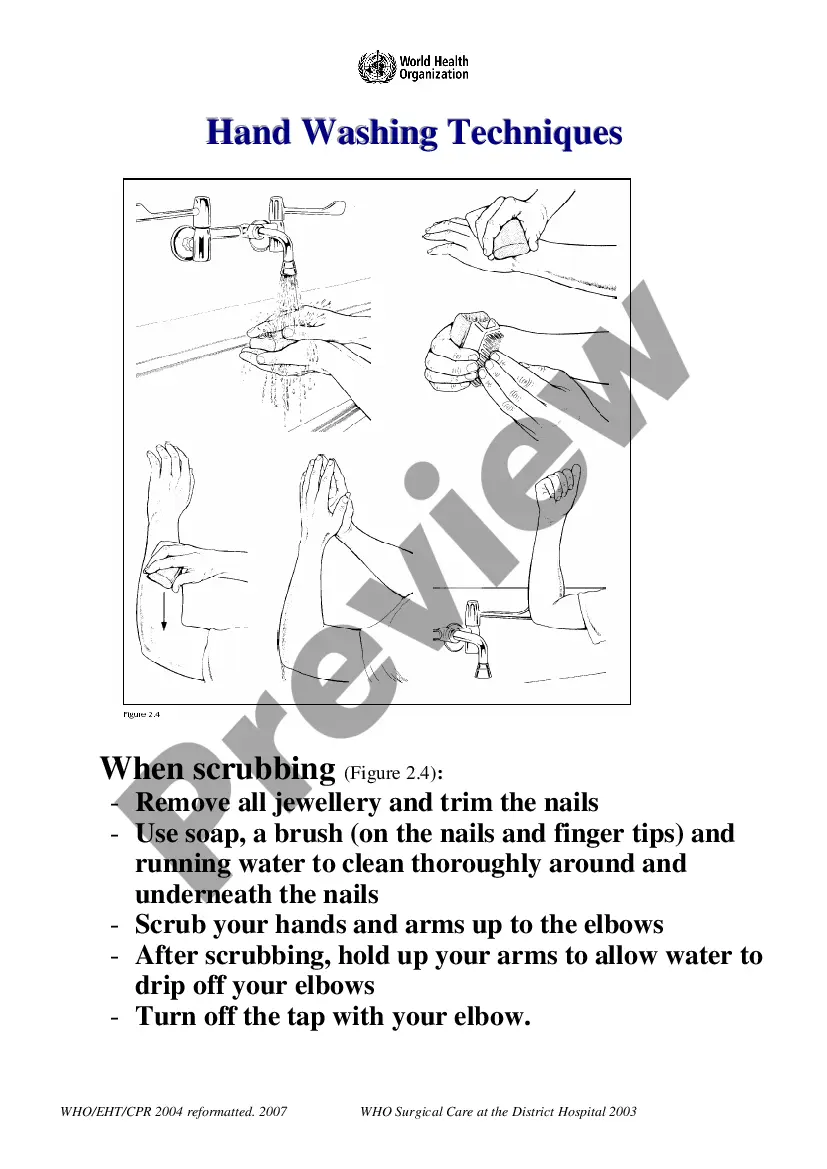
Wisconsin Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety
Instant download
Description
This form outlines the best practice protocols for clinical procedures safety.
Free preview
How to fill out Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety?
Are you currently in a position where you need documentation for either business or personal purposes almost every day.
There are numerous legal document templates available online, but finding reliable versions can be challenging.
US Legal Forms offers thousands of form templates, such as the Wisconsin Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety, designed to meet state and federal standards.
You can view all the document templates you have purchased in the My documents section.
You can obtain an additional copy of Wisconsin Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety anytime, if necessary. Just access the required form to download or print the document template.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and possess an account, simply Log In.
- After that, you can download the Wisconsin Best Practice Protocols Clinical Procedures Safety template.
- If you do not have an account and wish to use US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Find the form you need and ensure it is for your correct city/state.
- Utilize the Preview feature to review the form.
- Read the description to confirm that you have selected the right document.
- If the form is not what you are looking for, use the Search section to find the form that meets your needs and requirements.
- Once you find the correct form, click Purchase now.
- Choose the pricing plan you prefer, fill in the required details to create your account, and pay for your order using PayPal or credit card.
- Select a suitable file format and download your copy.