A patent is a grant of a property right by the Government to an inventor. The United States Constitution gives Congress the right to provide for patent protection in legislation in order to encourage useful inventions. The patent itself provides a detailed description of the invention, and how it is used or how to make it. Thus, if you obtain a patent you cannot keep the matter secret, which is the province of Trade Secret Law. A patent enables the owner to exclude others from making, using or selling the invention for the life of the patent.
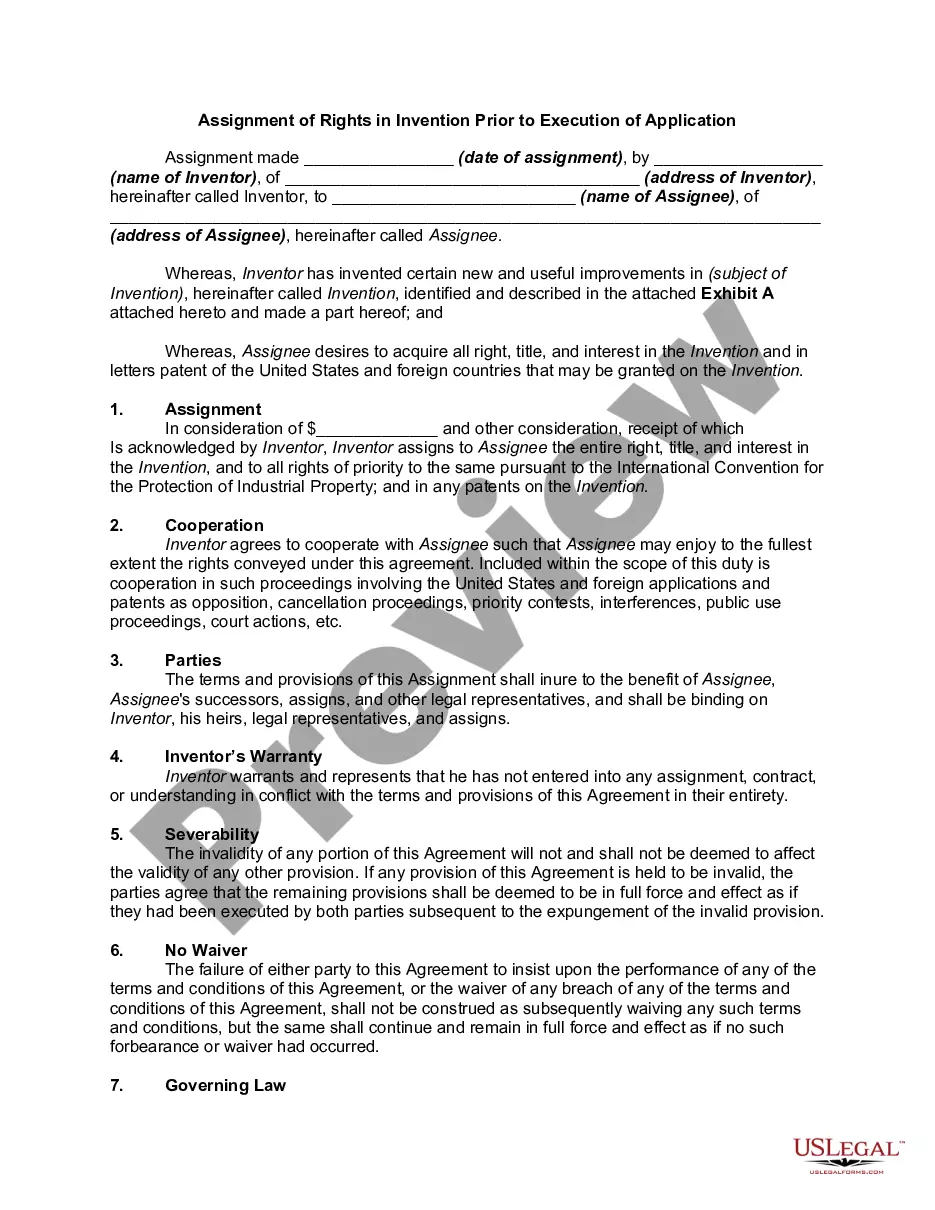
Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application
Description
How to fill out Assignment Of Rights In Invention Prior To Execution Of Application?
Finding the appropriate legal document format can be quite a challenge.
Of course, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how do you obtain the legal form you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website.
If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are straightforward instructions for you to follow: First, confirm that you have selected the correct form for your region. You can preview the form using the Review button and read the form description to ensure it fits your needs. If the form does not fulfill your requirements, utilize the Search box to find the appropriate form. Once you are sure that the form is suitable, click the Acquire now button to obtain the form. Choose the pricing plan you prefer and enter the required information. Create your account and place your order using your PayPal account or credit card. Select the file format and download the legal document format to your device. Complete, edit, print, and sign the acquired Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Application. US Legal Forms is the largest repository of legal forms where you can find various document templates. Utilize the service to download professionally crafted documents that comply with state regulations.
- The service provides thousands of templates, such as the Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Application Execution, suitable for both business and personal purposes.
- All documents are verified by experts and meet federal and state requirements.
- If you are already registered, sign in to your account and click on the Download button to retrieve the Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Application.
- Use your account to review the legal documents you have purchased previously.
- Navigate to the My documents section of your account to obtain another copy of the document you require.
Form popularity
FAQ
Proprietary information can include trade secrets, customer lists, manufacturing processes, and new product designs. This information is vital for a business’s competitive advantage and is often detailed in proprietary information agreements. By recognizing and protecting proprietary information, companies can better support the Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, ensuring that their innovations remain secure.
The proprietary information and inventions agreement provides a framework for protecting confidential business information and outlines the rights to inventions. This document is crucial for businesses that rely on innovation, as it safeguards proprietary knowledge from being disclosed. By understanding this agreement, parties can navigate the Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application effectively, ensuring inventors and businesses are protected.
An invention assignment agreement is a contract that establishes the ownership of inventions between an employee and an employer. This agreement typically aims to protect the employer's rights to any inventions developed by the employee during their time at the company. In many cases, this is essential to uphold the Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, ensuring that rights are clearly defined before legal filings.
The Piia agreement, or 'Proprietary Information and Inventions Agreement,' is a legal document often used in employment settings. It outlines the rights of an employer and the employee regarding inventions created during employment. This agreement typically ensures that any inventions made in the course of employment, especially those related to company business, are owned by the employer. Understanding the Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application is crucial for anyone entering into a Piia agreement.
Having executed a confidentiality and invention assignment agreement means that you have legally bound yourself to keep certain information private while transferring ownership of your invention rights. This is particularly relevant in the context of a Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, as it sets clear expectations about confidentiality and ownership. This agreement serves to protect both parties during the innovation process.
When you claim an invention, it is often referred to as 'making a claim' for patent rights or filing a patent application. This process is crucial for protecting your intellectual property through a Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application. Properly claiming an invention ensures that you have legal rights to your creation and can prevent others from using it without permission.
Yes, disclosing prior inventions is essential when entering into an invention assignment agreement. Failing to do so can lead to potential legal complications, particularly with a Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application. Transparency allows both parties to clarify the scope of the assignment and protects your ability to use or develop those prior inventions in the future.
An invention assignment is a legal document that transfers ownership rights of an invention from the inventor to another party, such as an employer. This is particularly important in the context of a Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, where clear definitions of ownership help streamline the patent application process. By assigning your rights, you enable the other party to manage and protect the invention effectively.
Claiming ownership of prior inventions is crucial when entering into agreements. If you intend to retain rights to inventions created before signing the Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, disclosure is necessary. Being transparent about prior inventions helps to avoid misunderstandings and protects your interests in future endeavors.
The ownership of inventions clause specifies who holds the rights to inventions created during employment or under a contract. This clause is essential in a Wisconsin Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, as it clarifies ownership to prevent future disputes. Typically, employers seek rights to inventions made with their resources or during work hours, ensuring that their interests are protected.