Wisconsin General Journal
Description
How to fill out General Journal?
Do you find yourself in a situation where you require documents for business or personal purposes almost every day.
There are numerous legal document templates available online, but finding reliable ones is challenging.
US Legal Forms offers thousands of form templates, including the Wisconsin General Journal, designed to comply with federal and state regulations.
You can find all the document templates you have purchased in the My documents menu.
You may obtain an additional copy of the Wisconsin General Journal at any time by clicking the desired form to download or print the document template.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and possess an account, simply Log In.
- After that, you can download the Wisconsin General Journal template.
- If you do not have an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Select the form you need and confirm it is for the correct state/region.
- Utilize the Review button to examine the document.
- Read the description to ensure you have chosen the right form.
- If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search field to find the document that suits your requirements.
- Once you have found the correct form, click Buy now.
- Select the pricing plan you prefer, enter the necessary information to create your account, and complete your purchase using PayPal or a credit card.
- Choose a convenient document format and download your version.
Form popularity
FAQ
The uslegalforms platform offers resources and tools specifically designed to simplify the management of a Wisconsin General Journal. You can access templates and guidance to ensure accurate journal entries and financial documentation. This support can significantly enhance your understanding and compliance with accounting requirements. With uslegalforms, taking control of your financial records becomes easier and more efficient.
Using a Wisconsin General Journal provides several benefits, including improved accuracy and enhanced financial organization. By documenting every transaction immediately, you minimize the risk of errors over time. Additionally, a well-maintained general journal streamlines the auditing process and helps in preparing financial statements. Therefore, adopting a general journal is vital for effective financial management.
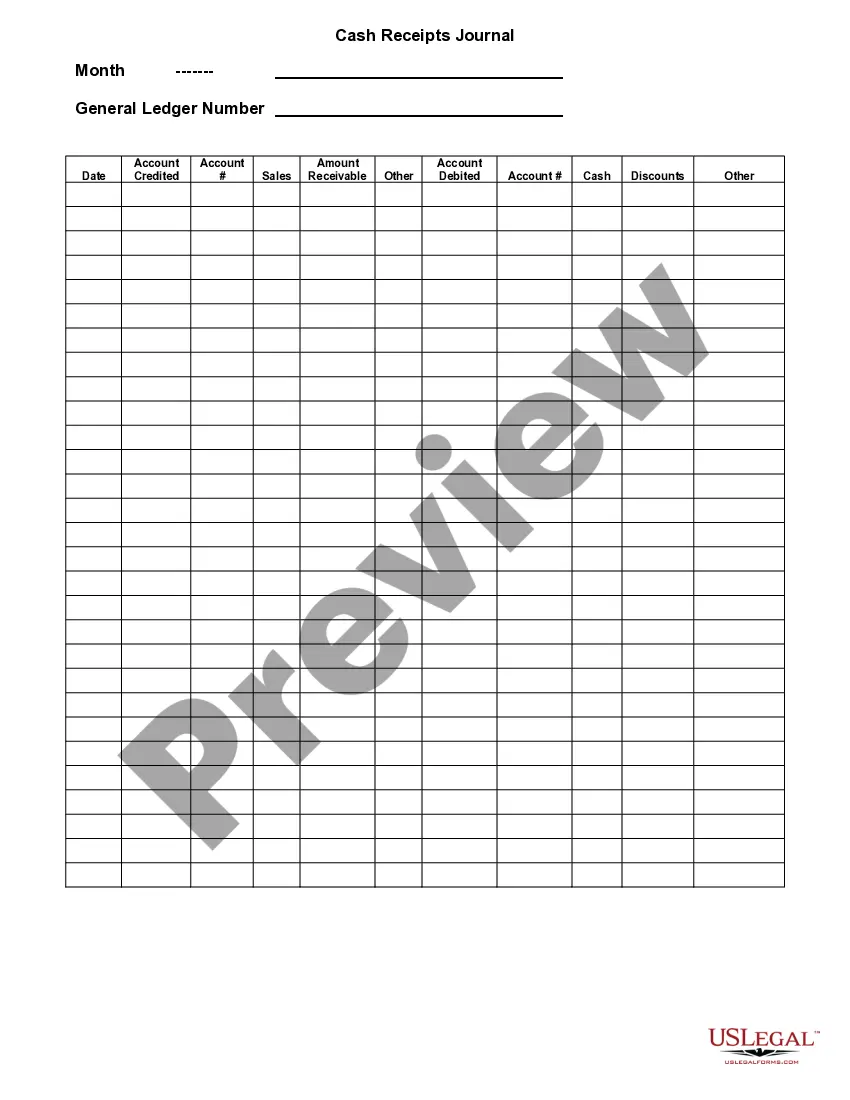
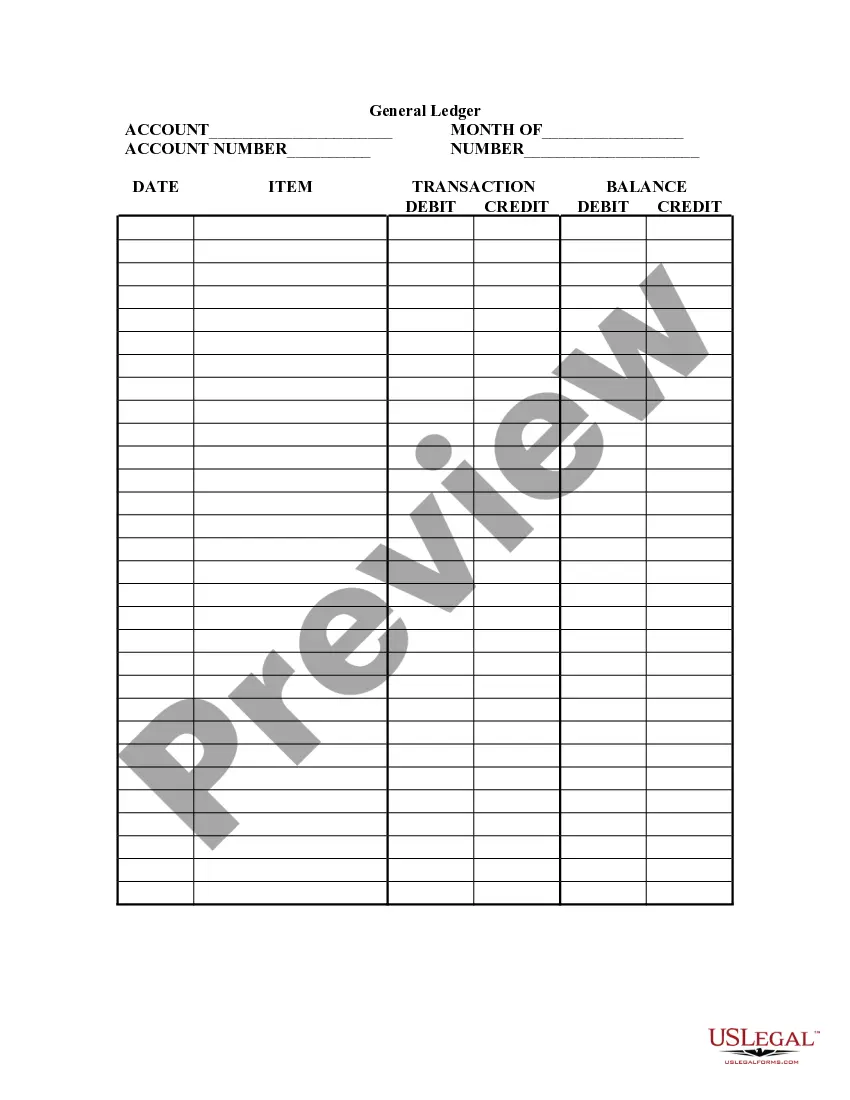
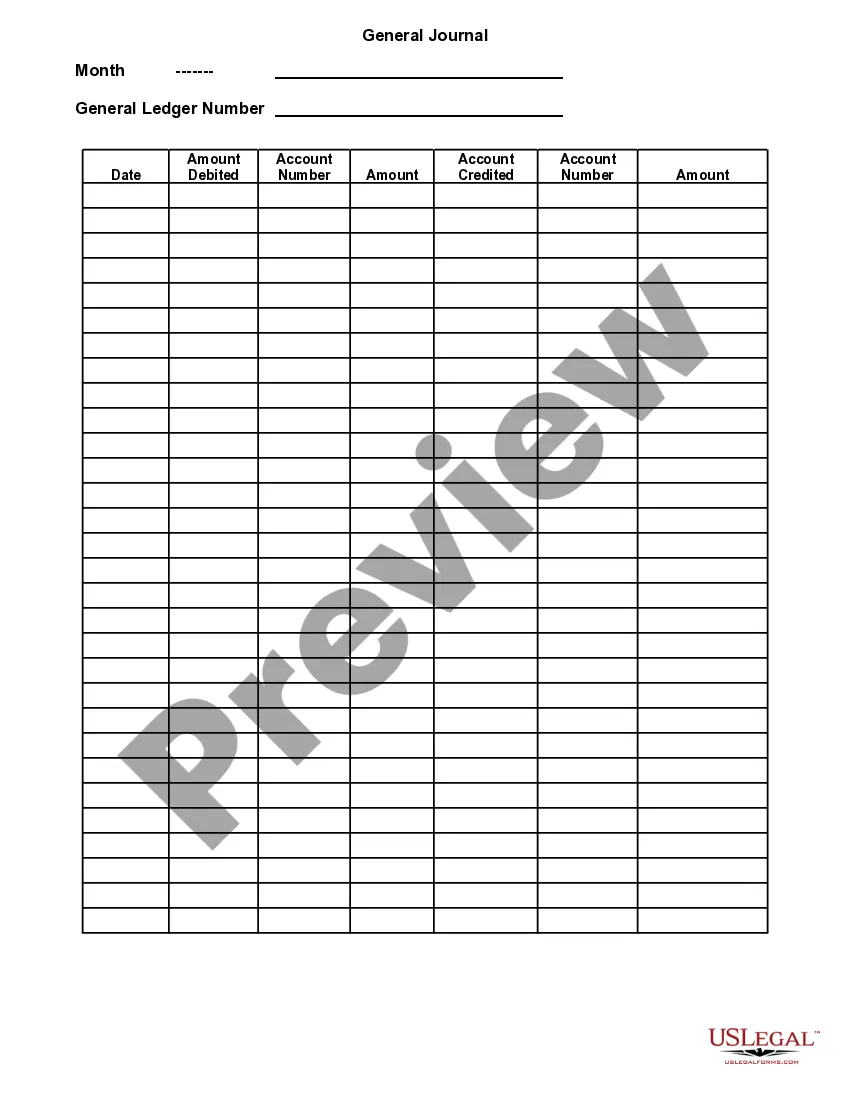
A general journal typically includes the date of the transaction, accounts debited and credited, amounts, and a description. In the context of a Wisconsin General Journal, it also serves as the first point for all financial entries before they are transferred to ledgers. This process ensures accuracy and accountability in financial reporting. Keeping your general journal organized boosts your business's overall financial health.
In a Wisconsin General Journal, you find detailed records of daily transactions. Each entry includes the date, accounts affected, amounts, and a brief description of the transaction. This clarity helps maintain an organized financial record. Thus, using a general journal is essential for accurate accounting and tax purposes.
The format for a journal entry in a Wisconsin General Journal includes the date, account names, debit amount, credit amount, and a brief description. Each entry starts with the transaction date followed by the relevant accounts, making it easy to see which funds are being moved. Clear distinction between debits and credits in designated columns simplifies understanding. This structured approach enhances clarity and aids in financial reviews.
Filling out a journal entry for the Wisconsin General Journal requires careful attention to detail. Begin with the date of the transaction, then list the accounts affected — one for the debit and another for the credit. Specify the amounts for each account, ensuring they match to maintain balance. Lastly, include a concise description to explain the purpose of the entry, which helps in future reference.
A standard journal format, including Wisconsin General Journal entries, generally consists of a sequential list of transactions. Each entry should clearly denote the date, accounts debited or credited, amounts, and a description. Maintaining this consistency ensures proper record-keeping and aids in financial reporting. Such an organized layout supports clear financial analysis and accountability.
The format of a Wisconsin General Journal typically includes columns for the date, account titles, debits, credits, and a description. Each entry should start with the date, followed by the accounts impacted by the transaction. Allocating separate columns for debits and credits enables clear tracking of financial activities. This structured approach facilitates easier review and auditing.
To complete a Wisconsin General Journal, start by entering the date of the transaction. Next, record the accounts involved, specifying whether each account is being debited or credited. Ensure that the amounts are accurate and balanced, as every debit must have a corresponding credit. Finally, add a brief description to clarify the nature of the transaction.
Writing in a general journal involves recording entries clearly and systematically. Start with the date of the transaction, identify the accounts involved, and note the amounts for debits and credits. Ensure each entry has a meaningful description to provide context. Using the Wisconsin General Journal can facilitate this process, making it easier to maintain precise financial records.