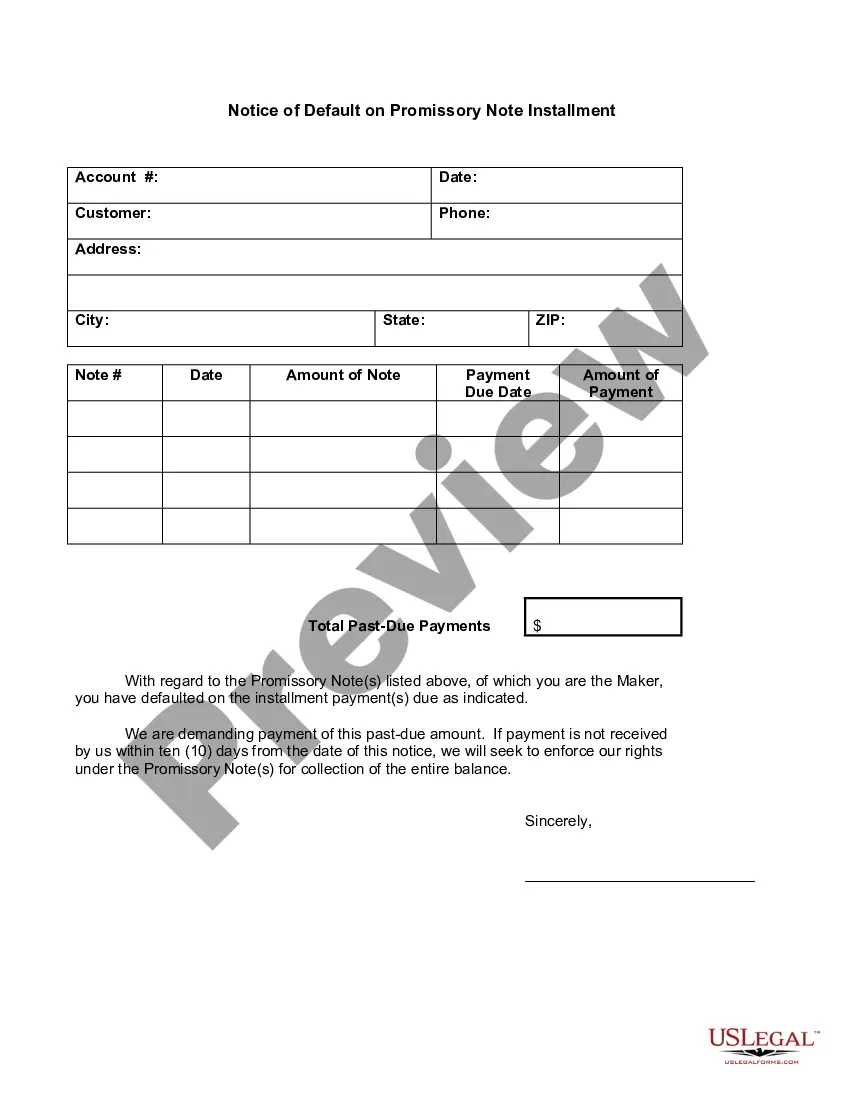
An assignment is a transfer of rights that a party has under a contract to another person, called an assignee. The assigning party is called the assignor. An assignee of a contract may generally sue directly on the contract rather than suing in the name of the assignor. The obligor is the person responsible to make payments to the assignee.
Virginia Notice of Default by Assignee to Obligor
Description
How to fill out Notice Of Default By Assignee To Obligor?
Discovering the right legal file web template can be a battle. Needless to say, there are plenty of layouts available on the net, but how can you obtain the legal form you want? Utilize the US Legal Forms web site. The service gives thousands of layouts, including the Virginia Notice of Default by Assignee to Obligor, which can be used for company and private requires. All of the varieties are checked by specialists and fulfill federal and state requirements.
In case you are already signed up, log in to the bank account and click on the Acquire switch to get the Virginia Notice of Default by Assignee to Obligor. Utilize your bank account to appear from the legal varieties you have bought earlier. Go to the My Forms tab of your own bank account and obtain an additional version from the file you want.
In case you are a new end user of US Legal Forms, allow me to share straightforward instructions so that you can stick to:
- First, make sure you have chosen the correct form for the area/state. It is possible to check out the shape while using Preview switch and study the shape information to ensure it is the best for you.
- In case the form fails to fulfill your expectations, utilize the Seach discipline to get the right form.
- Once you are certain the shape is suitable, click the Acquire now switch to get the form.
- Select the costs strategy you desire and type in the required info. Create your bank account and pay money for the transaction utilizing your PayPal bank account or bank card.
- Select the document formatting and acquire the legal file web template to the device.
- Total, change and printing and signal the obtained Virginia Notice of Default by Assignee to Obligor.
US Legal Forms may be the largest local library of legal varieties in which you can find numerous file layouts. Utilize the company to acquire professionally-manufactured paperwork that stick to condition requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
By statute the trustee is obligated to satisfy all real estate taxes to the date of sale and to submit to the Commissioner of Accounts evidence that those taxes have been paid. Section 55.1-324, Code of Virginia.
Title 55 - PROPERTY AND CONVEYANCES. Chapter 1 - Creation and Limitation of Estates; Their Qualities (55-1 thru 55-25.1) 55-17.1 - Trusts not to fail because no beneficiaries are specified by name and no duties laid on trustee; when interest of beneficiaries deemed personal property; liens.
The main difference between a deed and a deed of trust is that a deed is a transfer of ownership, while a deed of trust is a security interest. A deed of trust is used to secure a loan, while a deed is used to transfer ownership of a property.
The party secured by the deed of trust, or the holders of greater than fifty percent of the monetary obligations secured thereby, shall have the right and power to appoint a substitute trustee or trustees for any reason and, regardless of whether such right and power is expressly granted in such deed of trust, by ...
The grantor shall be deemed to covenant that he will pay all taxes, levies, assessments, and charges upon the property, including the fees and charges of such agents or attorneys as the trustee may deem advisable to employ at any time for the purpose of the trust, so long as any obligation upon the grantor under the ...
A mortgage involves only two parties: the borrower and the lender. A deed of trust has a borrower, lender and a ?trustee.? The trustee is a neutral third party that holds the title to a property until the loan is completely paid off by the borrower.
Protection of assignees or transferees of debts secured by real estate; form of certificate of transfer.
No person may be named or act, in person or by agent or attorney, as the trustee of a deed of trust conveying property to secure the payment of money or the performance of an obligation, either individually or as one of several trustees, unless such person is a resident of the Commonwealth.