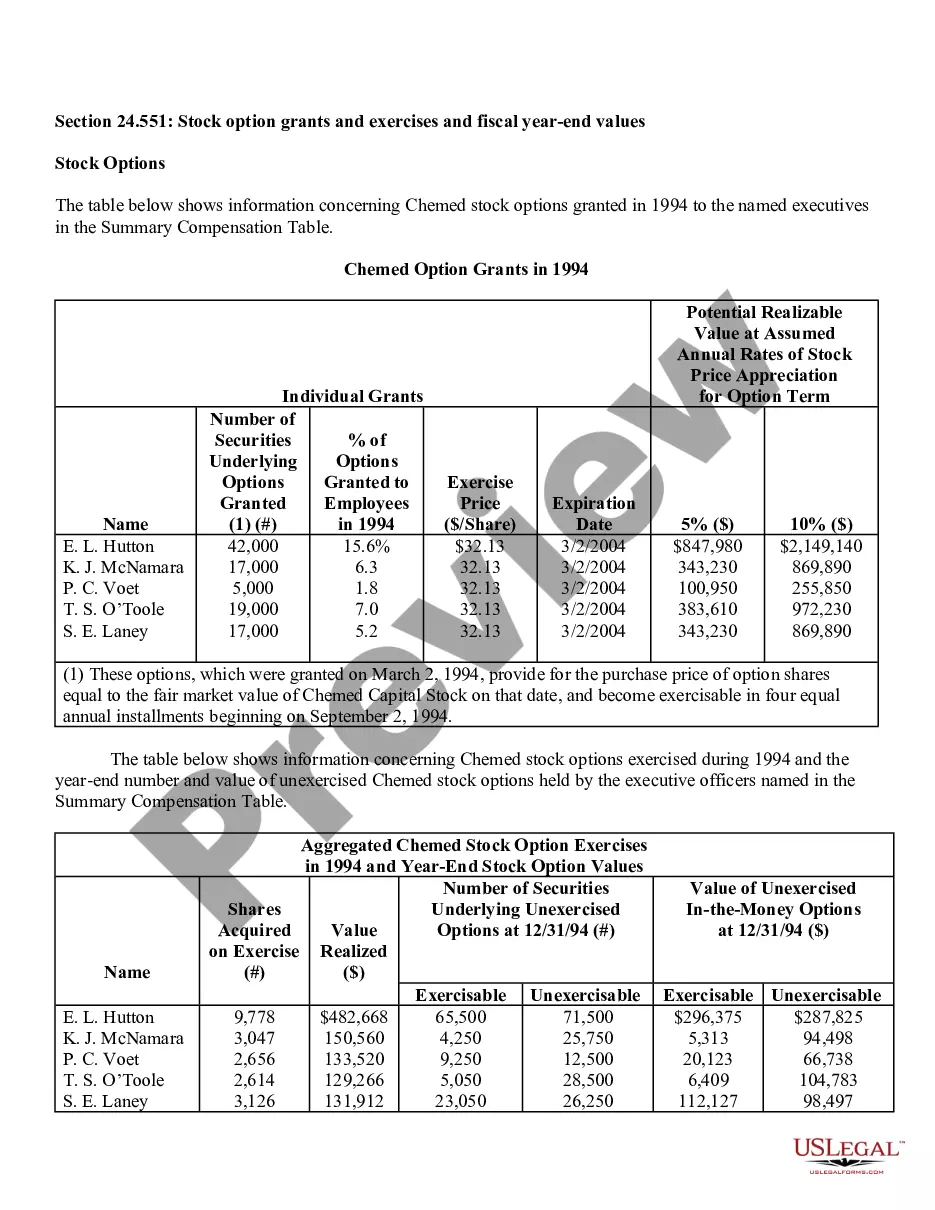
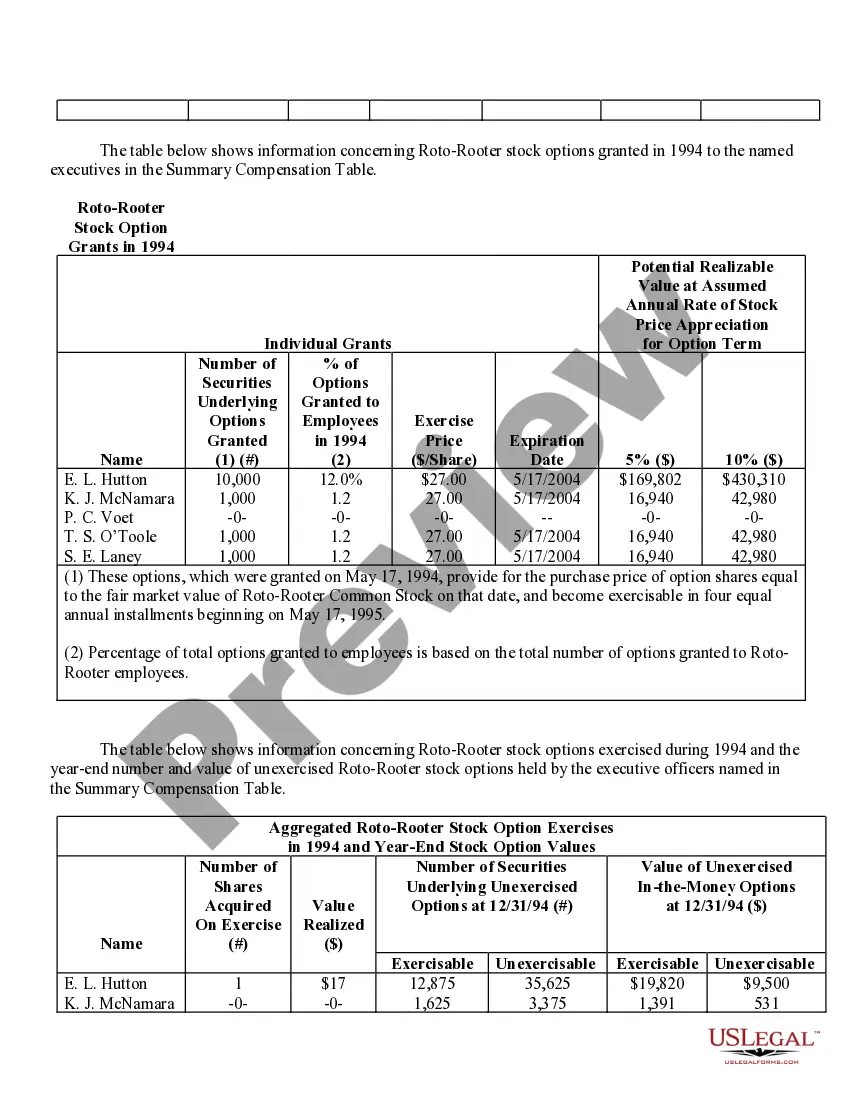
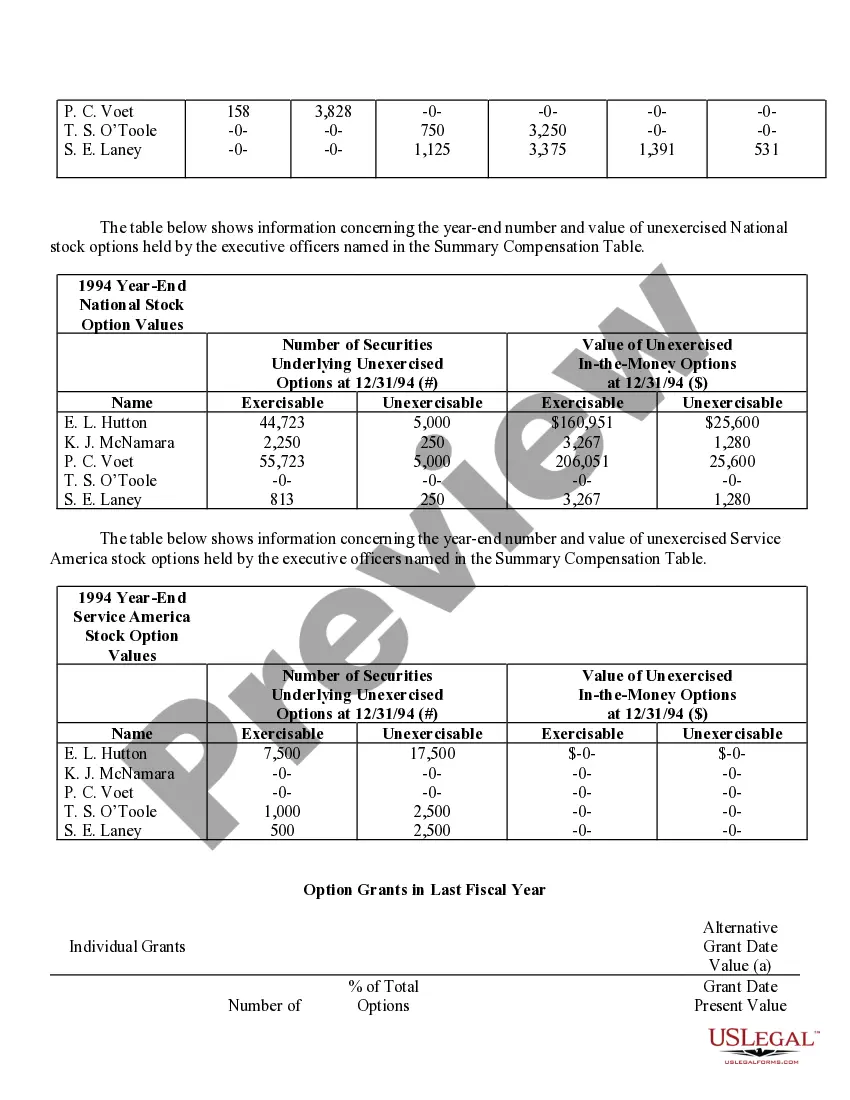
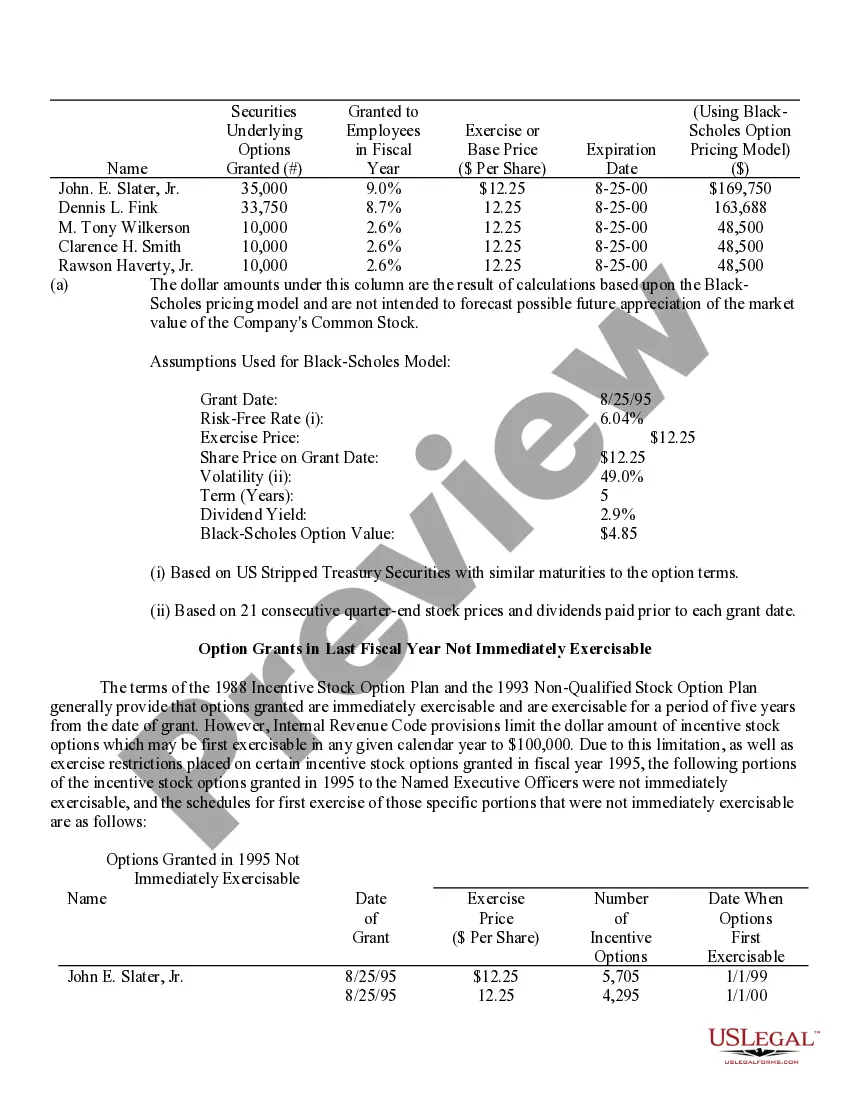
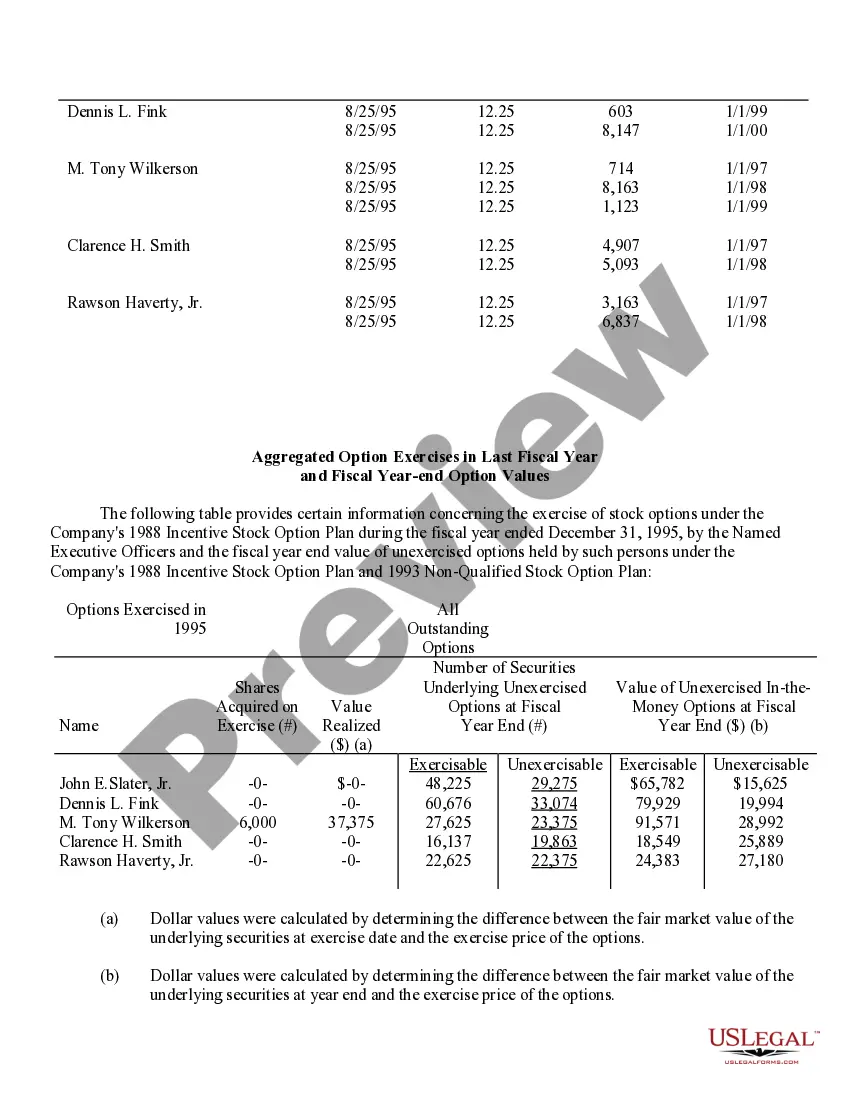
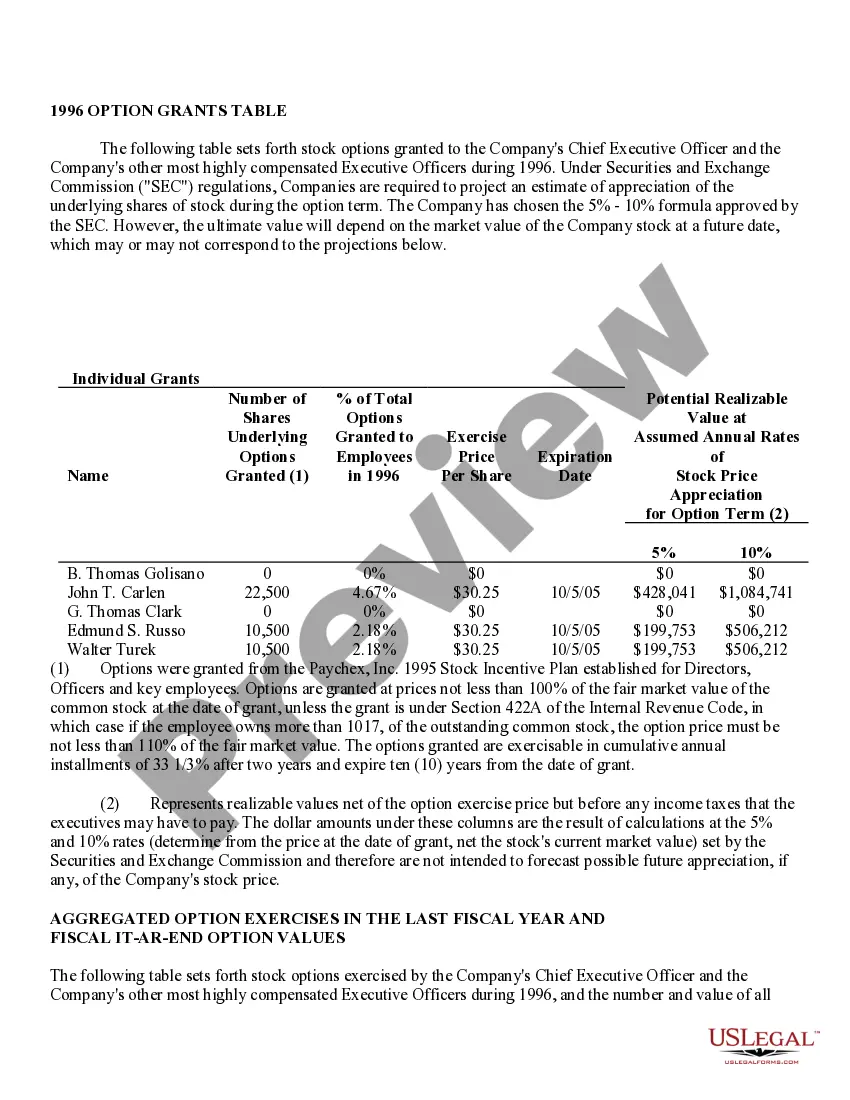
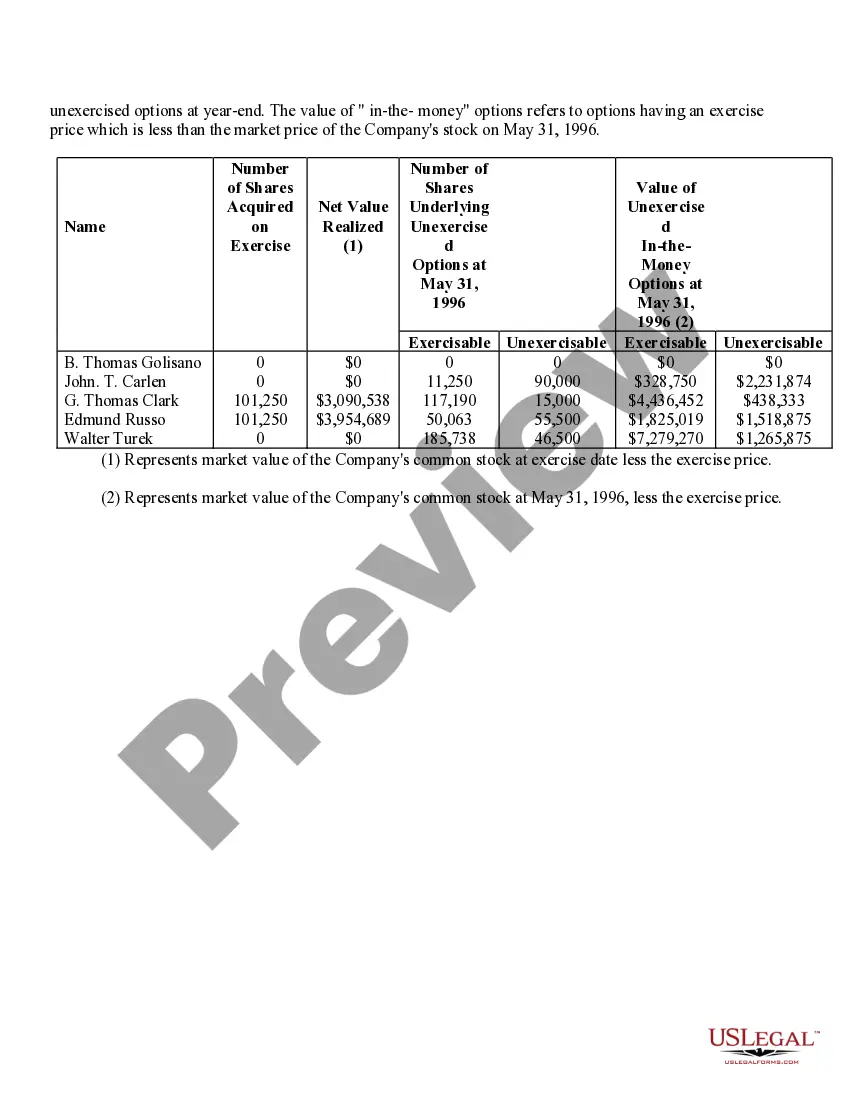
Virgin Islands Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values
Description
How to fill out Stock Option Grants And Exercises And Fiscal Year-End Values?
Are you currently within a situation that you need to have paperwork for either organization or individual uses just about every day? There are a variety of legitimate document web templates available online, but locating ones you can trust isn`t easy. US Legal Forms provides a large number of kind web templates, just like the Virgin Islands Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values, that are composed to meet federal and state needs.
Should you be already familiar with US Legal Forms web site and get an account, just log in. Following that, it is possible to download the Virgin Islands Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values template.
Unless you provide an bank account and need to begin to use US Legal Forms, abide by these steps:
- Get the kind you want and ensure it is for that proper metropolis/region.
- Use the Preview button to review the shape.
- Browse the explanation to ensure that you have selected the appropriate kind.
- If the kind isn`t what you are searching for, make use of the Search field to get the kind that meets your needs and needs.
- Once you find the proper kind, click on Acquire now.
- Choose the costs prepare you want, submit the desired details to make your money, and pay for your order with your PayPal or credit card.
- Decide on a practical data file structure and download your backup.
Get all of the document web templates you possess bought in the My Forms menu. You can obtain a more backup of Virgin Islands Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values whenever, if needed. Just go through the essential kind to download or print the document template.
Use US Legal Forms, the most considerable selection of legitimate kinds, to save lots of some time and avoid errors. The assistance provides professionally created legitimate document web templates that you can use for an array of uses. Make an account on US Legal Forms and initiate making your way of life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
You can calculate the aggregate exercise price by taking the strike price of the option and multiplying it by its contract size. In the case of a bond option, the exercise price is multiplied by the face value of the underlying bond.
You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option. You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss. However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income.
Exercise Price ? Also known as the strike price, the grant price is the price at which you can buy the shares of stock. Regardless of the future value of that particular stock, the option holder will have the right to buy the shares at the grant price rather than the current, actual price.
The current FMV is the value at which new employee option grants will be priced per share. For example, if I am hired at a company whose current 409a price is $1.00, the strike price of my options will be $1.00 per share. FMV is also used for tax purposes when exercising employee stock options.
Both call and put options have an exercise price. Investors also refer to the exercise price as the strike price. The difference between the exercise price and the underlying security's price determines if an option is ?in the money? or ?out of the money."
A strike price, also known as a grant price or exercise price, is the fixed cost that you'll pay per share in order to exercise your stock options so you can own them.
Every stock option has an exercise price, also called the strike price, which is the price at which a share can be bought. In the US, the exercise price is typically set at the fair market value of the underlying stock as of the date the option is granted, in order to comply with certain requirements under US tax law.
Exercising a stock option means purchasing the issuer's common stock at the price set by the option (grant price), regardless of the stock's price at the time you exercise the option.