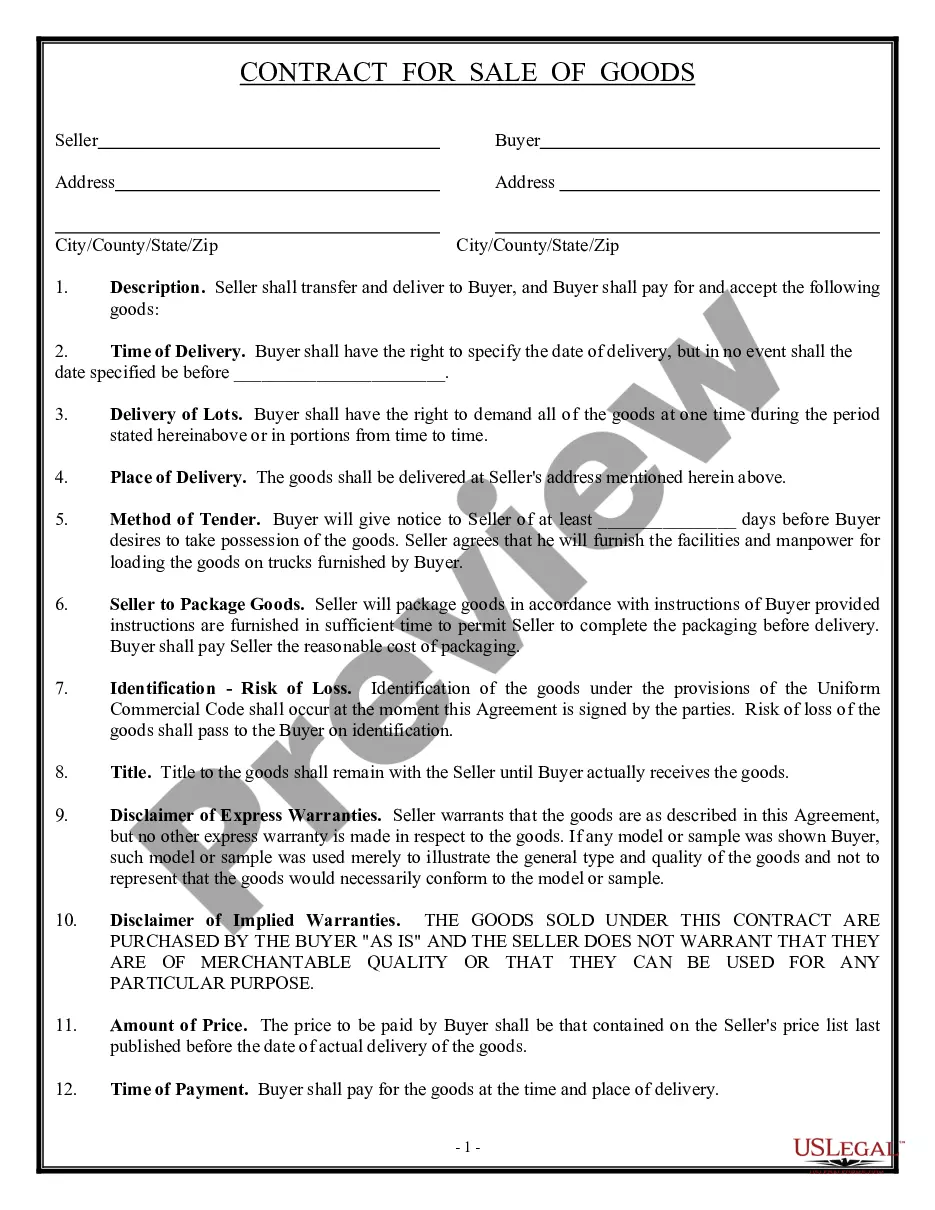
Virginia Contract — Sale of Goods refers to a legal agreement between two parties, where one party agrees to transfer ownership and title of goods to another party in exchange for monetary compensation. This contract follows the guidelines set forth by the Virginia Uniform Commercial Code (UCC), which governs commercial transactions within the state. The Virginia Contract — Sale of Goods encompasses various types of contracts, including: 1. Purchase Orders: This type of contract is initiated by a buyer, who issues a purchase order to a seller specifying the goods to be purchased, quantity, price, delivery terms, and other relevant details. 2. Sales Agreements: These contracts occur when a seller and a buyer agree upon the terms and conditions of a sale. The agreement contains information about the goods being sold, payment terms, delivery arrangements, warranties, and any other specific terms negotiated by the parties. 3. Supply Contracts: These contracts establish an ongoing relationship between a supplier and a buyer for the regular supply of goods over a specified period. They outline the terms of the agreement, including pricing, quality standards, delivery schedules, and dispute resolution mechanisms. 4. Conditional Sales Contracts: In this type of contract, ownership of the goods is initially retained by the seller until the buyer fulfills certain conditions, such as making all agreed-upon payments. Once the conditions are met, ownership of the goods transfers to the buyer. 5. Consignment Agreements: A consignment contract is formed when a party (consignor) entrusts goods to another party (consignee) for the purpose of selling them. The consignor retains ownership until the consignee successfully sells the goods and remits the agreed-upon proceeds. Key elements and clauses commonly found in a Virginia Contract — Sale of Goods include: a. Parties: Identification of the buyer (purchaser) and the seller, including their legal names and addresses. b. Goods: Detailed description of the goods being sold, including quantity, quality, specifications, and any applicable product codes or identifiers. c. Price: Stipulation of the purchase price and any agreed-upon payment terms, such as installment payments or a lump sum amount. d. Delivery and Acceptance: Terms outlining the delivery method, location, and timeframe, as well as the buyer's responsibility to inspect and accept the goods upon delivery. e. Warranties: Whether express or implied, the contract may state any warranties provided by the seller regarding the goods' condition, fitness for a particular purpose, or freedom from defects. f. Risk of Loss: Specification of when the risk of loss or damage to the goods transfers from the seller to the buyer. This is crucial in determining who bears responsibility if the goods are damaged or lost during transit. g. Remedies: The contract should outline the available remedies for both parties in case of breach or non-performance, including possible financial damages or specific performance. h. Governing Law and Jurisdiction: Designation of Virginia law as the governing law for the contract and designation of a specific jurisdiction for resolving disputes. In summary, a Virginia Contract — Sale of Goods encompasses various types of contracts that establish the terms and conditions of a transaction involving the sale of goods. It ensures that both parties are aware of their rights, responsibilities, and recourse in case of any disputes or breaches.
Virginia Contract - Sale of Goods
Description
How to fill out Virginia Contract - Sale Of Goods?
US Legal Forms - one of the greatest libraries of authorized kinds in America - offers a variety of authorized file layouts you are able to acquire or print. Using the internet site, you may get 1000s of kinds for business and individual purposes, categorized by classes, states, or key phrases.You can find the latest versions of kinds like the Virginia Contract - Sale of Goods in seconds.
If you currently have a subscription, log in and acquire Virginia Contract - Sale of Goods in the US Legal Forms catalogue. The Obtain key will appear on every single develop you view. You have access to all previously downloaded kinds from the My Forms tab of the bank account.
If you wish to use US Legal Forms initially, listed below are simple recommendations to help you get started off:
- Make sure you have picked the best develop for your personal city/county. Click on the Review key to review the form`s information. See the develop explanation to ensure that you have chosen the correct develop.
- If the develop doesn`t satisfy your demands, use the Look for field at the top of the monitor to obtain the one that does.
- Should you be pleased with the form, validate your option by clicking the Purchase now key. Then, select the prices prepare you want and offer your credentials to sign up to have an bank account.
- Procedure the financial transaction. Make use of bank card or PayPal bank account to finish the financial transaction.
- Find the formatting and acquire the form on your own system.
- Make changes. Load, revise and print and indication the downloaded Virginia Contract - Sale of Goods.
Every design you included with your money lacks an expiry time and is yours forever. So, if you would like acquire or print another duplicate, just go to the My Forms section and click on on the develop you require.
Gain access to the Virginia Contract - Sale of Goods with US Legal Forms, the most substantial catalogue of authorized file layouts. Use 1000s of specialist and state-certain layouts that satisfy your organization or individual requirements and demands.