Title: Understanding Wisconsin Contract — Sale of Goods: Key Concepts and Types Introduction: The Wisconsin Contract — Sale of Goods refers to the legal agreement governing the purchase and sale of goods within the state of Wisconsin, outlining the rights and obligations of the parties involved. This detailed description aims to provide an overview of the Wisconsin Contract — Sale of Goods, including its core elements, regulations, and relevant keywords. Additionally, it will delve into different types of contracts under this category. Key Elements of a Wisconsin Contract — Sale of Goods: 1. Offer and Acceptance: The contract initiates with an offer made by one party, which the other party can accept or reject. Acceptance occurs when both parties agree on the terms of a transaction. 2. Consideration: Both the buyer and seller must exchange valuable goods, services, or money as consideration for the contract to be legally binding. This ensures a mutual exchange of benefits for each party involved. 3. Agreement on the Goods: The contract must include a clear description of the goods being sold, including their quantity, quality, specifications, and any relevant details or warranties associated with the goods. 4. Price and Payment Terms: The contract should stipulate the agreed-upon price for the goods and the terms of payment, including the method of payment, due date, and any installment arrangements if applicable. 5. Delivery and Transfer of Title: The contract should define the mode of delivery, the responsibility for transportation, and indicate when the title of the goods will pass from the seller to the buyer. 6. Risk of Loss: The contract should address the allocation of risk in case of loss, damage, or destruction of the goods during transportation or any other unforeseen circumstances. 7. Remedies for Breach: The contract should outline the available remedies in case of breach by either party, such as specific performance, cancellation, or monetary damages. Types of Wisconsin Contracts — Sale of Goods: 1. Retail Sales Contracts: These contracts involve the sale of goods to individual consumers. They are subject to various consumer protection regulations. 2. Wholesale Purchase Agreements: Wholesale contracts involve the sale of goods in large quantities to retailers, distributors, or other businesses. 3. Auction Sales Contracts: These contracts cover goods offered for sale through public auctions. They often have specific terms and conditions relating to placing bids, withdrawal, or reserve prices. 4. International Sales Contracts: Contracts involving the sale of goods between parties located in different countries fall under this category. They may be subject to additional legal frameworks such as the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CSG). Conclusion: The Wisconsin Contract — Sale of Goods serves as the backbone of commercial transactions within the state, ensuring legal obligations and protecting the rights of both buyers and sellers. Understanding the core elements and types of contracts under this category is crucial for individuals and businesses engaging in sales activities in Wisconsin. Compliance with relevant laws and regulations helps foster fair and transparent business practices, reducing the risk of disputes, and facilitating successful commercial transactions.
Wisconsin Contract - Sale of Goods
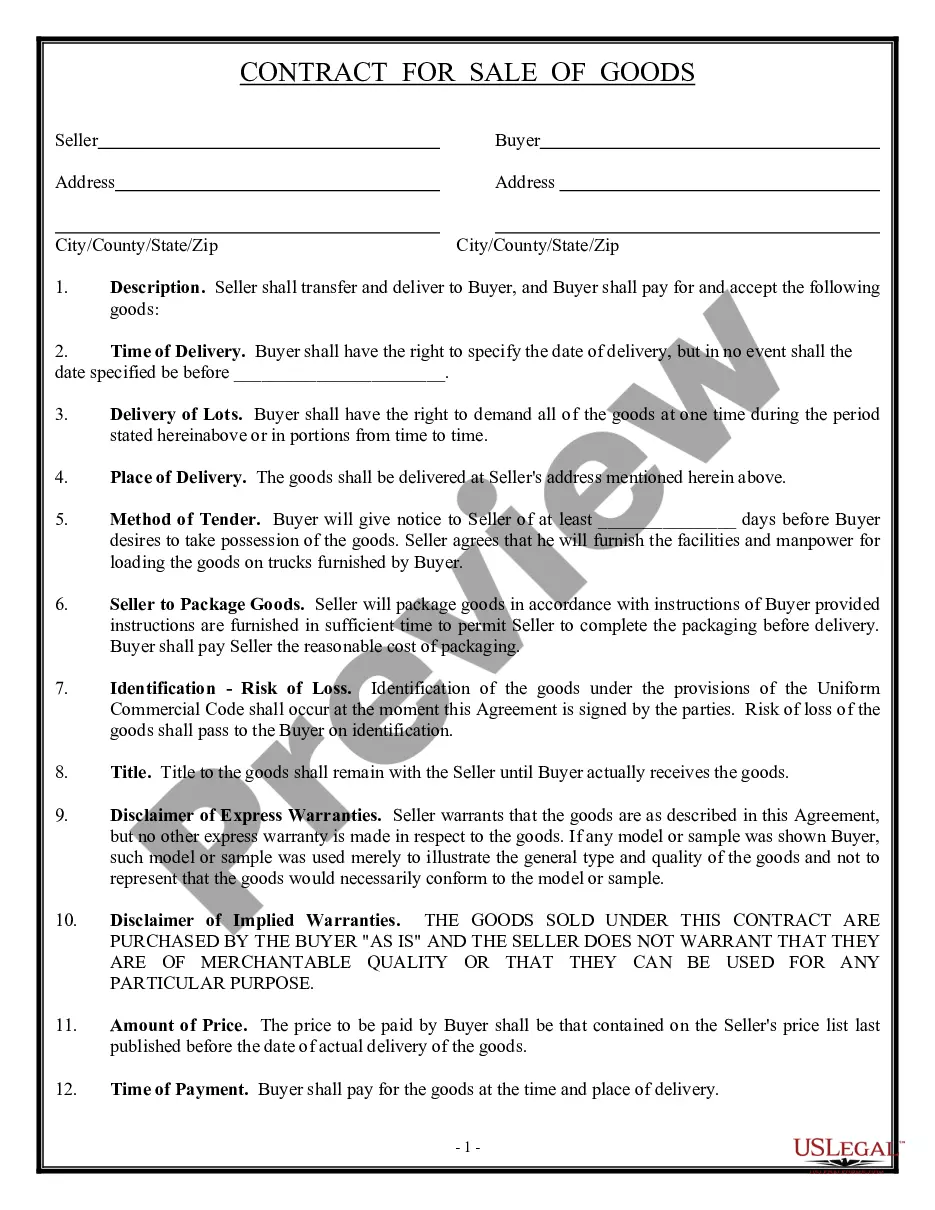
Description
How to fill out Wisconsin Contract - Sale Of Goods?
Finding the right authorized record format can be a struggle. Naturally, there are a lot of layouts available on the Internet, but how can you discover the authorized develop you require? Take advantage of the US Legal Forms site. The support delivers a huge number of layouts, including the Wisconsin Contract - Sale of Goods, that can be used for enterprise and personal demands. Each of the varieties are checked by pros and satisfy federal and state requirements.
In case you are already authorized, log in to your bank account and then click the Obtain option to obtain the Wisconsin Contract - Sale of Goods. Make use of your bank account to appear with the authorized varieties you have acquired earlier. Check out the My Forms tab of the bank account and have an additional backup in the record you require.
In case you are a whole new customer of US Legal Forms, here are simple guidelines for you to adhere to:
- Initially, make sure you have selected the proper develop for your town/area. It is possible to check out the shape utilizing the Review option and study the shape outline to make sure this is basically the right one for you.
- In the event the develop is not going to satisfy your needs, make use of the Seach area to obtain the right develop.
- When you are positive that the shape would work, select the Buy now option to obtain the develop.
- Choose the costs strategy you would like and enter in the essential details. Make your bank account and buy your order utilizing your PayPal bank account or charge card.
- Opt for the document structure and download the authorized record format to your device.
- Comprehensive, modify and print and indicator the received Wisconsin Contract - Sale of Goods.
US Legal Forms may be the biggest local library of authorized varieties that you can see a variety of record layouts. Take advantage of the service to download expertly-made papers that adhere to express requirements.