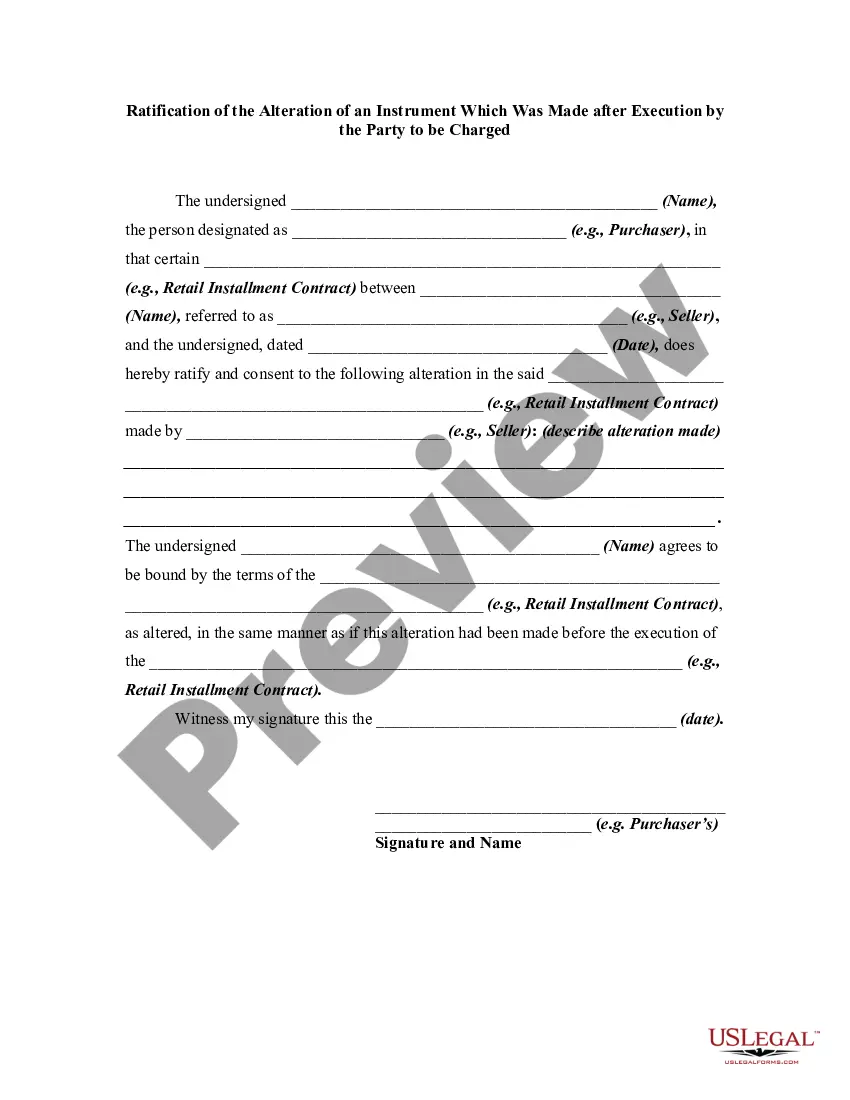
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought. If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Wisconsin Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged refers to a legal process where a party acknowledges and approves changes made to a document after its initial execution. This ratification becomes necessary when alterations are made to an instrument, such as a contract or a will, without the knowledge or consent of the party who is supposed to be charged or affected by those changes. The Wisconsin jurisdiction has specific laws governing this process to ensure fairness and protect the rights of individuals involved. In Wisconsin, the ratification of an alteration of an instrument is crucial to validate any modifications made post-execution. The party making the alterations may be attempting to gain an unfair advantage, withhold certain information, or deceive the party that needs to be charged. To prevent any unjust outcomes, Wisconsin law requires explicit ratification by the affected party after becoming aware of the changes. Keywords: Wisconsin, Ratification, Alteration of an Instrument, Execution, Party to be Charged, Legal Process, Contract, Will, Modifications, Post-execution, Fairness, Rights, Jurisdiction, Wisconsin Law, Unfair Advantage, Withhold Information, Deceive, Unjust Outcomes. Different types of Wisconsin Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged may include: 1. Contract Ratification: This type of ratification focuses on alterations made to a contract after its execution, where the affected party in Wisconsin must explicitly acknowledge and consent to the changes for them to be legally recognized. This can prevent any unintended modifications or manipulation of contractual terms and conditions. 2. Will Ratification: In the case of a will, if any changes are made to the document after execution, the party who is meant to be impacted must ratify those alterations in Wisconsin. This ensures that the individual's intentions are accurately reflected, preventing any fraudulent amendments or manipulation of the will. 3. Legal Document Ratification: Wisconsin Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument extends to various legal documents beyond contracts and wills, such as deeds, agreements, or powers of attorney. If any modifications are made to these instruments without the knowledge or agreement of the party to be charged, ratification becomes necessary to safeguard their rights and prevent any unlawful changes. In summary, Wisconsin Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a crucial legal process that ensures fairness and protects the rights of individuals in cases where alterations have been made to legal documents without their consent. Proper ratification is necessary to validate any modifications and prevent fraudulent or unjust changes.Wisconsin Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged refers to a legal process where a party acknowledges and approves changes made to a document after its initial execution. This ratification becomes necessary when alterations are made to an instrument, such as a contract or a will, without the knowledge or consent of the party who is supposed to be charged or affected by those changes. The Wisconsin jurisdiction has specific laws governing this process to ensure fairness and protect the rights of individuals involved. In Wisconsin, the ratification of an alteration of an instrument is crucial to validate any modifications made post-execution. The party making the alterations may be attempting to gain an unfair advantage, withhold certain information, or deceive the party that needs to be charged. To prevent any unjust outcomes, Wisconsin law requires explicit ratification by the affected party after becoming aware of the changes. Keywords: Wisconsin, Ratification, Alteration of an Instrument, Execution, Party to be Charged, Legal Process, Contract, Will, Modifications, Post-execution, Fairness, Rights, Jurisdiction, Wisconsin Law, Unfair Advantage, Withhold Information, Deceive, Unjust Outcomes. Different types of Wisconsin Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged may include: 1. Contract Ratification: This type of ratification focuses on alterations made to a contract after its execution, where the affected party in Wisconsin must explicitly acknowledge and consent to the changes for them to be legally recognized. This can prevent any unintended modifications or manipulation of contractual terms and conditions. 2. Will Ratification: In the case of a will, if any changes are made to the document after execution, the party who is meant to be impacted must ratify those alterations in Wisconsin. This ensures that the individual's intentions are accurately reflected, preventing any fraudulent amendments or manipulation of the will. 3. Legal Document Ratification: Wisconsin Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument extends to various legal documents beyond contracts and wills, such as deeds, agreements, or powers of attorney. If any modifications are made to these instruments without the knowledge or agreement of the party to be charged, ratification becomes necessary to safeguard their rights and prevent any unlawful changes. In summary, Wisconsin Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a crucial legal process that ensures fairness and protects the rights of individuals in cases where alterations have been made to legal documents without their consent. Proper ratification is necessary to validate any modifications and prevent fraudulent or unjust changes.