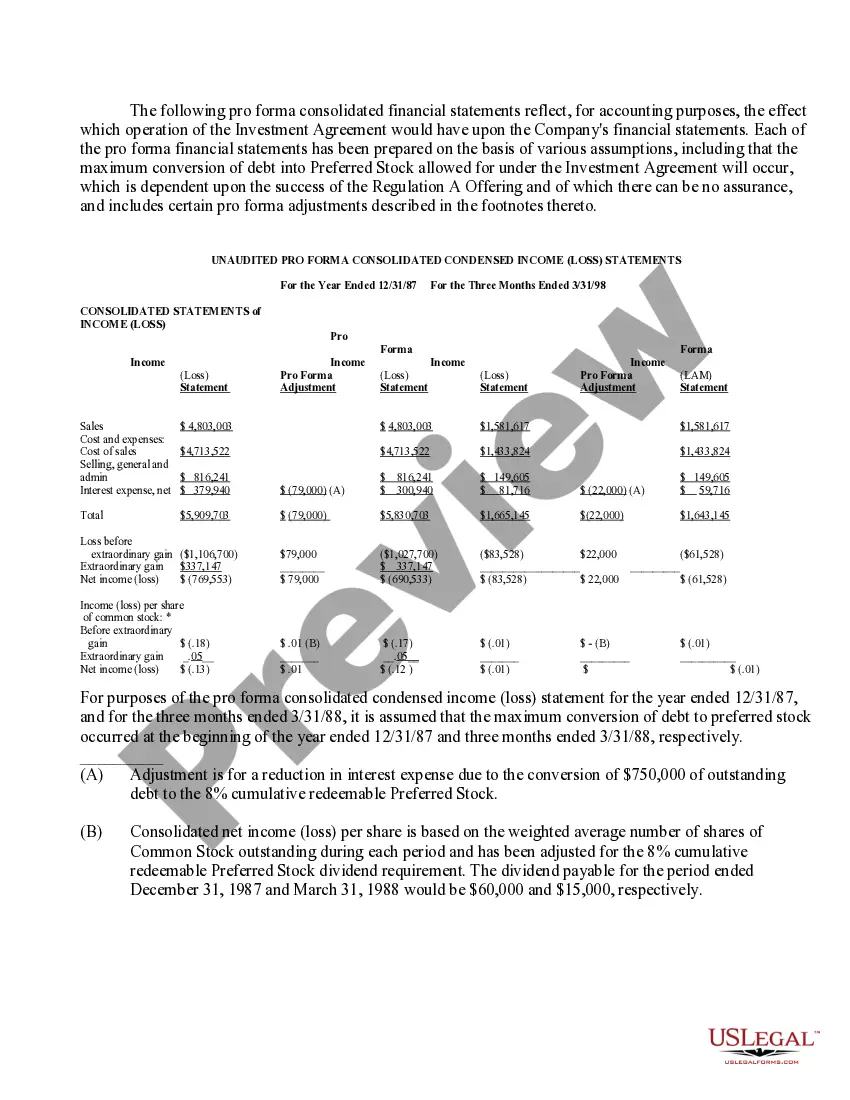
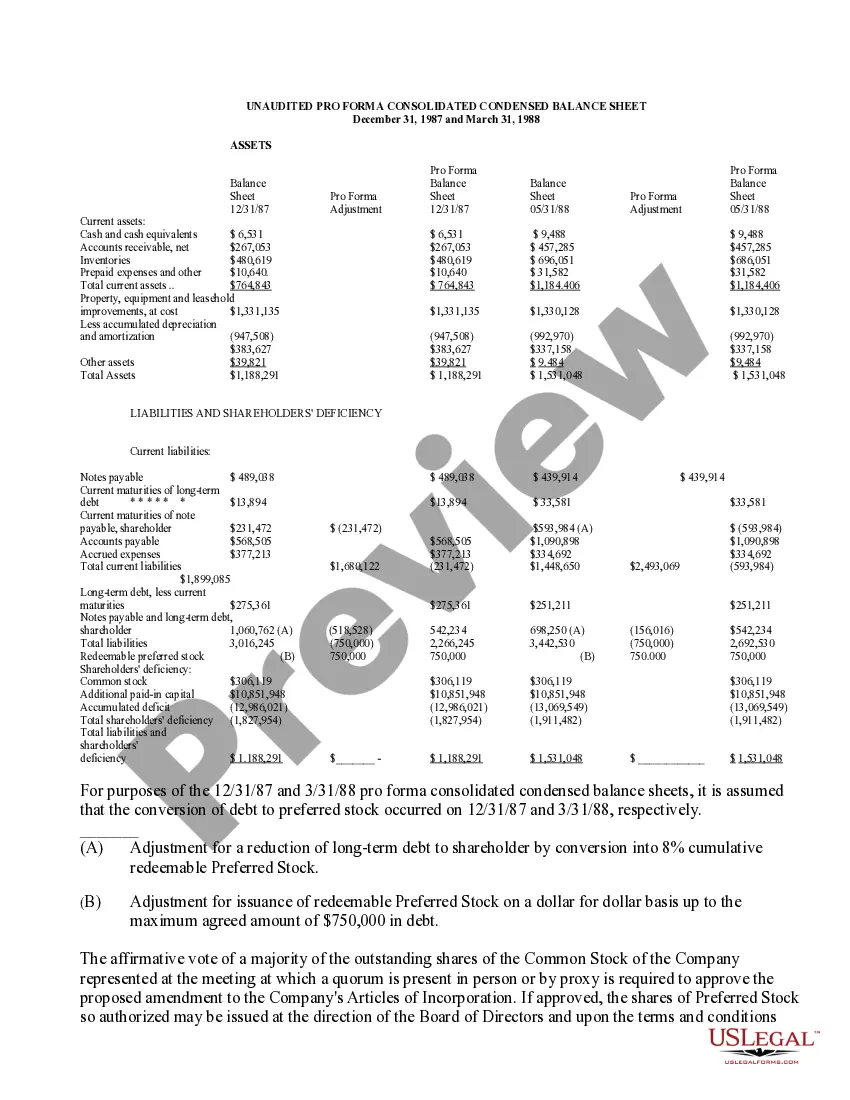
Washington Approval of authorization of preferred stock
Description
How to fill out Approval Of Authorization Of Preferred Stock?
You are able to invest several hours on the web searching for the legal document design which fits the federal and state demands you require. US Legal Forms offers a large number of legal forms which can be reviewed by experts. It is simple to down load or print out the Washington Approval of authorization of preferred stock from the services.
If you already have a US Legal Forms accounts, you can log in and click on the Obtain key. Next, you can full, modify, print out, or sign the Washington Approval of authorization of preferred stock. Each legal document design you purchase is your own property forever. To obtain an additional duplicate of the obtained develop, go to the My Forms tab and click on the related key.
If you work with the US Legal Forms web site the first time, follow the simple directions below:
- Initial, be sure that you have selected the best document design for the area/area of your liking. Read the develop description to ensure you have selected the appropriate develop. If offered, take advantage of the Preview key to look from the document design at the same time.
- If you want to get an additional variation of your develop, take advantage of the Lookup field to discover the design that fits your needs and demands.
- Once you have discovered the design you desire, just click Get now to continue.
- Choose the prices prepare you desire, key in your references, and register for your account on US Legal Forms.
- Complete the purchase. You should use your Visa or Mastercard or PayPal accounts to fund the legal develop.
- Choose the structure of your document and down load it to your product.
- Make modifications to your document if possible. You are able to full, modify and sign and print out Washington Approval of authorization of preferred stock.
Obtain and print out a large number of document layouts while using US Legal Forms website, that provides the largest selection of legal forms. Use skilled and condition-specific layouts to handle your company or individual requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
Blank check preferred stock facilitates the ability of the company to adopt a "white squire" defense when faced with a hostile bid, which involves sale to a friendly party (i.e., a party that is interested in making an investment in, but presumably is not seeking to gain control of, the target) of a block of the ...
The most common issuers of preferred stocks are banks, insurance companies, utilities and real estate investment trusts, or REITs. Companies issuing preferreds may have more than one offering for you to vet. Often you may find several different offerings of preferreds from the same issuer but with different yields.
Under current Section 312.03(b), shareholder approval is required when a company sells shares to a related party if the amount to be issued exceeds 1% of the number of shares or voting power outstanding before issuance.
Voting rights: Common stocks offer stockholders the opportunity to vote in company shareholder meetings on factors that impact their stock ownership. Preferred stockholders give up this right in exchange for consistent dividend payouts.
Issuance of Preferred Stock: When a company issues preferred stock, it debits (increases) the cash account on the balance sheet for the total value received and credits (increases) the ?preferred stock? account in the equity section of the balance sheet.
The number of authorized shares can be changed by way of a vote from shareholders, typically during the annual shareholder meeting.
Board approval, either by written consent or at a board meeting (for more about the differences between board consents and board meetings, please see our article), is required for every issuance of a security, whether that security is common stock, preferred stock, a warrant, an option or a note that is convertible ...
Issuing new shares typically requires approval from the company's shareholders. This may involve holding a vote at a shareholder meeting or obtaining written consent from a majority of shareholders. The approval process will depend on the company's bylaws and state laws governing the issuance of new shares.