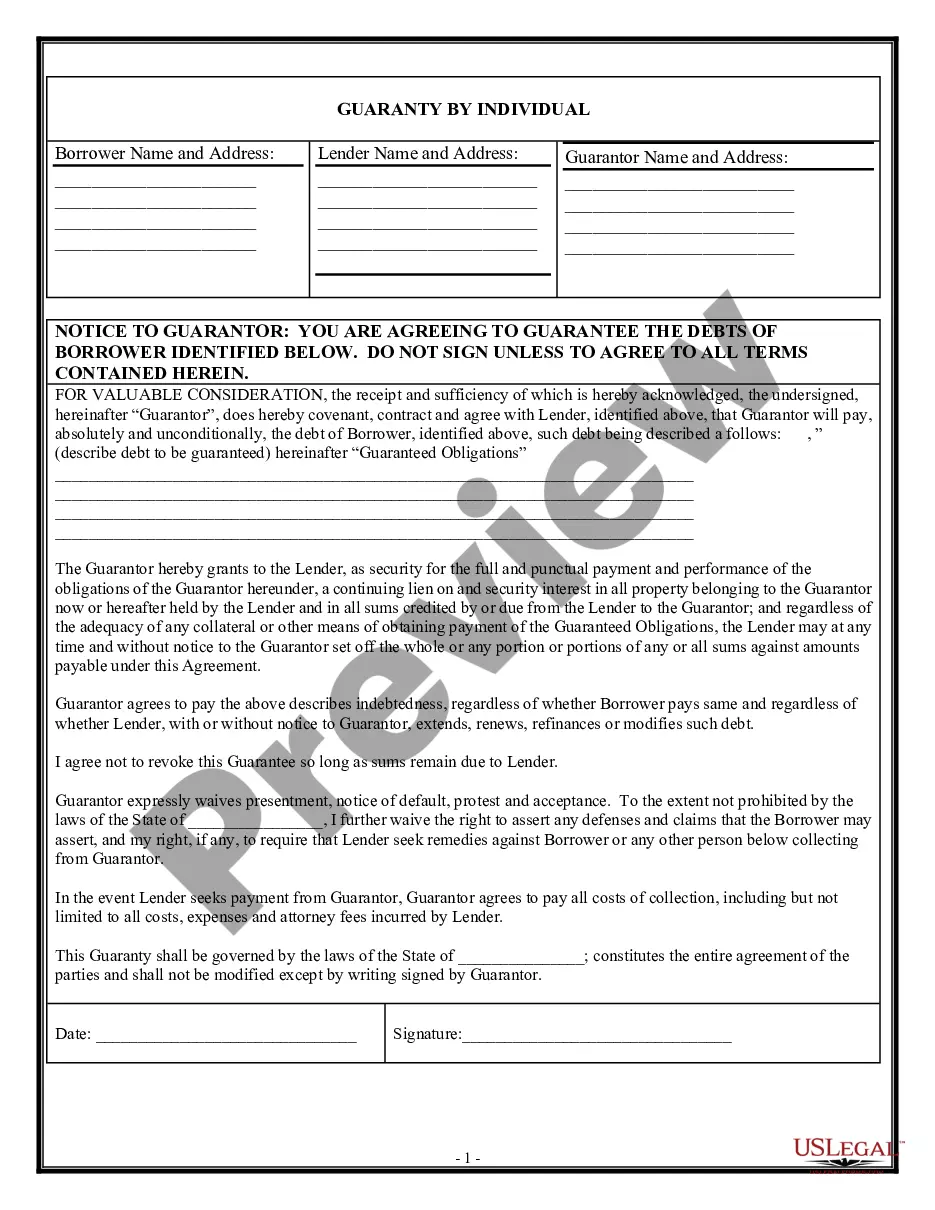
Wisconsin Complex Guaranty Agreement to Lender
Description
How to fill out Complex Guaranty Agreement To Lender?
If you wish to full, acquire, or printing legitimate papers themes, use US Legal Forms, the biggest selection of legitimate varieties, that can be found online. Use the site`s simple and handy search to get the papers you require. Numerous themes for enterprise and personal reasons are categorized by classes and says, or keywords. Use US Legal Forms to get the Wisconsin Complex Guaranty Agreement to Lender with a number of mouse clicks.
Should you be presently a US Legal Forms customer, log in to your account and click on the Download key to get the Wisconsin Complex Guaranty Agreement to Lender. You can also access varieties you earlier acquired inside the My Forms tab of the account.
Should you use US Legal Forms initially, refer to the instructions listed below:
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the shape to the right metropolis/region.
- Step 2. Make use of the Review choice to examine the form`s articles. Do not forget to read through the information.
- Step 3. Should you be not happy with the develop, make use of the Lookup industry near the top of the display to locate other variations from the legitimate develop template.
- Step 4. When you have located the shape you require, select the Buy now key. Opt for the prices strategy you favor and add your credentials to register on an account.
- Step 5. Method the financial transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to perform the financial transaction.
- Step 6. Select the format from the legitimate develop and acquire it on your gadget.
- Step 7. Comprehensive, change and printing or indication the Wisconsin Complex Guaranty Agreement to Lender.
Every legitimate papers template you acquire is yours forever. You have acces to each develop you acquired inside your acccount. Select the My Forms portion and pick a develop to printing or acquire again.
Contend and acquire, and printing the Wisconsin Complex Guaranty Agreement to Lender with US Legal Forms. There are many expert and express-distinct varieties you can use for the enterprise or personal demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
ANSWER: Guarantee, the broader and more common term, is both a verb and a noun. The narrower term, guaranty, today appears mostly in banking and other financial contexts; it seldom appears in nonlegal writing.
Guarantor agrees to the provisions of this Guaranty, and hereby waives notice of (a) any loans or advances made by Lender to Borrower, (b) acceptance of this Guaranty, (c) any amendment or extension of the Note, the Loan Agreement or of any other Loan Documents, (d) the execution and delivery by Borrower and Lender of ...
A loan guarantee is a legally binding commitment to pay a debt in the event the borrower defaults. This most often occurs between family members, where the borrower can't obtain a loan because of a lack of income or down payment, or due to a poor credit rating.
Noun. guar·?an·?ty ?gar-?n-t?, ?gar- plural guaranties. 1. : a pledge to pay another's debt or to perform another's duty in case of the other's default or inadequate performance compare letter of credit.
Dear Sir/Madam: This letter will serve as your notification that (Bank Name) will irrevocably honor and guarantee payment of any check(s) written by our customer (Customer's Name) up to the amount of (Amount Guaranteed) and drawn on account number (Customer's Account Number). No stop payments will be issued.
In order for a guaranty agreement to be enforceable, it has to be in writing, the writing has to be signed by the guarantor, and the writing has to contain each of the following essential elements: 1. the identity of the lender; 2. the identity of the primary obligor; 3.
A guaranty clause can take many forms; a primary example is a loan agreement that is co-signed, which can signify a guaranty from the co-signer to a specific amount, even if the loan agreement does not use a specific "guarantor" title.
IN WRITING Oral guaranties are almost never enforceable in California though many creditors have attempted to enforce them claiming that they only extended credit predicated on various oral assurances from the owners of the debtor.