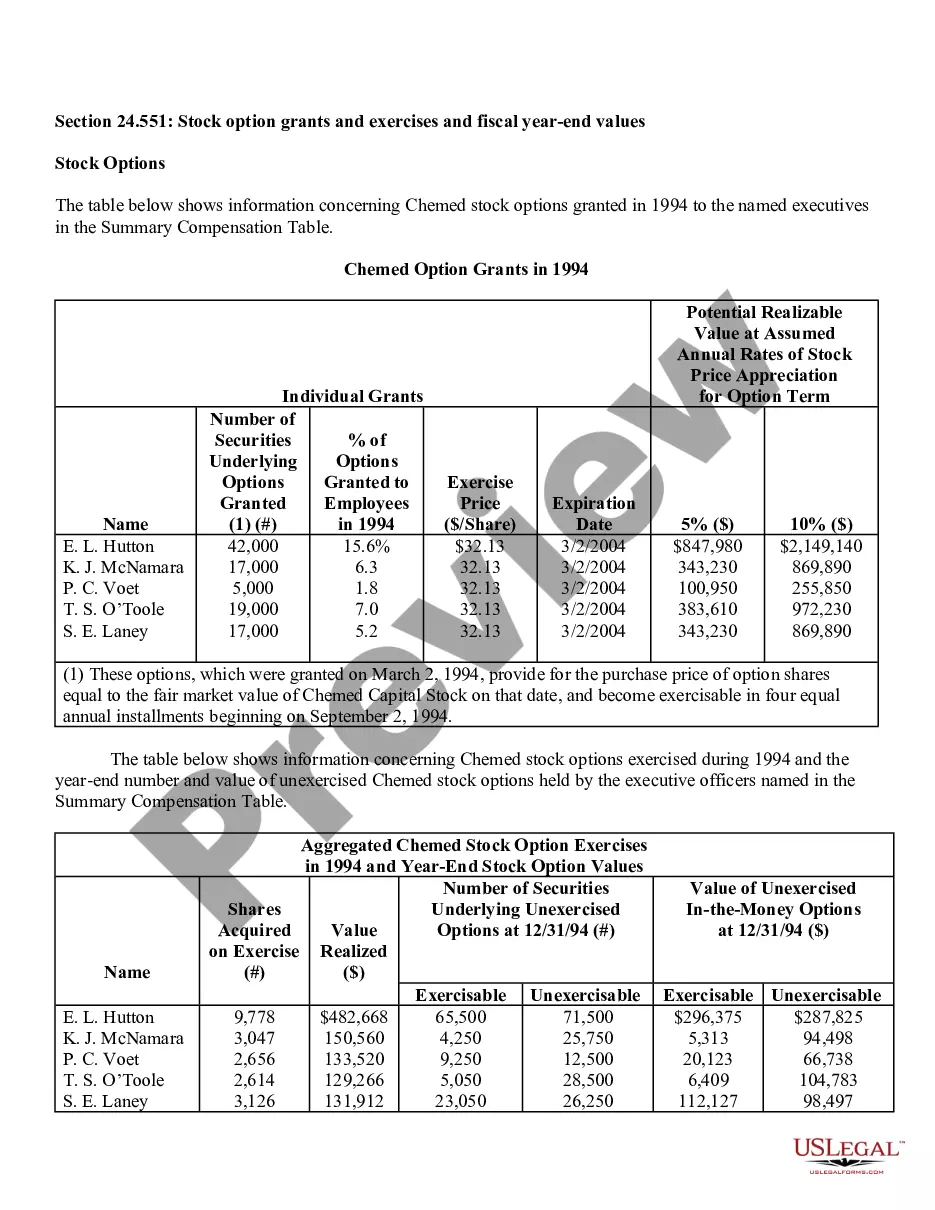
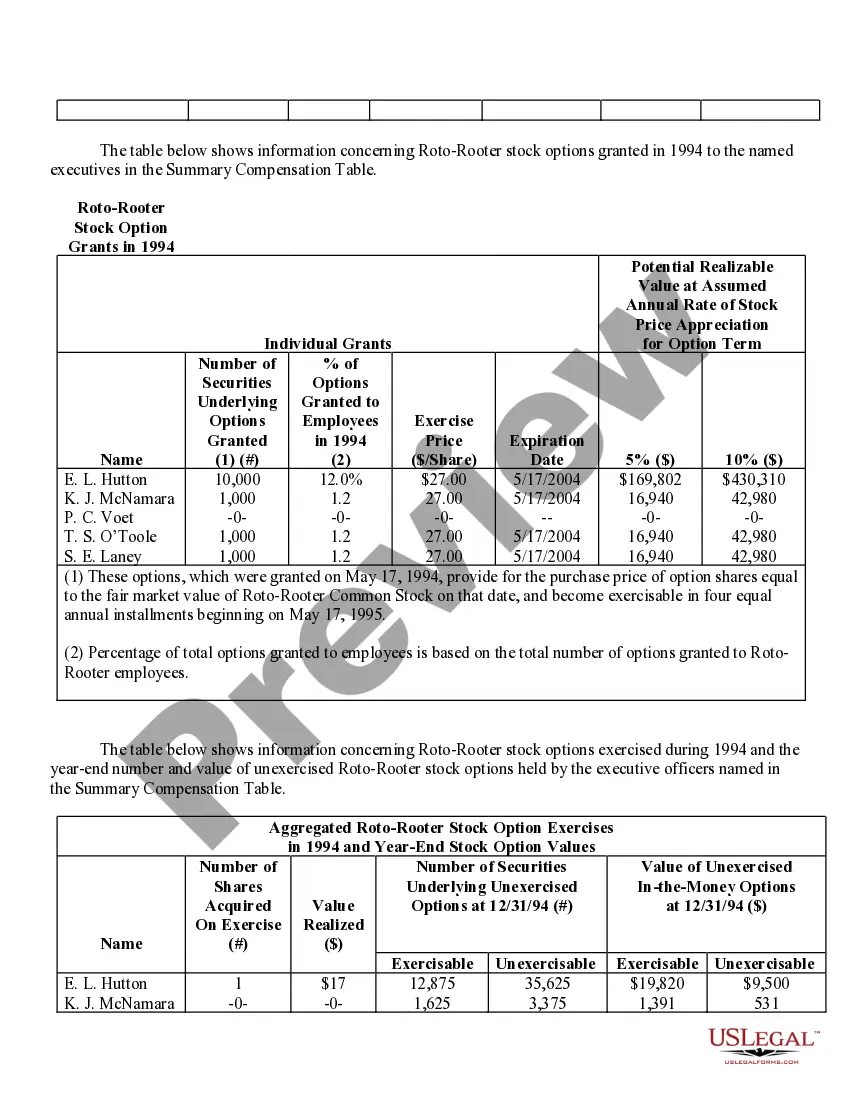
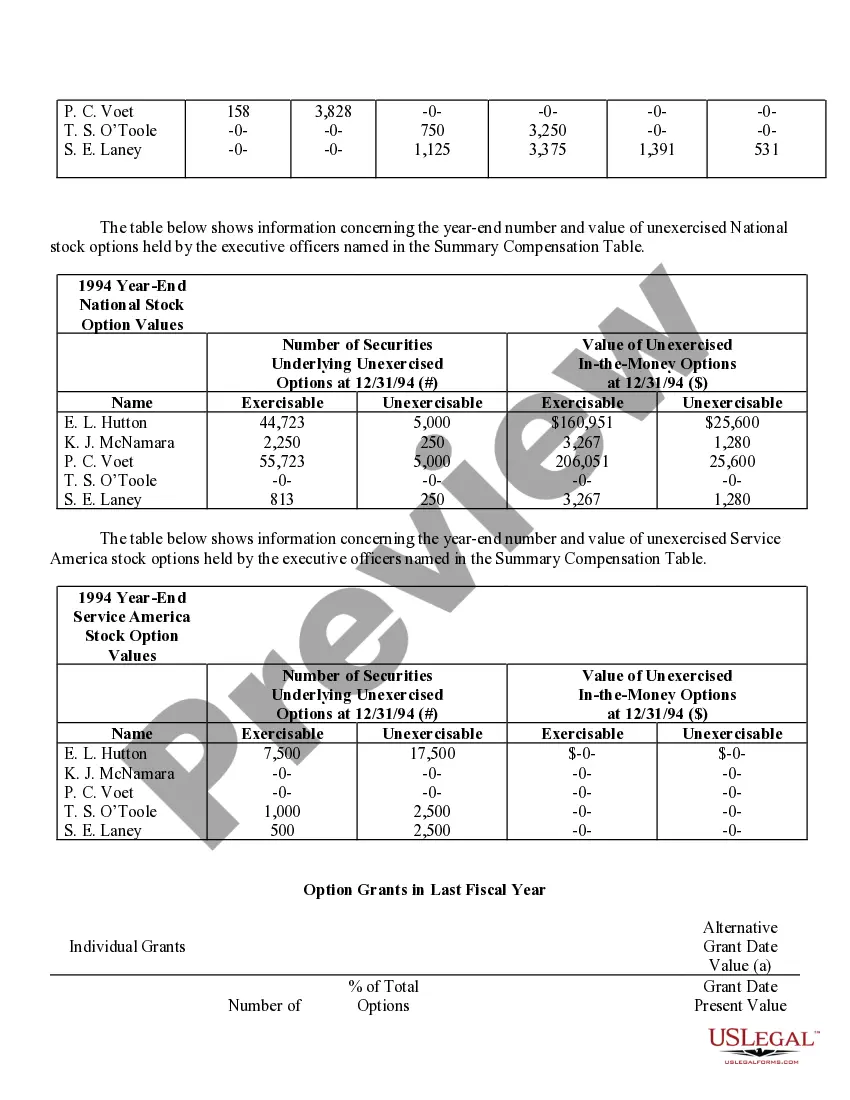
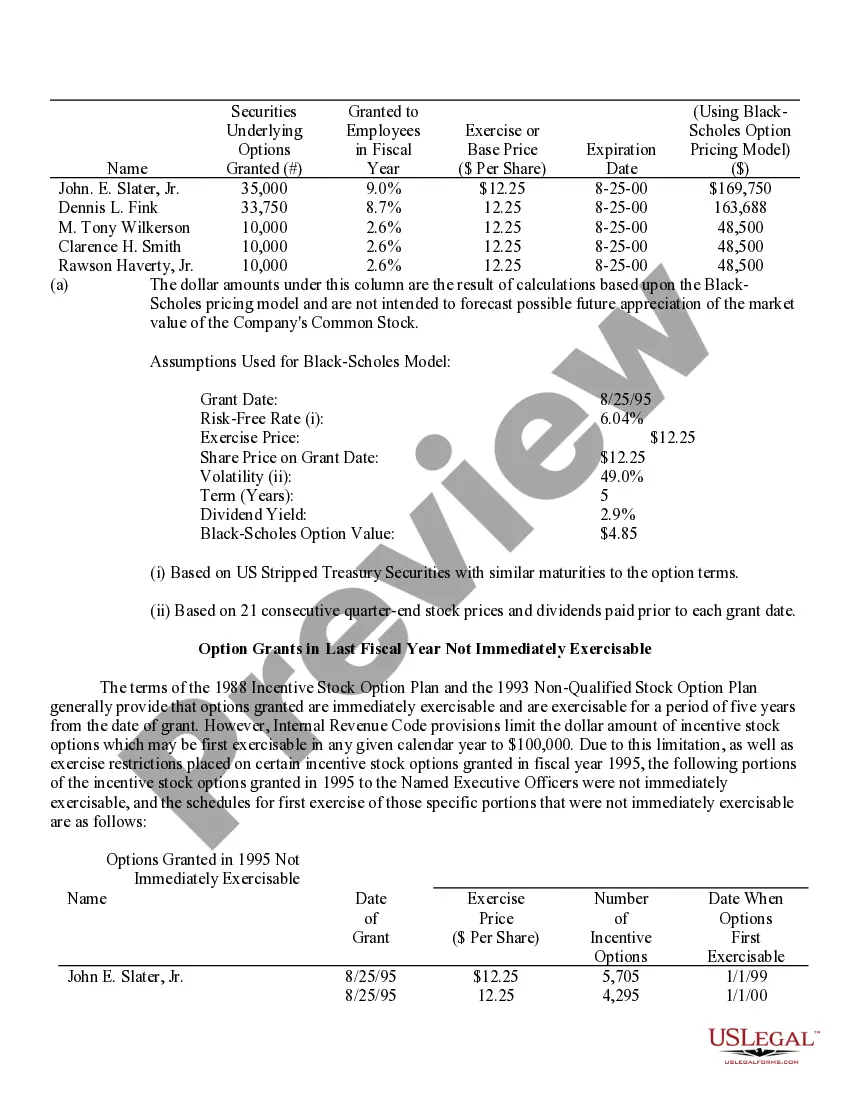
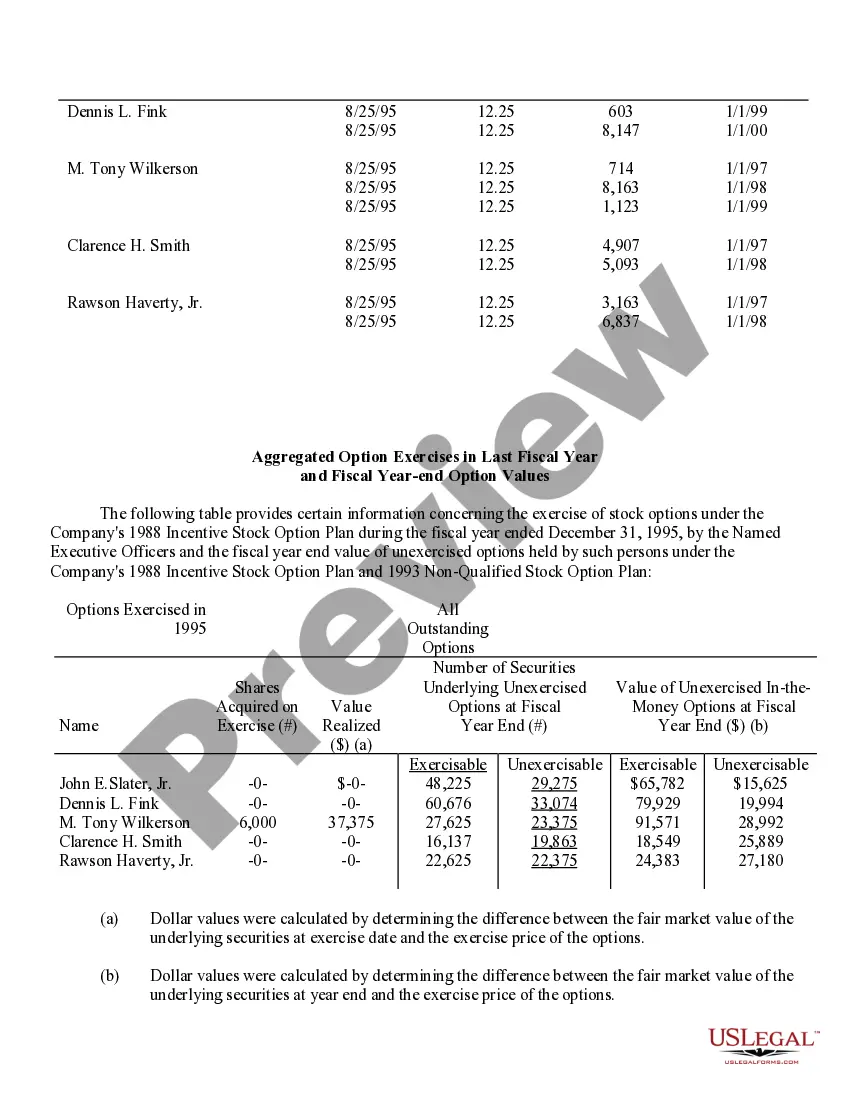
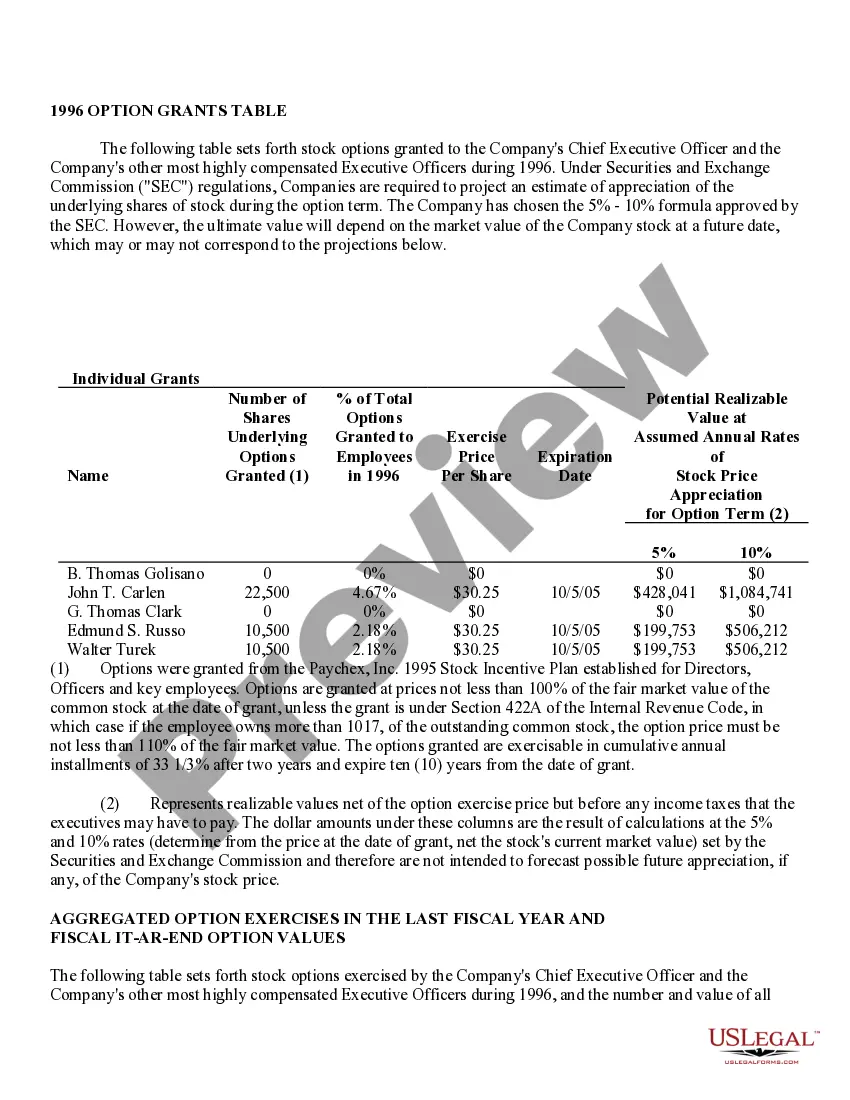
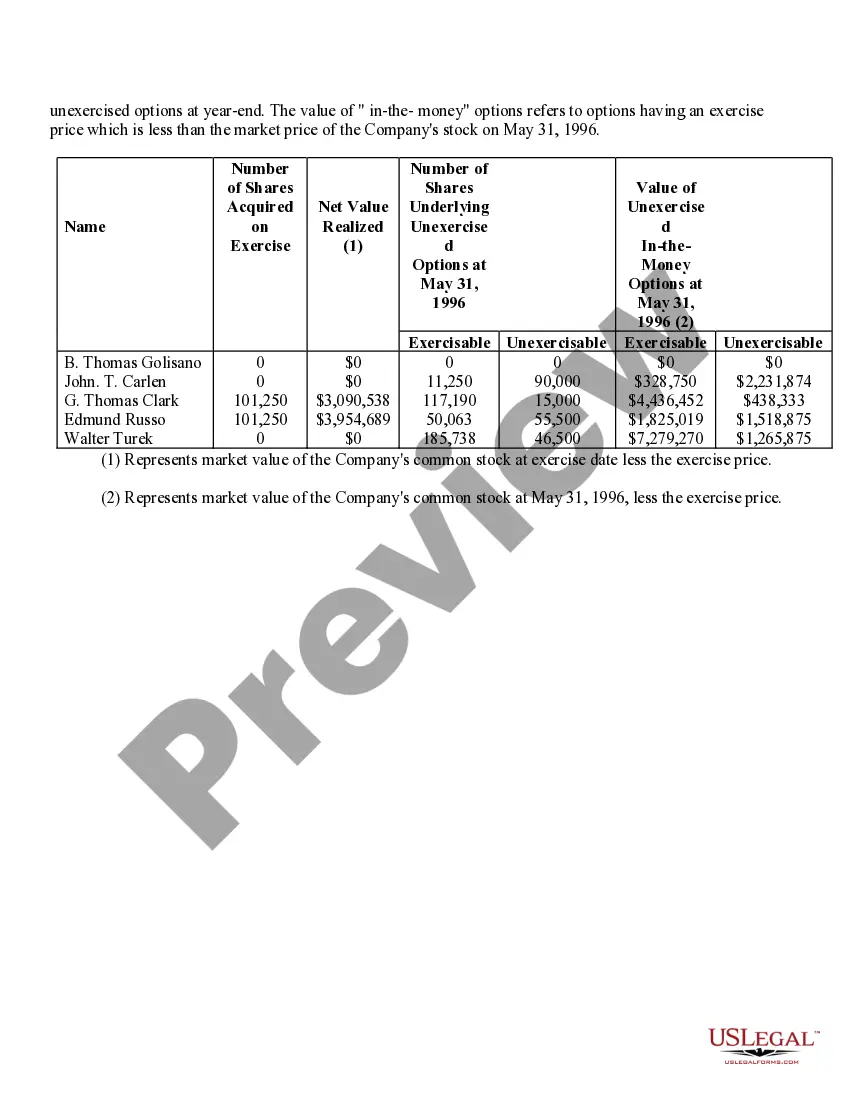
Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values refer to the various types of stock option grants, exercises, and their associated values at the end of a fiscal year in the state of Virginia. Stock options are a type of compensation provided by companies to their employees, giving them the right to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, known as the exercise price or strike price. In Virginia, there are multiple types of stock option grants, each with its own rules and regulations. Some common types include Incentive Stock Options (SOS) and Non-Qualified Stock Options (Nests). SOS are typically offered to key employees as a form of long-term incentive to drive company success. These options usually come with certain tax advantages, as any potential gain from the exercise of SOS can be eligible for preferential tax treatment. However, SOS are subject to specific conditions, such as holding periods, price limits, and employee eligibility criteria. Nests, on the other hand, are more flexible and can be granted to both employees and non-employees. They do not have the same tax advantages as SOS, as they are usually taxed as ordinary income upon exercise. However, they offer greater flexibility in terms of exercise price, expiration period, and eligibility requirements. When a stock option grant is exercised, the holder purchases the company stock at the predetermined strike price. The fiscal year-end value of a stock option grant refers to the value of the options at the end of the company's fiscal year, which typically determines the taxable income for the employee associated with the exercise of the options. Calculating the fiscal year-end values entails determining the fair market value of the company's stock at that time and multiplying it by the number of shares acquired through the stock option exercise. It is crucial to accurately assess the value, as it impacts not only the employee's taxable income but also their overall compensation and potential financial gains. Companies in Virginia need to comply with the rules and regulations set forth by both federal and state authorities regarding stock option grants and exercises. These regulations aim to ensure fair treatment of employees and proper reporting and taxation of stock option-related income. In summary, Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values encompass the various types of stock option grants available in Virginia, such as SOS and Nests, and the determination of their values at the end of the fiscal year. Compliance with the applicable rules and accurate evaluation of these values are crucial to facilitate fair compensation practices and ensure appropriate taxation procedures.
Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values
Description
How to fill out Virginia Stock Option Grants And Exercises And Fiscal Year-End Values?
Finding the right authorized document template can be quite a have difficulties. Obviously, there are a variety of layouts available on the Internet, but how can you find the authorized type you need? Take advantage of the US Legal Forms website. The assistance gives a large number of layouts, like the Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values, that you can use for enterprise and private demands. Every one of the varieties are examined by experts and meet up with federal and state demands.
If you are currently registered, log in for your accounts and click the Obtain button to obtain the Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values. Make use of accounts to check from the authorized varieties you have acquired formerly. Go to the My Forms tab of your own accounts and have one more version of your document you need.
If you are a new customer of US Legal Forms, allow me to share straightforward guidelines for you to adhere to:
- Initial, make sure you have selected the right type for your personal town/state. You may look over the form while using Review button and study the form description to guarantee this is basically the right one for you.
- If the type will not meet up with your requirements, utilize the Seach area to find the proper type.
- When you are positive that the form is proper, go through the Acquire now button to obtain the type.
- Select the prices strategy you would like and enter the needed information. Make your accounts and buy the order utilizing your PayPal accounts or credit card.
- Pick the data file file format and download the authorized document template for your device.
- Complete, change and produce and indication the acquired Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values.
US Legal Forms is the biggest local library of authorized varieties where you can discover various document layouts. Take advantage of the company to download skillfully-manufactured paperwork that adhere to status demands.