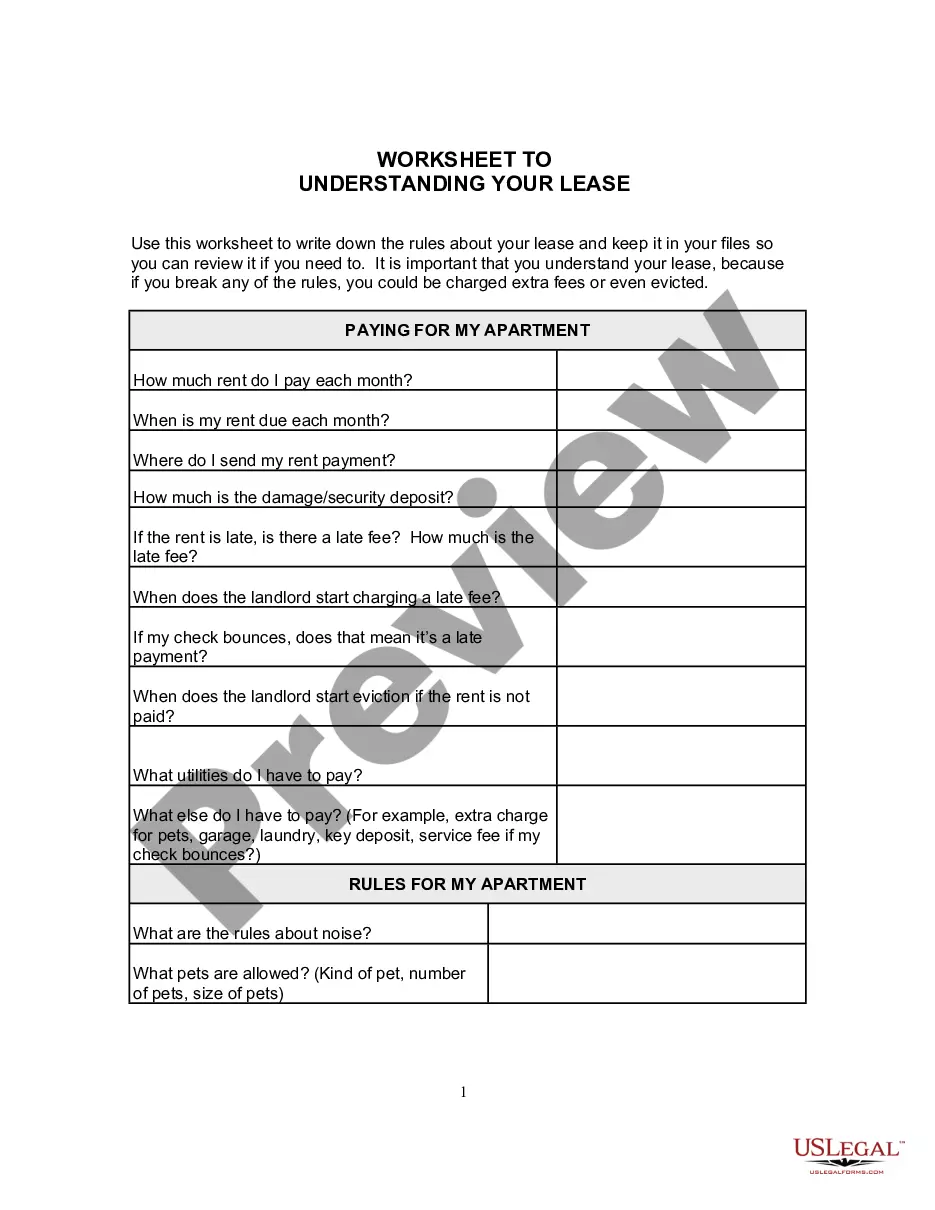
The Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance, also known as Signaturverordnung or Sign, is a set of regulations and guidelines established by the state of Vermont regarding the use of digital signatures. Digital signatures are electronic signatures that provide authentication and integrity for digital documents, ensuring their validity and confirming the identity of the signer. The main purpose of the Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance is to create a legal framework for the recognition and acceptance of digital signatures in various areas, such as electronic contracts, government transactions, online banking, and e-commerce. It aims to enhance security, efficiency, and convenience in the digital realm by eliminating the need for physical signatures and reducing paperwork. The Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance utilizes advanced cryptographic technologies to ensure the authenticity and integrity of digital signatures. It outlines the requirements for creating valid digital signatures, including the use of secure cryptographic algorithms, private key protection, and certificate-based authentication mechanisms. One of the key provisions of the Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance is the concept of a trusted third party, also known as a certification authority. These authorities are responsible for verifying the identity of the digital signature holder and issuing digital certificates that bind the signer's identity to their public key. This helps establish trust and confidence in the digital signature process. Different types of digital signatures are recognized and supported by the Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance. These include basic electronic signatures, advanced electronic signatures, and qualified electronic signatures. Each type varies in terms of the level of security, legal recognition, and compliance with specific requirements outlined in the ordinance. Basic electronic signatures are the most commonly used type and provide a basic level of security. Advanced electronic signatures offer a higher level of security and incorporate additional authentication mechanisms. Qualified electronic signatures, on the other hand, meet the highest standards and have the same legal effect as handwritten signatures under certain conditions. The Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance also covers various aspects related to the creation, verification, and storage of digital signatures. It addresses issues such as the use of time stamps, revocation of digital certificates, liability of the parties involved, and the evidentiary value of digitally signed documents in legal proceedings. Overall, the Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance — Signaturverordnun— - SigV plays a crucial role in promoting the adoption and acceptance of digital signatures in Vermont. It provides a comprehensive legal framework that ensures the security and legal validity of digital signatures, enabling individuals, organizations, and government entities to conduct secure and efficient digital transactions.
Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV
Description
How to fill out Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV?
Are you currently in the situation the place you will need papers for either enterprise or individual purposes nearly every day time? There are a variety of legal record themes available online, but getting versions you can trust isn`t effortless. US Legal Forms delivers a large number of type themes, like the Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV, that happen to be composed to meet state and federal demands.
If you are currently informed about US Legal Forms site and possess your account, just log in. Next, you are able to acquire the Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV format.
Unless you offer an account and want to start using US Legal Forms, abide by these steps:
- Obtain the type you need and make sure it is for that appropriate town/area.
- Utilize the Review option to examine the shape.
- Read the information to actually have selected the appropriate type.
- If the type isn`t what you`re seeking, utilize the Lookup area to find the type that fits your needs and demands.
- Whenever you get the appropriate type, just click Purchase now.
- Select the prices program you want, fill out the necessary details to generate your money, and buy the transaction utilizing your PayPal or bank card.
- Pick a hassle-free file structure and acquire your version.
Locate each of the record themes you possess bought in the My Forms menus. You can get a additional version of Vermont Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV any time, if required. Just go through the needed type to acquire or print out the record format.
Use US Legal Forms, the most considerable assortment of legal kinds, to save efforts and prevent blunders. The support delivers skillfully made legal record themes which can be used for a selection of purposes. Make your account on US Legal Forms and start producing your way of life easier.