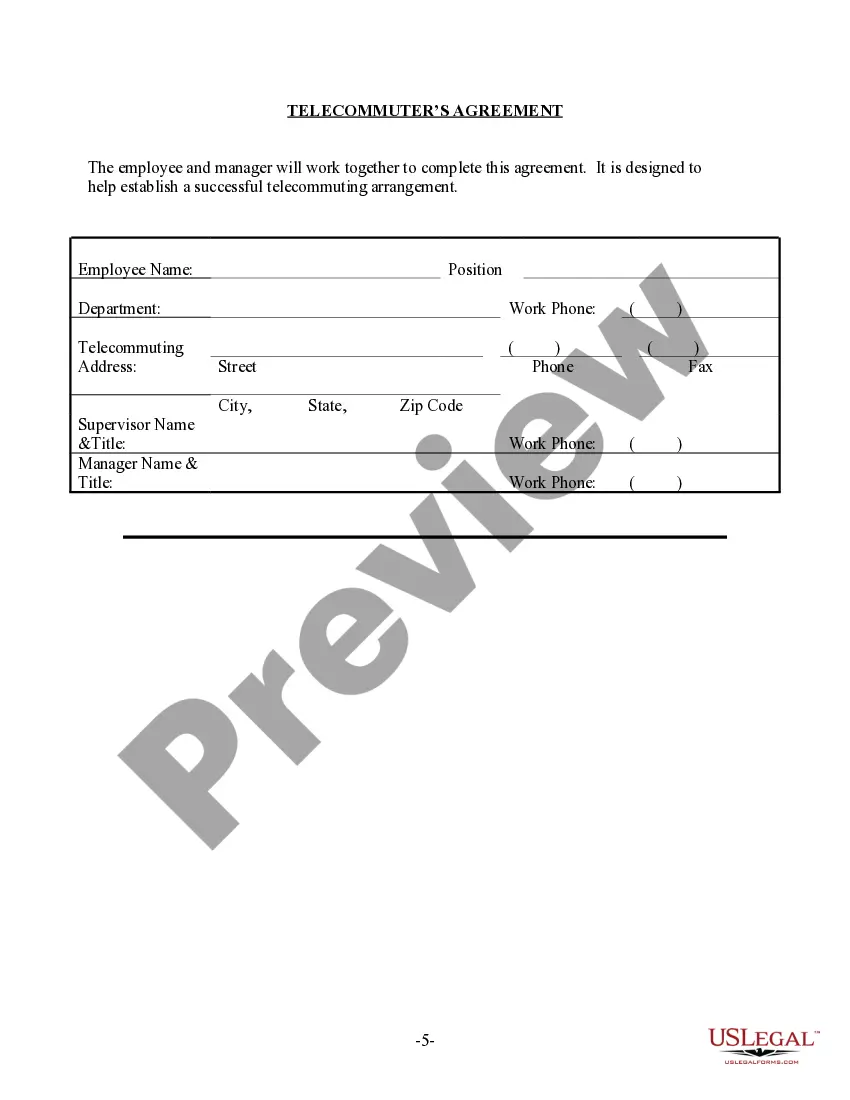
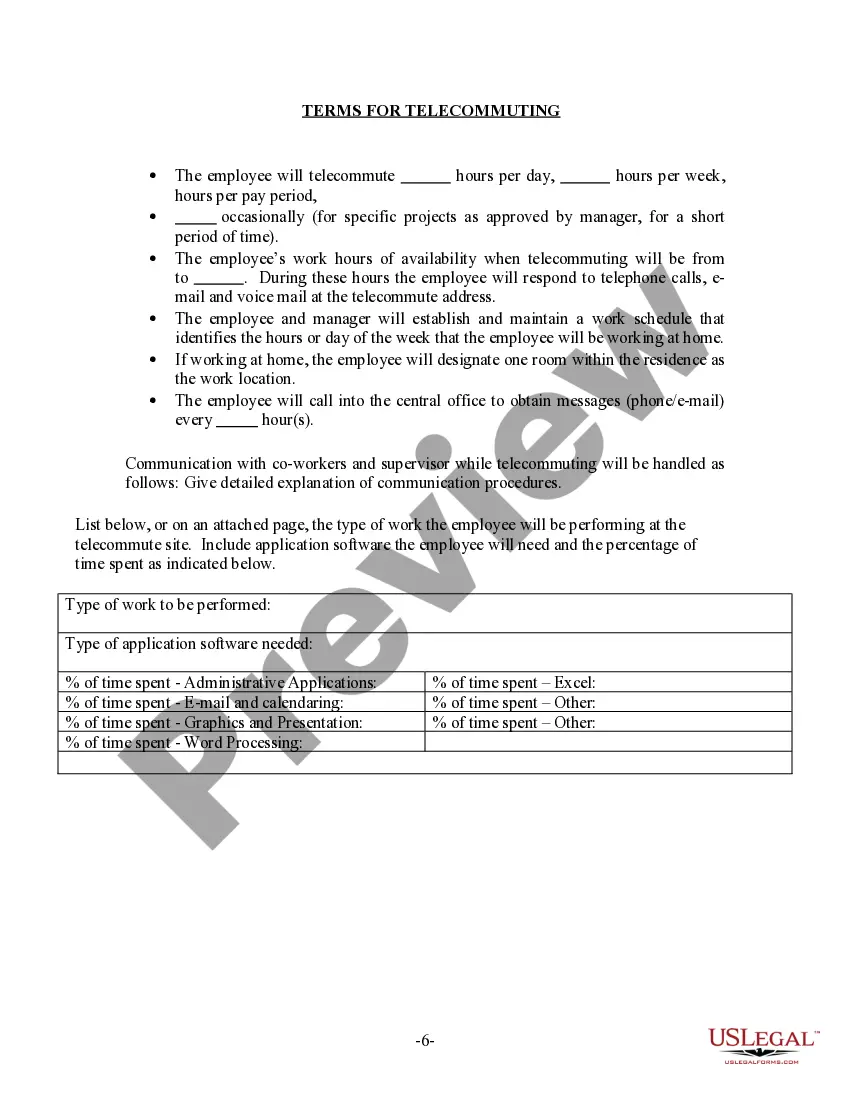
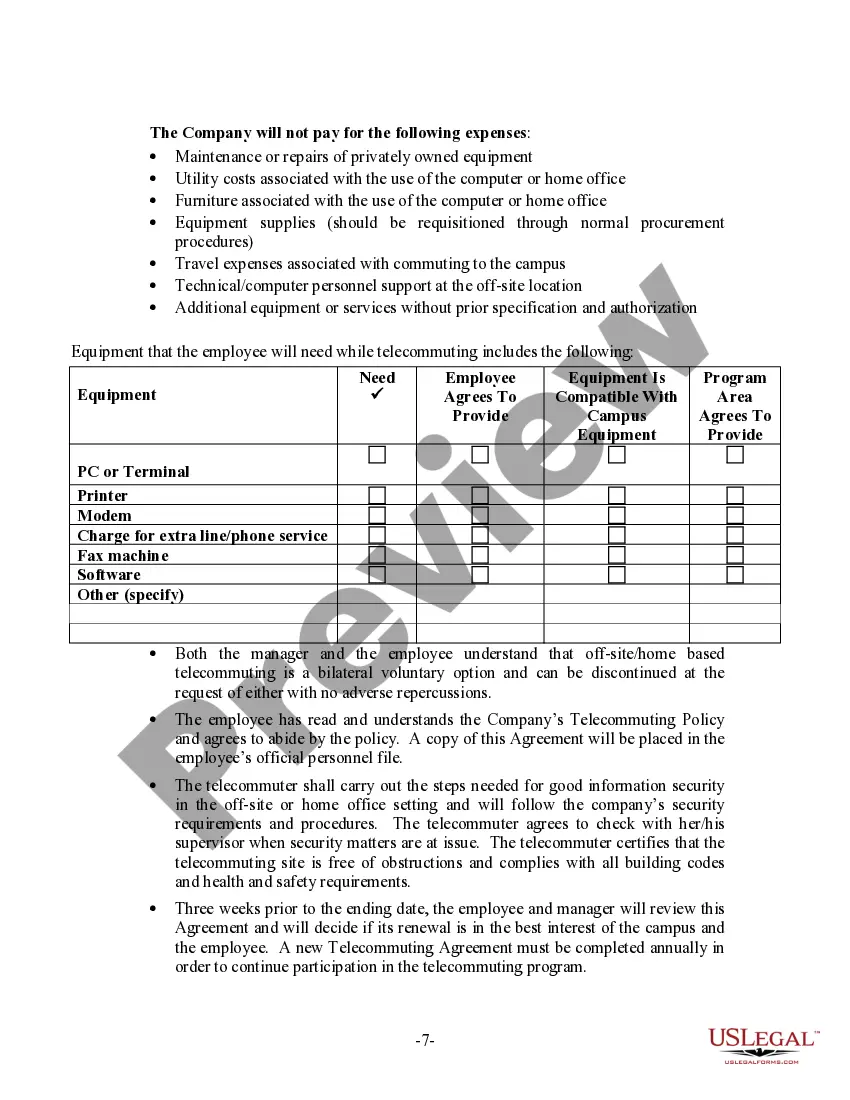
The Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy is a set of guidelines and regulations that govern the practice of working remotely in the state of Wisconsin. This policy aims to promote work flexibility, improve employee satisfaction, reduce traffic congestion, and enhance work-life balance. Under the Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy, employees are allowed to perform their job duties remotely, without the need to be physically present in the office. This arrangement allows employees to work from home, satellite offices, or other suitable remote locations within the state. The policy emphasizes the importance of clear and effective communication between telecommuting employees and their managers. It encourages the use of technology tools and platforms to facilitate collaboration, including virtual meetings, cloud-based storage, project management software, and instant messaging. To implement the Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy, organizations are required to establish telecommuting agreements with employees participating in the program. These agreements outline the expectations, responsibilities, and terms of the remote work arrangement. They may also address issues such as equipment and technology requirements, data security, and reimbursement for expenses incurred while telecommuting. Wisconsin recognizes different types of telecommuting arrangements to cater to the diverse needs of employees and employers. These include: 1. Full-time Telecommuting: Employees work remotely on a full-time basis and are not required to report to the office regularly. This arrangement is suitable for positions that can be performed entirely from a remote location. 2. Part-time Telecommuting: Employees work remotely for a portion of their regular work schedule, while also being present in the office for a designated number of days or hours. This arrangement allows for a balance between remote work and in-person collaboration. 3. Ad-hoc Telecommuting: Employees have the flexibility to work remotely on an as-needed basis, such as during inclement weather, personal emergencies, or other circumstances that make it impractical or unsafe to commute to the office. Ad-hoc telecommuting provides a temporary solution without a fixed remote work schedule. 4. Hybrid Telecommuting: This arrangement combines remote work with regular office attendance. Employees typically work remotely for a certain number of days per week or month, allowing for a blend of independent work and in-person team collaboration. Implementing the Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy can offer several benefits to both employees and employers. It helps attract and retain top talent, reduces office space requirements, lowers transportation costs, and contributes to a more sustainable work environment. However, it's essential for organizations and employees to adhere to the established guidelines and ensure that remote work does not compromise productivity, communication, or data security.
Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy
Description
How to fill out Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy?
You can spend hrs online searching for the legal file format that suits the federal and state needs you require. US Legal Forms gives a huge number of legal varieties that are evaluated by pros. You can easily download or print the Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy from our assistance.
If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, it is possible to log in and click on the Obtain switch. Afterward, it is possible to complete, revise, print, or signal the Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy. Each and every legal file format you get is the one you have eternally. To acquire an additional copy for any acquired type, proceed to the My Forms tab and click on the corresponding switch.
If you use the US Legal Forms web site the very first time, keep to the straightforward guidelines below:
- Initially, be sure that you have chosen the best file format to the county/city of your liking. See the type outline to ensure you have picked the appropriate type. If offered, take advantage of the Preview switch to look from the file format too.
- In order to get an additional edition in the type, take advantage of the Look for industry to discover the format that meets your needs and needs.
- Upon having discovered the format you desire, click on Acquire now to proceed.
- Select the pricing strategy you desire, type your references, and sign up for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Total the deal. You can utilize your credit card or PayPal account to fund the legal type.
- Select the file format in the file and download it in your system.
- Make changes in your file if possible. You can complete, revise and signal and print Wisconsin Telecommuting Policy.
Obtain and print a huge number of file layouts using the US Legal Forms Internet site, which provides the greatest variety of legal varieties. Use specialist and status-distinct layouts to deal with your organization or personal demands.