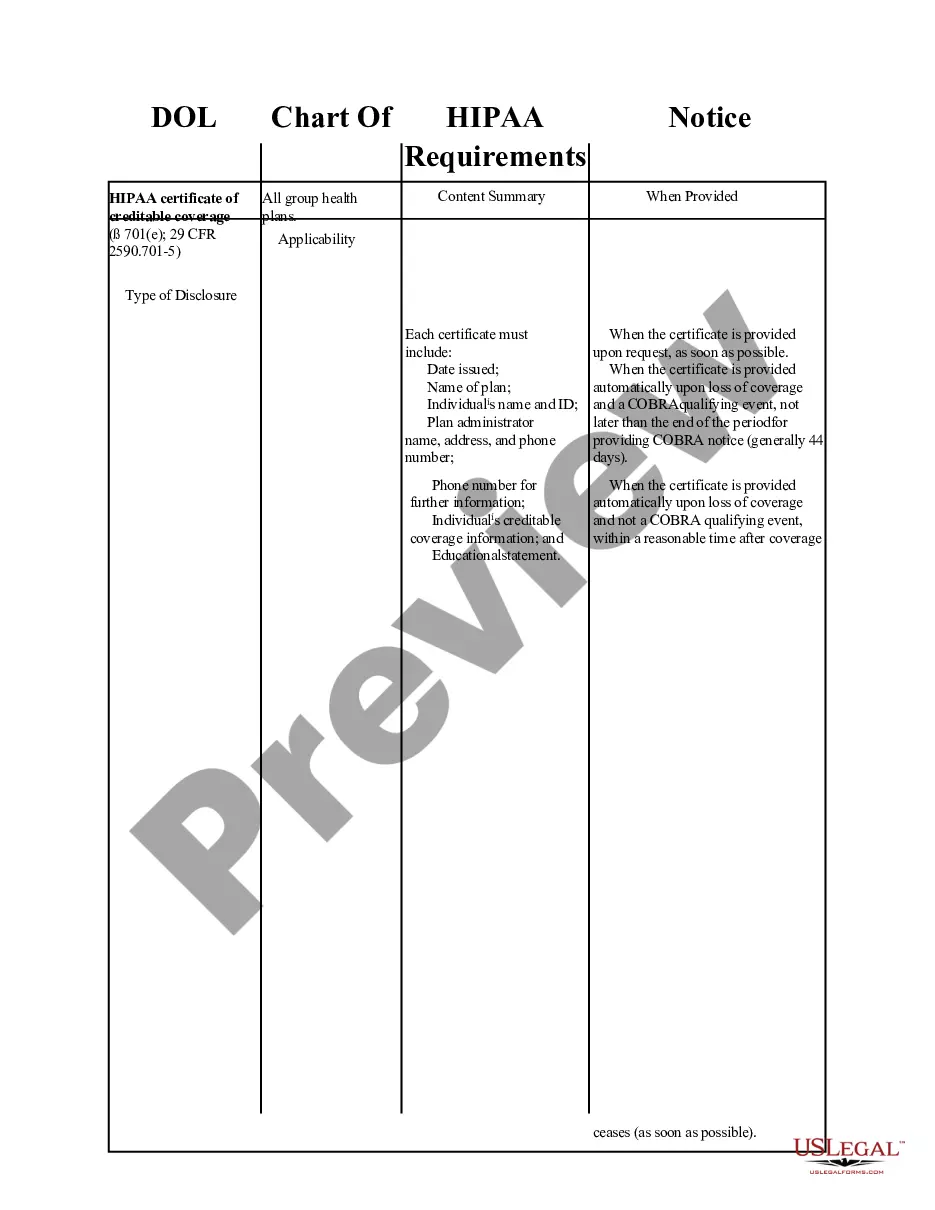
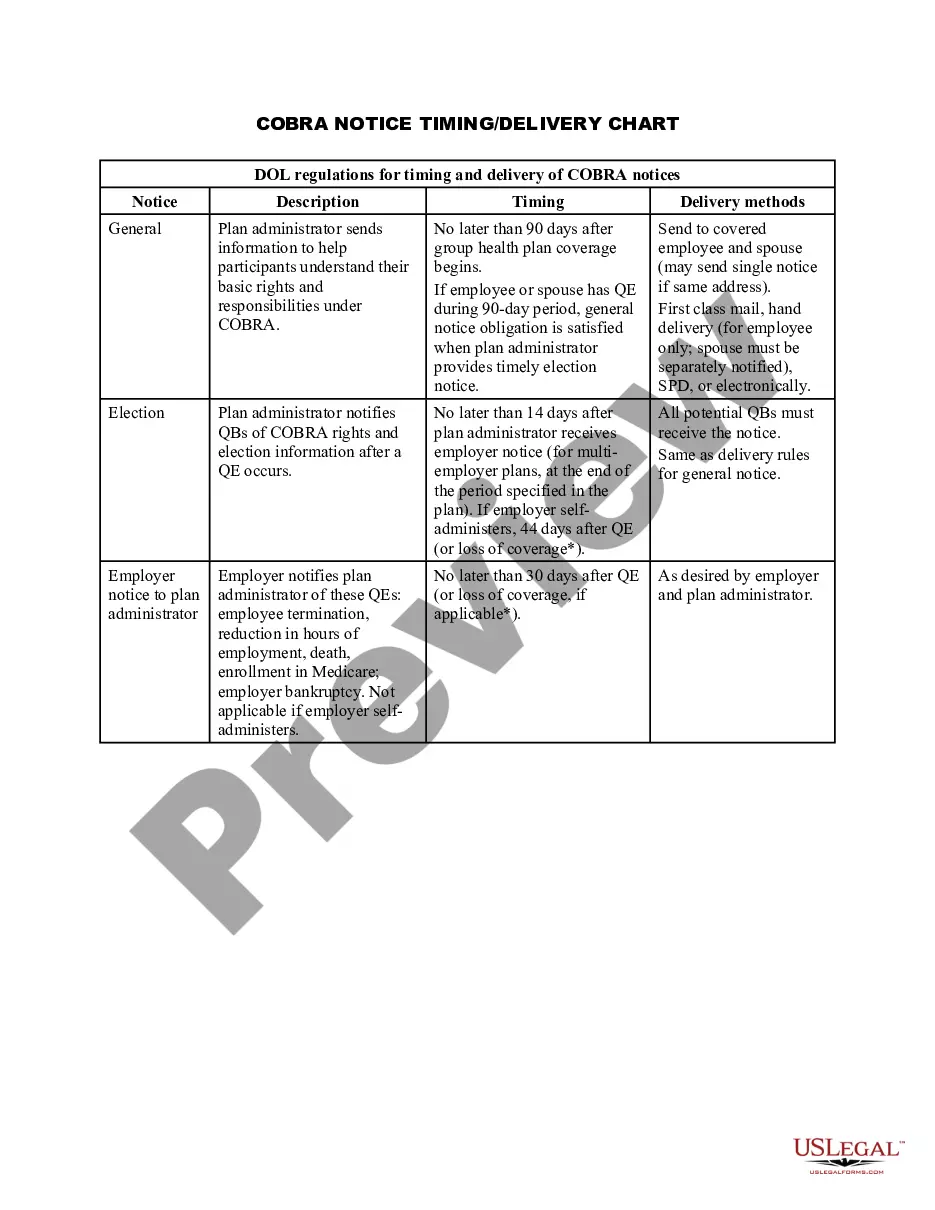
Wisconsin DOL Chart of HIPAA Notice Requirements
Description
How to fill out DOL Chart Of HIPAA Notice Requirements?
You can dedicate hours on the web searching for the legal document template that satisfies both federal and state requirements you need.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of legal forms that can be reviewed by experts.
It is easy to access or print the Wisconsin DOL Chart of HIPAA Notice Requirements from our services.
If available, utilize the Preview button to browse the document template as well. If you wish to find another version of the form, use the Lookup section to discover the template that fits your preferences and requirements.
- If you have an existing US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click on the Download button.
- After that, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Wisconsin DOL Chart of HIPAA Notice Requirements.
- Every legal document template you purchase is yours indefinitely.
- To obtain another copy of any purchased form, navigate to the My documents tab and click on the relevant button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms site for the first time, follow the simple instructions below.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct document template for the county/city of your choice.
- Review the form description to confirm that you have chosen the correct template.
Form popularity
FAQ
(1) The notification required by paragraph (a) of this section shall include, to the extent possible, the identification of each individual whose unsecured protected health information has been, or is reasonably believed by the business associate to have been, accessed, acquired, used, or disclosed during the breach.
The notice must describe: How the Privacy Rule allows provider to use and disclose protected health information. It must also explain that your permission (authorization) is necessary before your health records are shared for any other reason. The organization's duties to protect health information privacy.
Organisation must notify the DPA and individuals The data included the personal addresses, family composition, monthly salary and medical claims of each employee. In that case, the textile company must inform the supervisory authority of the breach.
Mandatory data breach notification provides affected individuals with notice after a breach to provide time to protect against potential harms related to the breach, e.g., by changing online passwords or cancelling credit cards.
These individual notifications must be provided without unreasonable delay and in no case later than 60 days following the discovery of a breach and must include, to the extent possible, a brief description of the breach, a description of the types of information that were involved in the breach, the steps affected
HIPAA's Breach Notification Rule requires covered entities to notify patients when their unsecured protected heath information (PHI) is impermissibly used or disclosedor breached,in a way that compromises the privacy and security of the PHI.
A description of the information that will be used/disclosed. The purpose for which the information will be disclosed. The name of the person or entity to whom the information will be disclosed. An expiration date or expiration event when consent to use/disclose the information is withdrawn.
The NPP is a document that tells your patients, employees, or clients how their health information may be used and shared and lists their health privacy rights related to Protected Health Information (PHI). It's a part of the HIPAA Privacy Rule and a key requirement for your organization.
Write Your HIPAA Policies and Procedures. Your policies should establish the following:Make Policies and Procedures Available to Staff.Train Staff on Policies and Procedures.Develop a Review and Approval Process.Maintain Version Control.Use Templates/Software to Streamline Policy Management.
The required information includes: A statement that the covered entity is required by law to maintain the privacy of PHI. A statement that the covered entity must provide individuals with notice of its legal duties and privacy practices with respect to PHI.