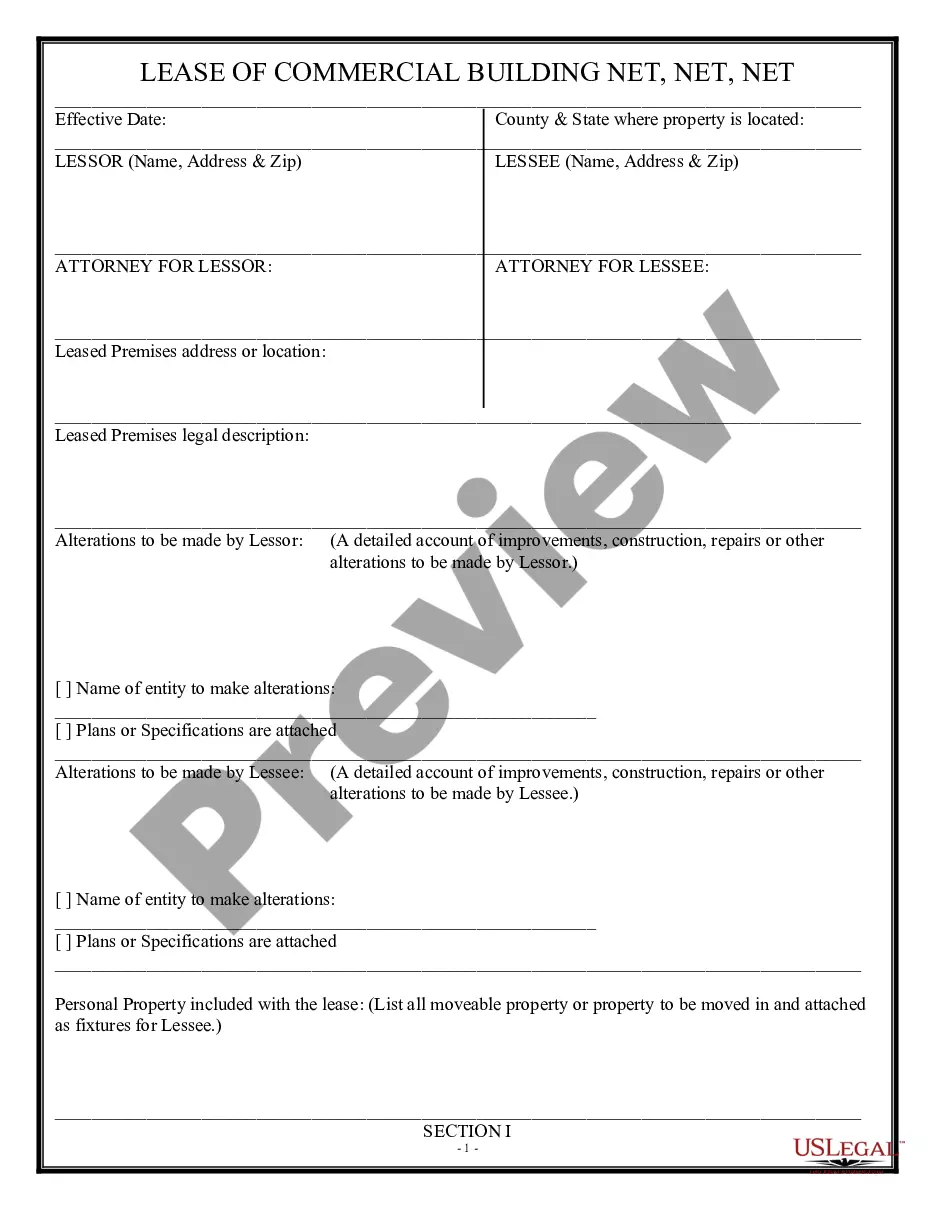
Wisconsin Triple Net Lease for Residential Property: A Comprehensive Overview In Wisconsin, a triple net lease (NNN lease) for residential property is a legally binding agreement between a landlord (lessor) and a tenant (lessee). This lease type places extensive financial responsibilities on the tenant, making it different from the common residential lease arrangements. The term "triple net" refers to the three primary expenses a tenant is required to cover: property taxes, building insurance, and maintenance costs. Under a Wisconsin Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, the tenant assumes more financial burdens usually borne by the landlord in traditional lease agreements. In addition to the monthly rent, the lessee must cover the property's property tax payments, insurance costs, and maintenance expenses. This arrangement is typically seen in commercial leases, but it can also apply to residential properties. It is important to highlight that these leases usually cater to high-end or luxury properties. There are different types of Wisconsin Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, each with its own specific terms and conditions. These lease types provide options for both landlords and tenants, allowing them to tailor the agreement to their unique requirements. Let's explore the most common types: 1. Absolute Triple Net Lease: This lease type places the highest financial responsibility on the tenant. The tenant assumes all costs, including property taxes, insurance, and maintenance expenses, leaving the landlord with minimal financial obligations. However, this arrangement may also allow the tenant more control over the property. 2. Modified Triple Net Lease: In this type of lease, the tenant bears most expenses, including property taxes and insurance. However, maintenance costs might be shared between the landlord and tenant, or the landlord might retain responsibility for specific structural repairs or replacements. 3. Double Net Lease: While not considered a true triple net lease, the double net lease still requires the tenant to cover property taxes and insurance costs. The landlord remains responsible for property maintenance and repairs under this arrangement. 4. Triple Net Lease with Reserves: This lease type includes a mechanism where the tenant pays into a reserve fund for future property expenses. This reserve fund is then utilized for any necessary repairs or unforeseen circumstances. The tenant is typically responsible for tracking and managing the reserve fund. It's important to note that Wisconsin Triple Net Leases for Residential Property generally provide longer lease terms than standard residential leases, often ranging from five to ten years. This extended term allows tenants to potentially negotiate more favorable rental rates and lease conditions with the landlord. In summary, the Wisconsin Triple Net Lease for Residential Property is a unique lease agreement that places significant financial responsibilities on the tenant. With various types available, landlords and tenants can select the arrangement that best suits their needs. Tenants should carefully consider the financial implications before entering into such a lease, as the costs can add up significantly over time.
Wisconsin Triple Net Lease for Residential Property
Description
How to fill out Wisconsin Triple Net Lease For Residential Property?
Discovering the right authorized document design can be a battle. Of course, there are a lot of templates accessible on the Internet, but how will you find the authorized develop you require? Use the US Legal Forms internet site. The assistance delivers a huge number of templates, including the Wisconsin Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, which you can use for company and private requires. Every one of the varieties are checked out by pros and meet up with federal and state requirements.
If you are currently signed up, log in for your bank account and click the Down load switch to have the Wisconsin Triple Net Lease for Residential Property. Make use of bank account to search from the authorized varieties you possess purchased formerly. Go to the My Forms tab of the bank account and have yet another copy of the document you require.
If you are a fresh user of US Legal Forms, listed here are easy directions that you should comply with:
- Initially, be sure you have chosen the appropriate develop for the city/state. You are able to check out the shape using the Preview switch and read the shape information to make certain this is the best for you.
- If the develop fails to meet up with your requirements, take advantage of the Seach field to obtain the appropriate develop.
- When you are sure that the shape is acceptable, click the Acquire now switch to have the develop.
- Select the pricing program you desire and enter in the necessary details. Make your bank account and buy the transaction utilizing your PayPal bank account or charge card.
- Select the data file format and down load the authorized document design for your gadget.
- Complete, modify and print and indication the acquired Wisconsin Triple Net Lease for Residential Property.
US Legal Forms may be the most significant collection of authorized varieties for which you will find various document templates. Use the service to down load skillfully-produced papers that comply with condition requirements.