Arbitration is an alternative means of settling a dispute by impartial persons without proceeding to a court trial. It is sometimes preferred as a means of settling a matter in order to avoid the expense, delay, and acrimony of litigation. There is no discovery and there are simplified rules of evidence in arbitration. The arbitrator or arbitrators are selected directly by the parties or are chosen in accordance with the terms of a contract in which the parties have agreed to use a court-ordered arbitrator or an arbitrator from the American Arbitration Association. If there is no contract, usually each party chooses an arbitrator and the two arbitrators select a third to comprise the panel. When parties submit to arbitration, they agree to be bound by and comply with the arbitrators' decision. The arbitrators' decision is given after an informal proceeding where each side presents evidence and witnesses. Arbitration hearings usually last only a few hours and the opinions are not public record. Arbitration has long been used in labor, construction, and securities regulation, but is now gaining popularity in other business disputes.
Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General
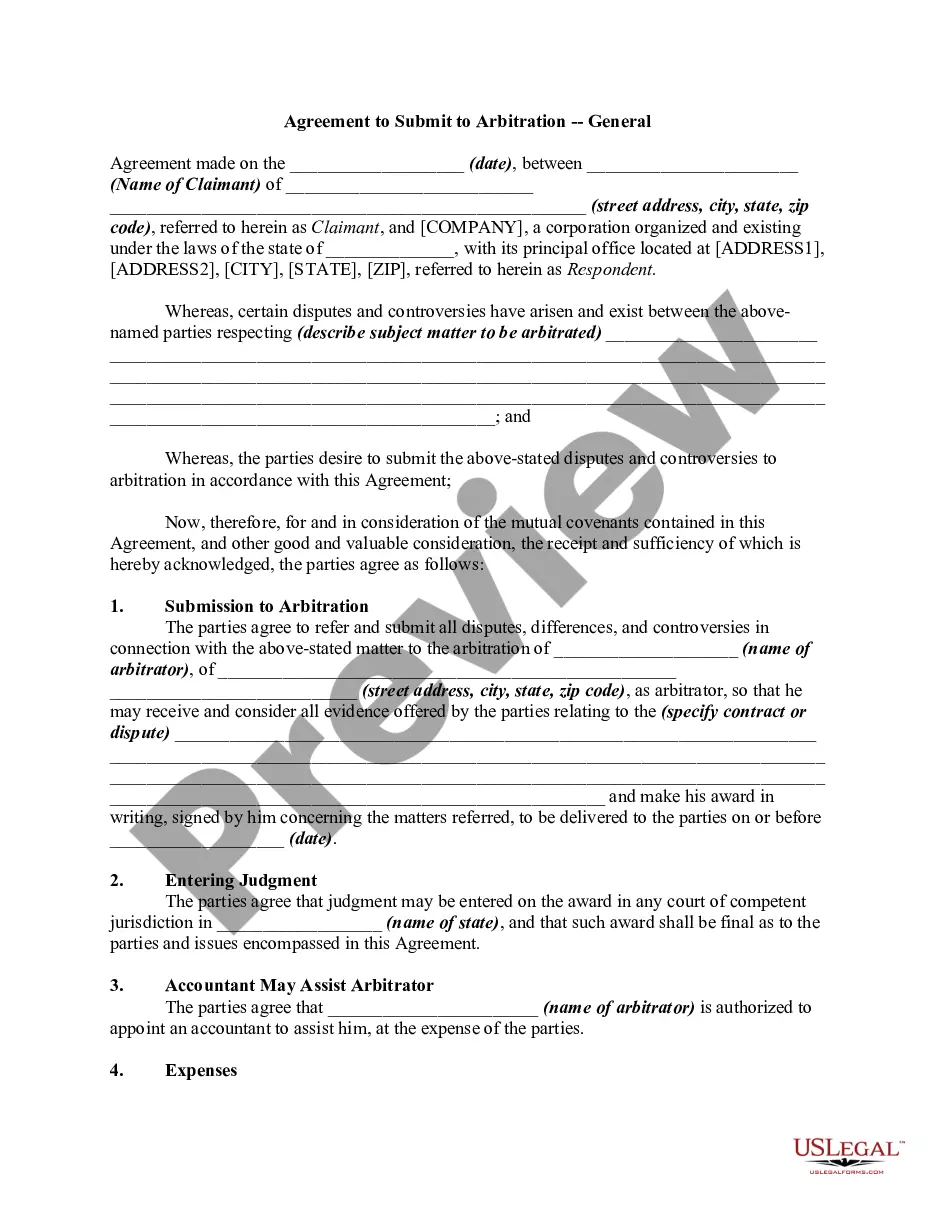
Description
How to fill out Agreement To Submit To Arbitration - General?
If you need to fill, download, or print authorized document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest collection of legal forms available online.
Take advantage of the site’s user-friendly and convenient search feature to find the documents you require.
Various templates for business and personal purposes are categorized by types and states, or keywords. Use US Legal Forms to quickly locate the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General.
Every legal document template you purchase is yours indefinitely. You have access to every form you downloaded in your account. Navigate to the My documents section and select a form to print or download again.
Obtain and download, and print the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General with US Legal Forms. There are millions of professional and state-specific forms available for your business or personal needs.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms customer, Log In to your account and click the Acquire button to obtain the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded from the My documents tab in your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the steps below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Utilize the Preview option to review the form’s details. Remember to read the summary.
- Step 3. If you are not content with the form, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find alternative versions of the legal form format.
- Step 4. Once you have located the form you need, click the Buy now button. Choose the pricing plan you prefer and enter your details to register for an account.
- Step 5. Complete the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the purchase.
- Step 6. Select the format of the legal form and download it to your device.
- Step 7. Fill out, modify, and print or sign the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General.
Form popularity
FAQ
The arbitration clause serves as a stipulation within a contract that directs the parties to arbitration, while the submission agreement outlines specific terms regarding how arbitration will be conducted. Both are integral to the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General but serve different purposes. Understanding this distinction can help you navigate your contract more effectively and ensure compliance.
The arbitration clause or agreement is a provision in a contract that mandates parties to resolve disputes through arbitration rather than through the court system. Within the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General, this clause defines the arbitration process, ensuring that disputes will be handled efficiently and systematically. It provides a roadmap for resolution that prioritizes effective outcomes.
A submission agreement relates to the commitment of parties to settle a dispute through arbitration as outlined in the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General. This document formalizes the agreement to adhere to arbitration rules, ensuring that all parties are clear on the process to resolve any potential conflicts. It creates a legally binding commitment to arbitrate.
Your company may send you an arbitration agreement to establish a clear path for resolving potential disputes. The Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General provides a framework that can save time and reduce costs associated with litigation. It sets expectations for resolving conflicts while maintaining a professional relationship.
The British Islands Arbitration Act governs arbitration proceedings in the British Islands, ensuring that disputes can be resolved efficiently and fairly. While the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General functions independently, understanding this act can clarify the legal framework surrounding your arbitration. Familiarity with both can enhance your strategic approach to conflict resolution.
Typically, you must agree to an arbitration agreement if it is a part of your contract or terms of service. The Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General establishes this expectation, creating a commitment to arbitration. However, it remains crucial to review the terms and consider legal advice if you have concerns.
Deciding between settlement and arbitration often depends on the specifics of your situation. Settling might seem appealing for a quick resolution, while arbitration through the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General provides a structured process. Arbitration can offer more predictability and enforceability compared to informal settlements.
An arbitration clause example could read: 'All disputes between the parties shall be submitted to arbitration in accordance with the Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General.' This clause ensures that any conflicts will be handled outside the court system, providing a structured and timely resolution.
An example of an arbitration clause in an agreement might state that any disputes arising from the agreement will be resolved by arbitration according to the 'Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General.' This clause should set forth the procedure for appointing arbitrators and any rules that will govern the arbitration process.
To write an arbitration statement, present your case in a structured format, starting with an introduction that outlines the dispute. Use clear language to explain your position and evidence, and conclude with a summary of your requests. Including 'Virgin Islands Agreement to Submit to Arbitration - General' helps to clarify the framework under which you are operating.