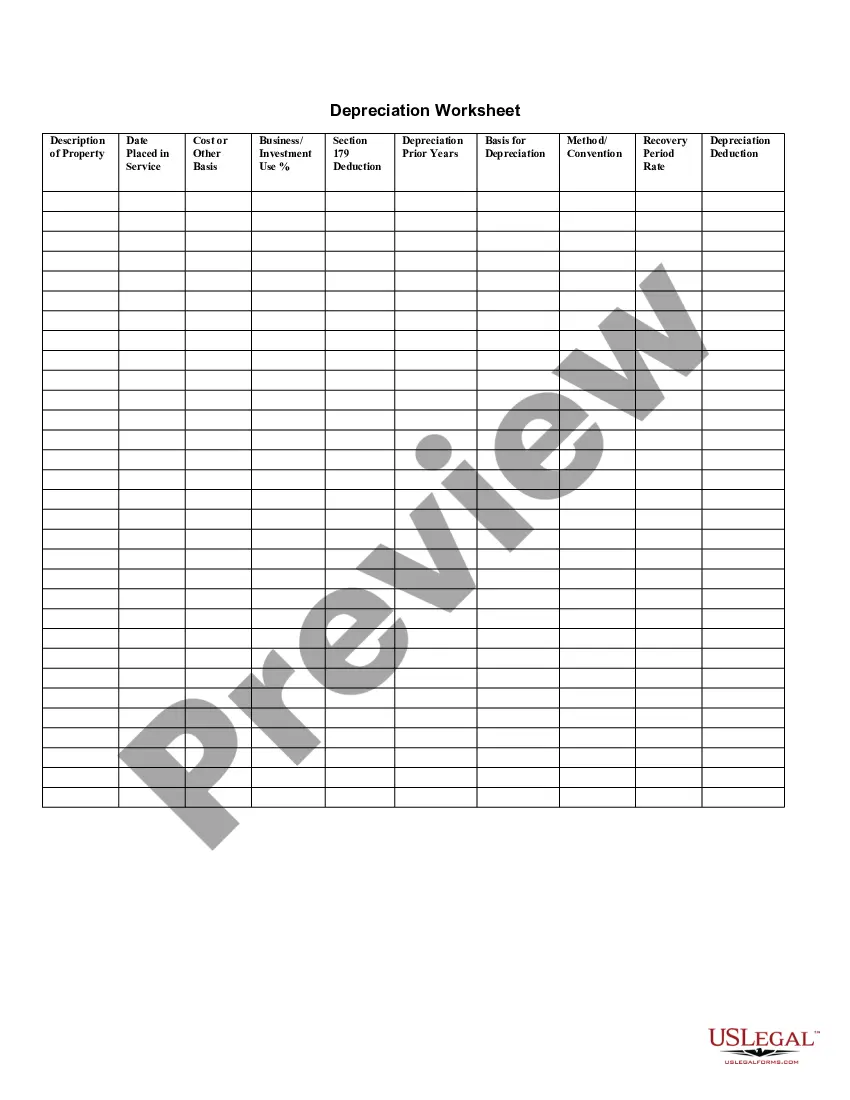
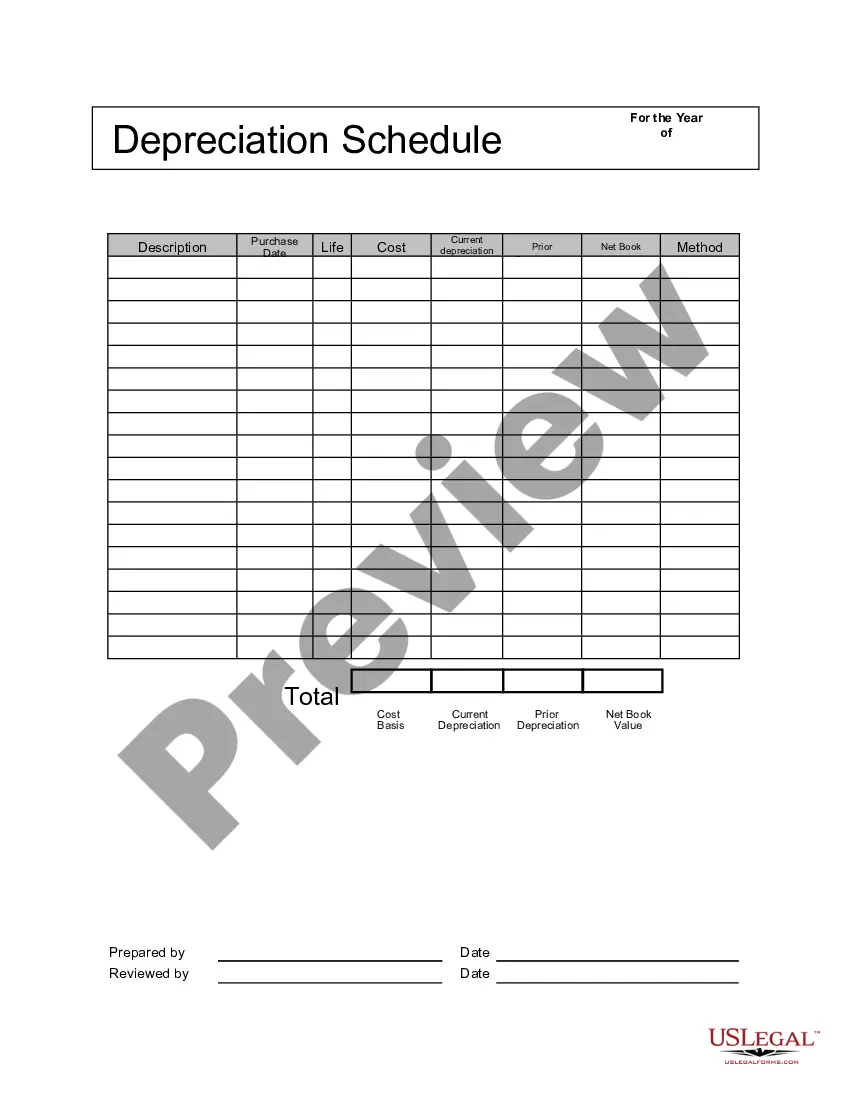
Virgin Islands Depreciation Schedule
Description
How to fill out Depreciation Schedule?
If you wish to be thorough, obtain, or download legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest assortment of legal forms available online.
Take advantage of the website's simple and convenient search to find the documents you require.
A diverse range of templates for business and personal applications are organized by categories and jurisdictions, or keywords.
Step 5. Process the payment. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
Step 6. Choose the format of your legal document and download it to your device. Step 7. Complete, modify, and print or sign the Virgin Islands Depreciation Schedule.
- Use US Legal Forms to locate the Virgin Islands Depreciation Schedule in just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms user, Log In to your account and then click the Download button to retrieve the Virgin Islands Depreciation Schedule.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded in the My documents section of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow these steps.
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Preview option to review the form's contents. Be sure to read through the description.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find other variations of the legal form template.
- Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, click on the Get now button. Choose the pricing plan you prefer and provide your information to sign up for the account.
Form popularity
FAQ
To be depreciable, the property must meet all the following requirements.It must be property you own.It must be used in your business or income-producing activity.It must have a determinable useful life.It must be expected to last more than 1 year.
According to South Carolina Instructions for Form SC1040, here is a list of South Carolina's Other Additions. Taxpayers that claim bonus depreciation under federal law must add back the difference between the bonus depreciation taken and the depreciation which would have been allowed without bonus depreciation.
The System calculates the state depreciation for these assets from your federal depreciation entries on the Depreciation worksheet. For assets acquired before January 1, 1985, South Carolina does NOT allow the Section 179 and ITC basis adjustment.
South Carolina does not recognize bonus depreciation in IRC Section 168(k). With or without bonus depreciation, the depreciable life of the property is the same for federal and state purposes.
The depreciation method used for rental property is MACRS. There are two types of MACRS: ADS and GDS. GDS is the most common method that spreads the depreciation of rental property over its useful life, which the IRS considers to be 27.5 years for a residential property.
Since 2008, North Carolina has not recognized the bonus depreciation, and requires tax payers to add back 85% of any bonus depreciation taken that year on the federal return, in calculating their state taxable income.
To calculate the annual amount of depreciation on a property, you divide the cost basis by the property's useful life. In our example, let's use our existing cost basis of $206,000 and divide by the GDS life span of 27.5 years. It works out to being able to deduct $7,490.91 per year or 3.6% of the loan amount.
What happens if you don't depreciate rental property? In essence, you lose the opportunity to claim a massive tax benefit. If/when you decide to sell the property, you will still pay depreciation recapture tax, regardless of whether or not you claimed the depreciation during your tenure as the owner of the property.
Property acquired by gift or inheritance, as well as property purchased from related parties does not qualify for the Section 179 Deduction (in other words, you can't sell equipment to yourself and qualify for Section 179).
The balance of depreciation is written off in the year after the last class life year. For 5-year property that's the sixth year. So, 1/2 + 5 + 1/2 (the balance remaining in the last year after the class life year) equals 6 years.