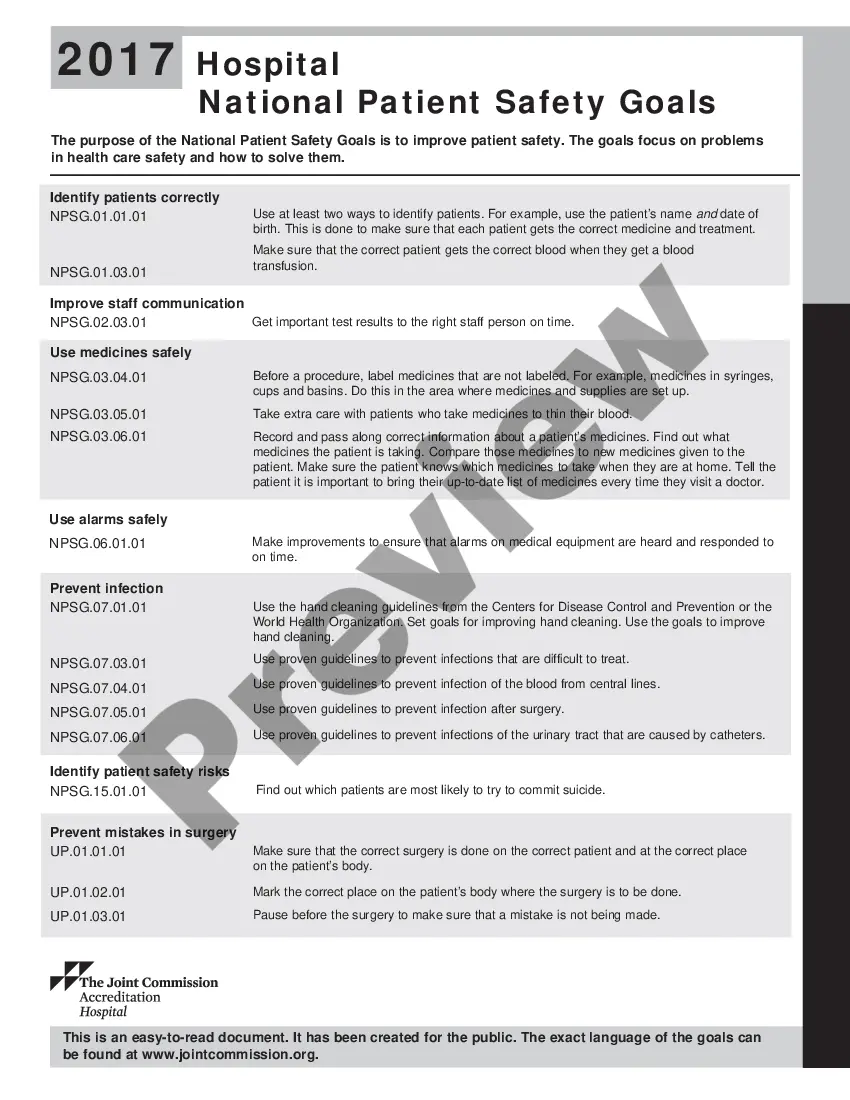
The Vermont Hospital National Patient Safety Goals (VH Nests) are a set of guidelines established by the Vermont Hospital Association (VIA) and aligned with the national patient safety goals set by The Joint Commission. These goals aim to enhance patient safety and minimize potential errors or risks within healthcare organizations in Vermont. The VH Nests encompass various domains of patient care and cover a wide range of areas to ensure comprehensive safety protocols are implemented. Here are some key areas and types of VH Nests: 1. Medication Safety: This goal focuses on reducing medication errors by implementing processes to accurately identify and administer medications, ensuring the right drug, dose, route, and patient. Strategies involve barcoding technology, proper medication labeling, standardizing medication storage, and providing education on high-alert medications. 2. Patient Identification: Patient identification can lead to errors in treatment or medication administration. This goal aims to prevent mix-ups by implementing standardized protocols for patient identification using two unique identifiers (e.g., name, date of birth, medical record number). 3. Infection Prevention: This goal emphasizes reducing healthcare-associated infections (His) by implementing evidence-based practices. It involves strict adherence to hand hygiene protocols, proper sterilization and disinfection techniques, catheter-associated urinary tract infection (CACTI) prevention, and addressing multidrug-resistant organisms (MDR Os). 4. Fall Prevention: Patient falls can cause serious injuries, including fractures and head trauma. This goal aims to assess patients' fall risk and implement preventive measures such as frequent rounding, using bed alarms, ensuring a clutter-free environment, and providing education on fall prevention. 5. Surgical Site Infections (SSI) Prevention: This goal focuses on preventing post-operative infections by following evidence-based practices. Measures include appropriate preoperative skin preparation, antimicrobial stewardship, maintaining sterile techniques, surgical site hair removal, and timely administration of prophylactic antibiotics. 6. Communication: Effective communication among healthcare providers plays a crucial role in patient safety. This goal emphasizes the use of standardized communication tools, such as the "STAR" (Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation) technique, ensuring clear hand-offs during shift changes or transfers, and encouraging open and effective communication among the healthcare team. 7. Emergency Preparedness: This goal focuses on preparing healthcare organizations for emergencies and ensuring patient safety during such events. It involves conducting regular drills and simulations, maintaining emergency equipment and supplies, establishing emergency communication protocols, and educating staff and patients on emergency response procedures. By adhering to these Vermont Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, healthcare organizations in Vermont aim to create a safer environment for patients, minimize errors, and improve overall healthcare outcomes.
Vermont Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Vermont Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
If you have to complete, acquire, or produce authorized papers themes, use US Legal Forms, the greatest variety of authorized types, that can be found on the Internet. Utilize the site`s simple and convenient research to obtain the files you will need. A variety of themes for business and person functions are categorized by types and claims, or keywords and phrases. Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Vermont Hospital National Patient Safety Goals with a number of clicks.
In case you are previously a US Legal Forms client, log in for your accounts and click on the Obtain option to obtain the Vermont Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. You can even entry types you in the past downloaded from the My Forms tab of your own accounts.
If you are using US Legal Forms the very first time, follow the instructions beneath:
- Step 1. Be sure you have chosen the form for the appropriate town/land.
- Step 2. Make use of the Preview choice to check out the form`s content. Do not neglect to learn the description.
- Step 3. In case you are not happy with the kind, use the Lookup discipline towards the top of the display screen to discover other types of the authorized kind web template.
- Step 4. After you have discovered the form you will need, select the Buy now option. Opt for the prices plan you like and add your credentials to register to have an accounts.
- Step 5. Procedure the purchase. You should use your credit card or PayPal accounts to finish the purchase.
- Step 6. Choose the format of the authorized kind and acquire it on the product.
- Step 7. Full, change and produce or sign the Vermont Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
Every authorized papers web template you get is yours permanently. You might have acces to each kind you downloaded with your acccount. Select the My Forms area and decide on a kind to produce or acquire once more.
Compete and acquire, and produce the Vermont Hospital National Patient Safety Goals with US Legal Forms. There are millions of skilled and status-particular types you can utilize for your business or person needs.