Irreparable harm is a legal concept which argues that the type of harm threatened cannot be corrected through monetary compensation or conditions cannot be put back the way they were. Examples of such irreparable harm may arise in cutting down shade trees, polluting a stream, not giving a child needed medication, not supporting an excavation which may cause collapse of a building, tearing down a structure, among other actions or omissions.
Irreparable harm is often required to be shown to claim that a judge should order an injunction, writ, temporary restraining order or other equitable judicial action. The party seeking such relief will argue that the judicial action is required to prevent an imminent injury for which there is no other way to prevent the threatened harm.
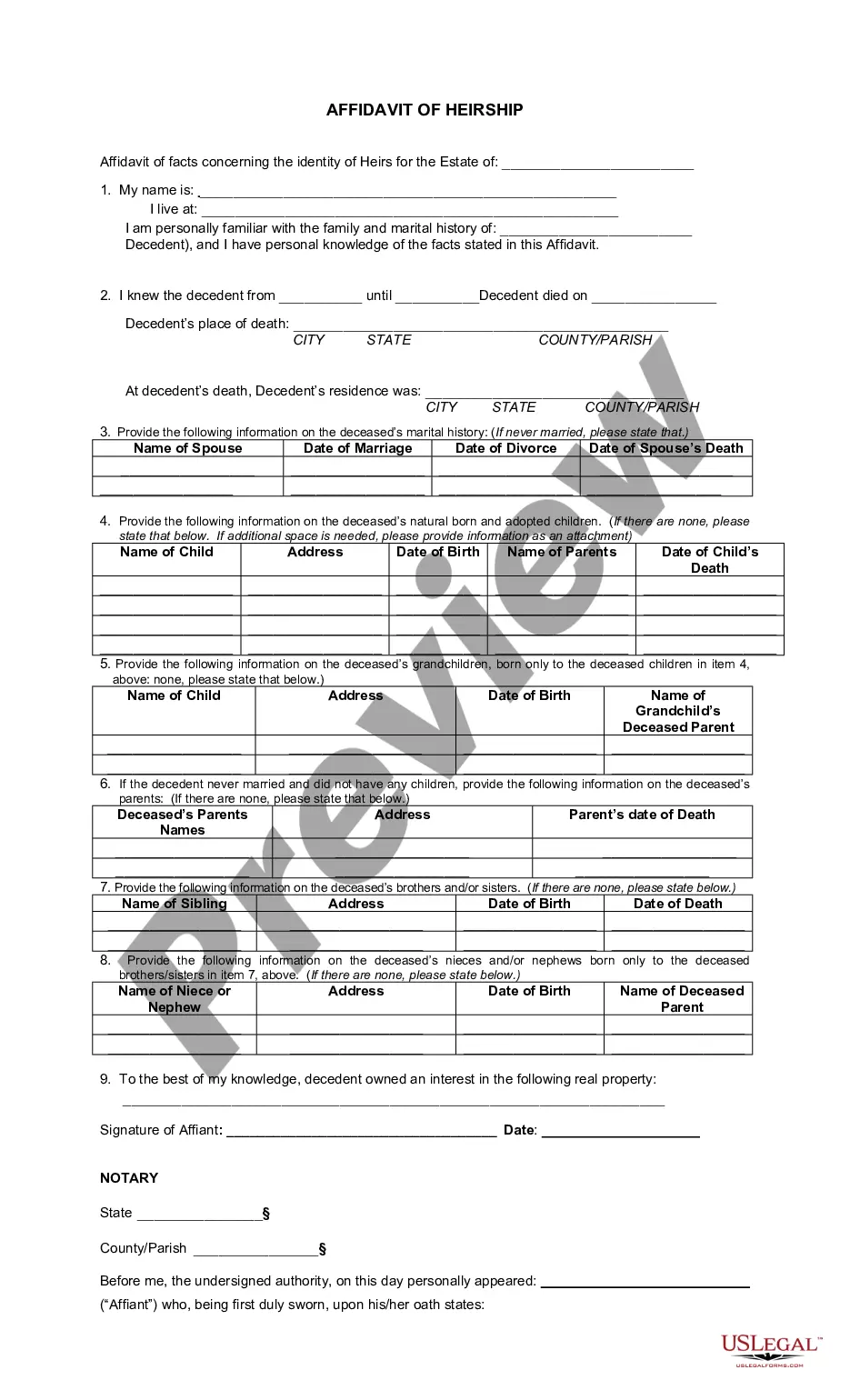
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.