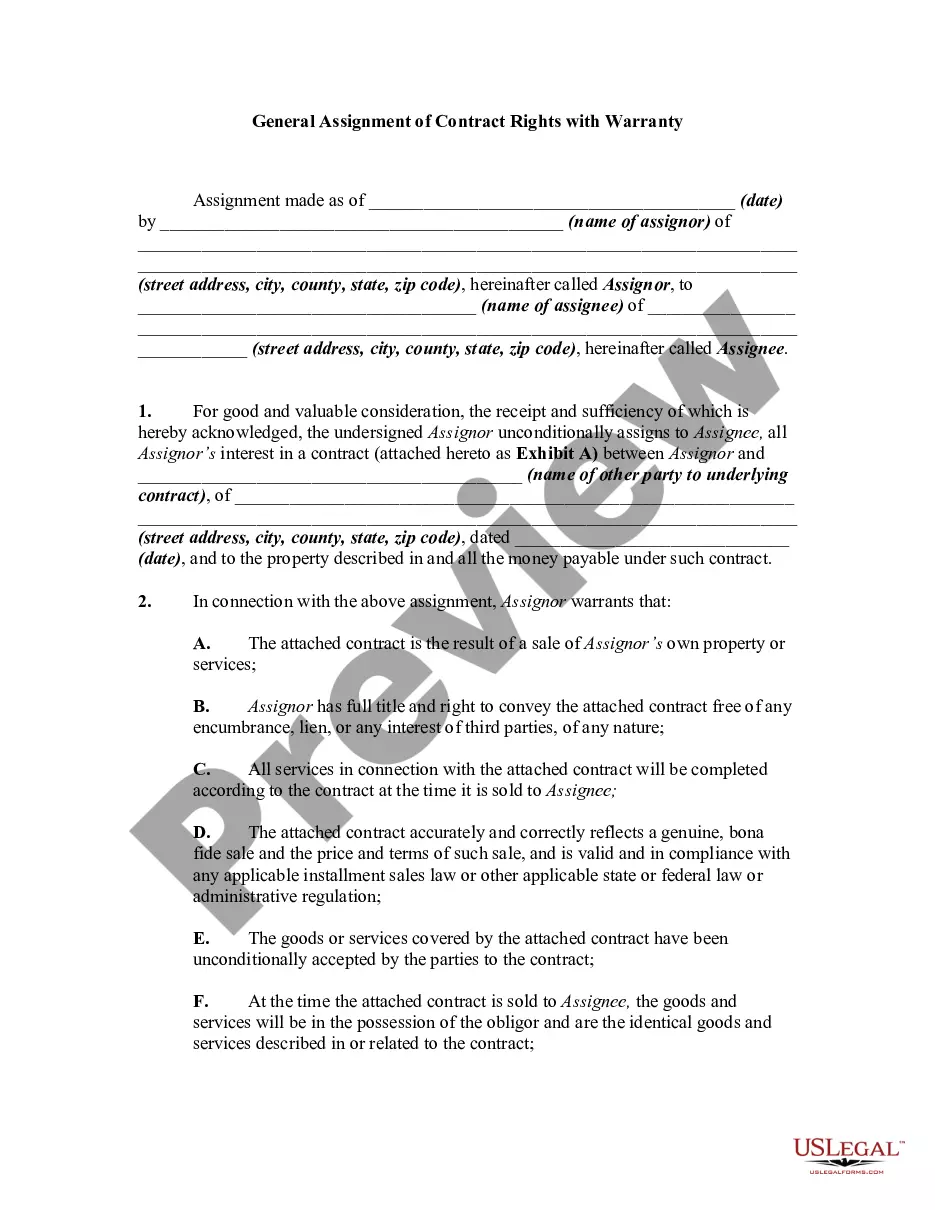
An assignment consists of a transfer of property or some right or interest in property from one person to another. Unless an assignment is qualified in some way, it is generally considered to be a transfer of the transferor's entire interest in the interest or thing assigned. Unless there is a statute that requires that certain language be used in an assignment or that the assignment be in writing, there are really no formal requirements for an assignment. Any words which show the intent to transfer rights under a contract are sufficient to constitute an assignment.
Virginia Assignment of Accounts Receivable Regarding Manufactured Goods with Warranty of Assignor
Description
How to fill out Assignment Of Accounts Receivable Regarding Manufactured Goods With Warranty Of Assignor?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest libraries of legal kinds in America - provides a variety of legal papers themes you are able to acquire or produce. Making use of the web site, you can find a huge number of kinds for enterprise and specific reasons, sorted by types, states, or search phrases.You can find the most up-to-date types of kinds just like the Virginia Assignment of Accounts Receivable Regarding Manufactured Goods with Warranty of Assignor in seconds.
If you already have a subscription, log in and acquire Virginia Assignment of Accounts Receivable Regarding Manufactured Goods with Warranty of Assignor in the US Legal Forms library. The Acquire button can look on each and every type you view. You have accessibility to all previously acquired kinds within the My Forms tab of your own bank account.
In order to use US Legal Forms the first time, listed below are simple guidelines to get you started off:
- Ensure you have chosen the best type for your personal area/region. Go through the Preview button to analyze the form`s content. See the type explanation to ensure that you have selected the proper type.
- When the type doesn`t fit your requirements, use the Research industry near the top of the monitor to discover the one who does.
- When you are content with the form, validate your selection by clicking the Get now button. Then, opt for the costs program you favor and supply your accreditations to register to have an bank account.
- Procedure the purchase. Utilize your bank card or PayPal bank account to perform the purchase.
- Find the file format and acquire the form on your device.
- Make adjustments. Load, revise and produce and sign the acquired Virginia Assignment of Accounts Receivable Regarding Manufactured Goods with Warranty of Assignor.
Each and every web template you added to your money does not have an expiration day which is your own permanently. So, if you want to acquire or produce yet another version, just proceed to the My Forms section and click on in the type you need.
Get access to the Virginia Assignment of Accounts Receivable Regarding Manufactured Goods with Warranty of Assignor with US Legal Forms, probably the most considerable library of legal papers themes. Use a huge number of professional and express-specific themes that satisfy your company or specific requires and requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
Firstly, factoring is a financial service of selling and purchasing, which implies consideration, unlike assignment, which may take place either with or without consideration. In addition, non-matured or future accounts receivable can be subject to factoring.
In the accounts receivable assignment process, a company assigns receivables to a lending institution to borrow money. The borrower pays interest plus additional fees. The borrowing company retains ownership of the accounts receivable and collects payment from its customers.
A Notice of Assignment (?NOA?) is a letter sent by the factoring company (?factor?) to your customers (aka ?account debtors?) notifying them that the ownership of your accounts receivable, or invoices, has changed hands to the factor, and payments should be made in ance with the instructions provided.
Assignment of accounts receivable is a lending agreement whereby the borrower assigns accounts receivable to the lending institution. In exchange for this assignment of accounts receivable, the borrower receives a loan for a percentage, which could be as high as 100%, of the accounts receivable.
A receivable assignment agreement is an agreement by which a creditor ? the ?assignor? ? assigns to another person ? the ?assignee? ? a receivable it holds against a third person ? the ?assigned debtor?. The assigned debtor is not a party to the assignment agreement.
What are the journal entries for assigning Accounts Receivable as collateral for a loan? The entry to record assignment of Accounts Receivable as collateral would be a credit to cash, and a debit to assign Accounts Receivable. The cash account is debited because the company gave up the assigned receivables.
Assignment of receivables would mean sale of the lease rentals, not the asset. In that case, the leased asset still remains the property of the assignor ? that is, the assignor has retained the residual interest in the asset. However, it would be different if the lessor sells the asset that has been leased out.
Accounts Receivable are amounts due from customers from the sale of services or merchandise on credit. They are usually due in 30 ? 60 days. They are classified on the Balance Sheet as current assets.