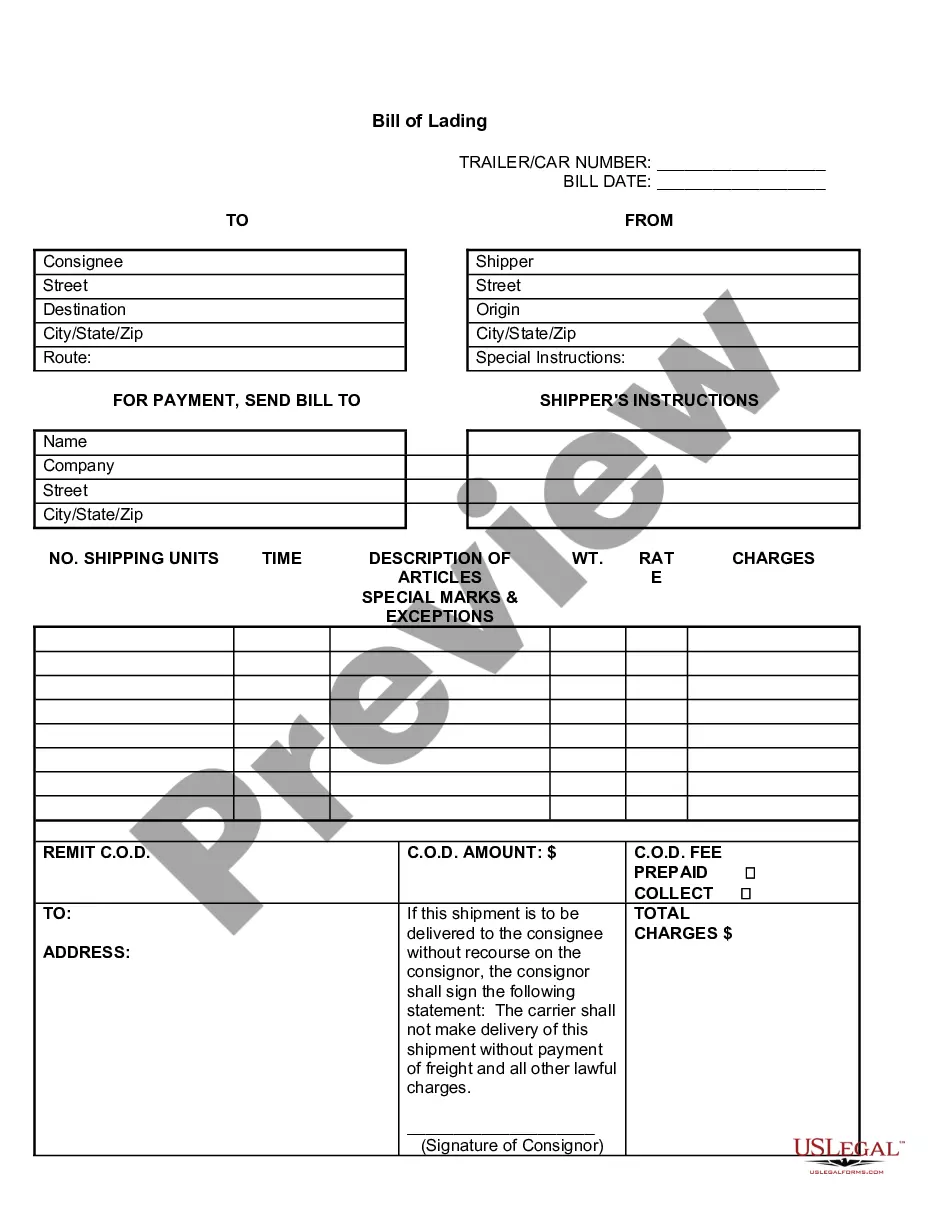
When applying for government grants there are a number of things to remember so the proposal is not rejected. Make sure they are on forms, and make sure that they comply with the stated guidelines. To ensure your proposal gets full consideration:
" Make sure the projects fit the guidelines and intent.
" Special categories of costs to reflect the areas that funding can cover. In some cases, only actual costs are allowed.
" Keep accurate records of expenditures and receipts.
" Submit the required number of application copies.
" Submit the application on time.
" Consider payment procedures, schedules, and partial payment schedules.
" Evaluation reports are often essential to final funding.
" Check on copyrights and credits.
" Make sure you know the funding organization requires credit.
" Check where copyright of materials is necessary and whose responsibility it is to get it.
" Note the decision date, so you can follow up if necessary.
Virginia Writing the Grant Proposal is a comprehensive and in-depth process of creating a proposal document to secure funding for various projects or initiatives. It involves carefully outlining the goals and objectives of the project, conducting thorough research, and presenting a persuasive case to potential funders. Throughout the process of Virginia Writing the Grant Proposal, several key components are included to ensure the proposal's success. These components may vary depending on the specific type of grant proposal being written, but they typically encompass the following: 1. Executive Summary: This section provides a concise overview of the project, outlining its purpose, expected outcomes, and the amount of funding requested. It acts as a summary to capture the attention of funders and encourage further exploration of the proposal. 2. Introduction: The introduction provides background information about the organization or institution submitting the proposal, highlighting its mission, track record, and credibility. It also establishes a connection between the project and the funder's area of interest or philanthropic goals. 3. Need Statement: This section outlines the problem, issue, or need that the project aims to address. It includes relevant statistics, research findings, and testimonials to demonstrate the significance and urgency of the project. Clear and compelling justifications are vital to convince funders of the project's merit. 4. Goals and Objectives: Virginia Writing the Grant Proposal requires a clear articulation of the project's overarching goals and specific, measurable objectives. These objectives should be realistic, time-bound, and align with the funder's priorities. They serve as a roadmap for evaluating the success and impact of the proposed project. 5. Project Plan: This section details the specific activities, milestones, and timeline for implementing the project. It provides a comprehensive plan that demonstrates the organization's capacity and readiness to execute the proposed activities. Resource allocation, staffing, and collaboration strategies are often included in this section. 6. Budget: Accurate and transparent financial planning is crucial in Virginia Writing the Grant Proposal. This section outlines the estimated costs for each project component, including personnel, supplies, equipment, and any necessary training or evaluation expenses. A clear budget justification explains how the funds will be utilized and demonstrates responsible financial management. 7. Evaluation and Sustainability: Grant funders are interested in long-term impact and the viability of the project beyond the grant period. The proposal should outline evaluation methods to measure progress and success, along with strategies for sustainability. This may include plans for securing additional funding, leveraging partnerships, or outlining other revenue streams to ensure the project's continuation. Different types of grant proposals include: 1. Program Development Grants: These proposals are focused on developing new programs or expanding existing ones to address specific needs or gaps in services. 2. Research Grants: These proposals aim to secure funding for scientific, academic, or social research projects. They typically require a detailed methodology, literature review, and clear research objectives. 3. Capacity-Building Grants: These proposals target organizations seeking funding to improve their internal infrastructure, such as technology upgrades, staff training, or strategic planning initiatives. 4. Operating Grants: Operating grants provide support for general organizational expenses, including staff salaries, rent, utilities, and administrative costs. They are often sought by nonprofit organizations to cover ongoing operational expenses. In summary, Virginia Writing the Grant Proposal involves a systematic and strategic approach to secure funding for a project. The proposal should illustrate a clear need, provide a well-thought-out project plan with objectives and strategies, and demonstrate a budget that aligns with the project's goals and objectives. Different types of grant proposals vary based on the specific nature and purpose of the project being proposed.