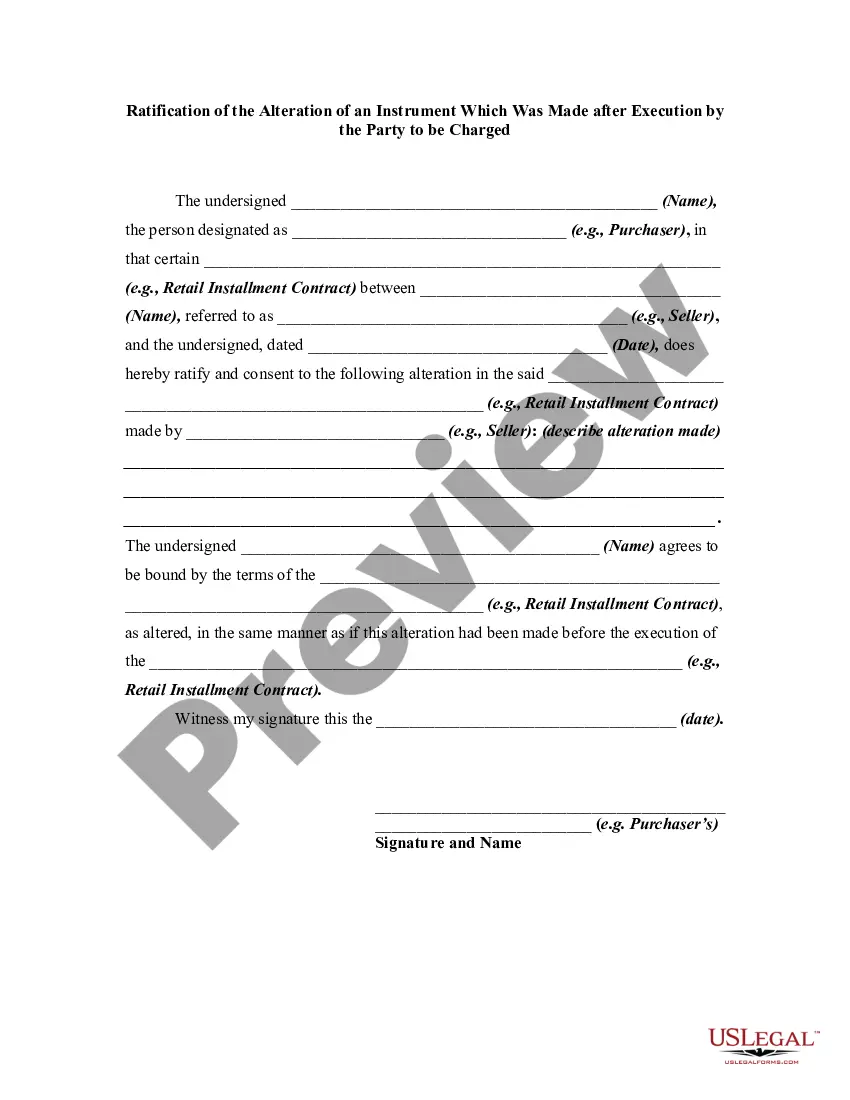
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought.
If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged
Description
How to fill out Ratification Of The Alteration Of An Instrument Which Was Made After Execution By The Party To Be Charged?
US Legal Forms - one of the biggest collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a diverse selection of legal document templates that you can download or create.
By using the website, you can access thousands of forms for business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords.
You can find the latest versions of forms such as the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged in just seconds.
If the form does not meet your requirements, utilize the Search field at the top of the page to find one that does.
Once you are satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking the Get Now option. Then, select the payment plan you desire and provide your details to create an account.
- If you possess a monthly subscription, Log In and download the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged from your US Legal Forms library.
- The Download option will appear on each form you view.
- You can access all previously downloaded forms in the My documents section of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, here are simple guidelines to get started.
- Ensure that you have chosen the appropriate form for your city/region.
- Review the form by clicking the Preview option to examine its content.
Form popularity
FAQ
The jurisdiction of the BVI court typically covers civil matters, including contract disputes, property issues, and corporate governance. The court system is designed to handle a variety of cases efficiently, ensuring fair and timely resolutions. For any concerns relating to the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, exploring resources on uslegalforms can facilitate your legal journey.
The British Virgin Islands (BVI) is renowned for its offshore jurisdiction, offering favorable regulations for businesses and individuals. It provides a secure environment for asset protection, investment, and international business operations. When considering the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, understanding BVI’s offshore benefits can be crucial for effective legal planning.
The British Virgin Islands, while a self-governing territory, maintains a legal framework that is largely based on UK law. However, local legislation may diverge to address unique circumstances. To understand the implications of the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, consulting local legal resources is advisable.
The legal jurisdiction of the British Islands encompasses both civil and criminal law within its territories. Each island has its own system of courts, which resolve matters based on local statutes and common law. If you require assistance with legal documents related to the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, uslegalforms can provide you with the necessary tools.
The legal system in the British Islands is derived from English common law, which has evolved to meet local needs. Courts in the British Virgin Islands operate under this framework, implementing statutes and precedents. Understanding the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is vital for anyone navigating legal issues in this jurisdiction.
Common law in the Caribbean, including the Virgin Islands, refers to a legal system developed through court decisions rather than written statutes. This system promotes legal consistency and offers guidance for resolving disputes. It plays a significant role in processes like the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, helping individuals navigate legal challenges with clarity.
No, residents of the Virgin Islands are not considered U.S. citizens by birth. Instead, they are U.S. nationals, which grants them certain rights but does not include voting in federal elections. This distinction is important for legal matters, including those pertaining to the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
The Islands follow a mix of local legislation and the inherited common law from the British legal system. This combination shapes the legal landscape, enabling strong business practices and regulatory frameworks. For instance, understanding these laws is essential when dealing with the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Yes, the British Virgin Islands (BVI) is a common law jurisdiction. This legal system is based on decisions made in past court cases, ensuring consistent application of the law. Residents and businesses in the BVI can rely on this framework, which facilitates processes like the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged.
Yes, individuals born in the Virgin Islands are U.S. citizens, which grants them the same fundamental rights as other citizens. This status allows residents to participate in federal programs and benefits while also facing the unique legal landscape. When discussing issues like the Virgin Islands Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, being aware of these citizenship rights can be advantageous. Seeking legal advice through platforms like uslegalforms can provide clarity and support.