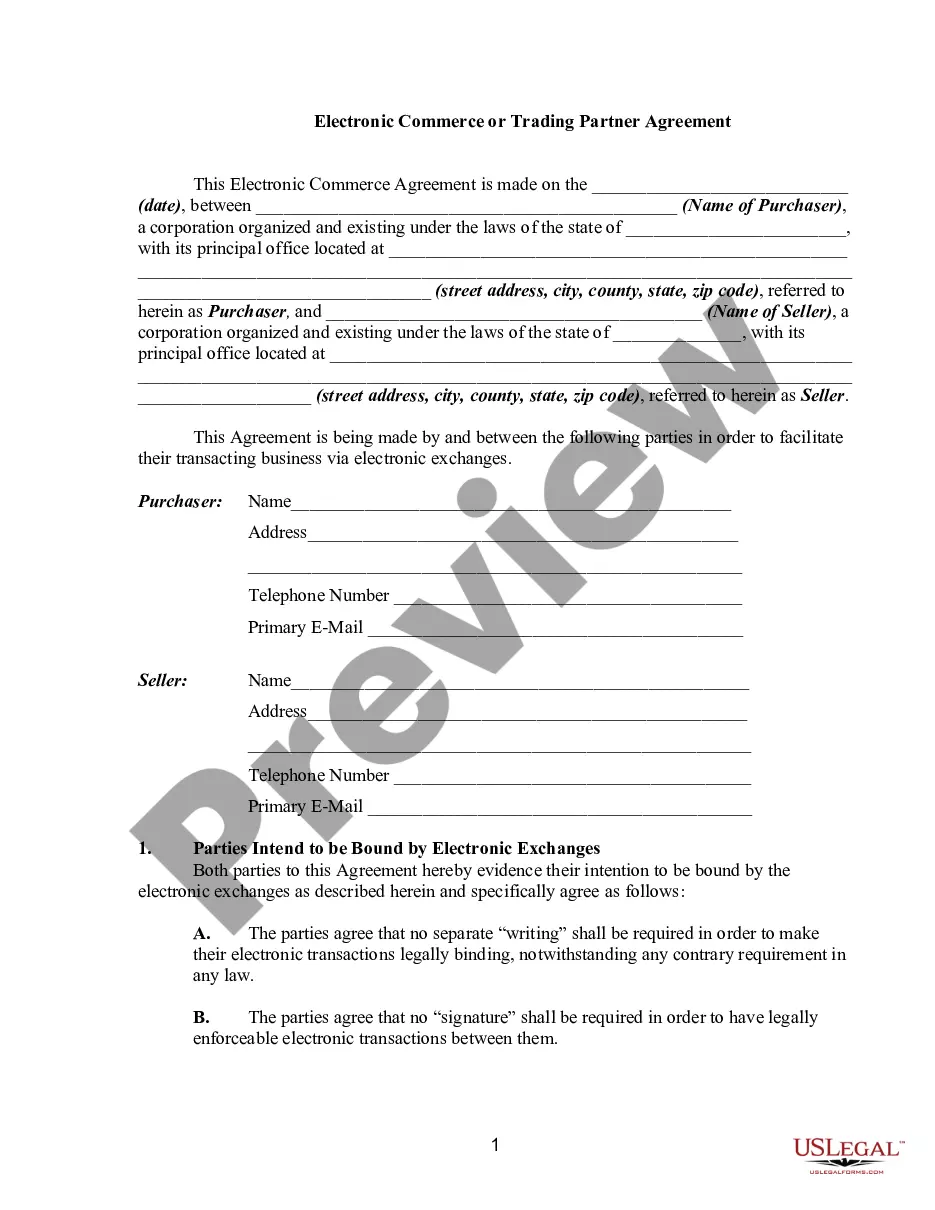
Wisconsin Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement
Description
How to fill out Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement?
If you need to complete, obtain, or printing legitimate file templates, use US Legal Forms, the most important assortment of legitimate types, which can be found on the Internet. Use the site`s easy and hassle-free search to discover the documents you need. Various templates for enterprise and personal purposes are categorized by classes and says, or search phrases. Use US Legal Forms to discover the Wisconsin Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement in a couple of click throughs.
When you are presently a US Legal Forms buyer, log in to your bank account and click on the Acquire switch to obtain the Wisconsin Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement. You can even gain access to types you in the past delivered electronically in the My Forms tab of your bank account.
If you work with US Legal Forms the very first time, refer to the instructions listed below:
- Step 1. Be sure you have chosen the shape for your appropriate town/country.
- Step 2. Use the Review method to look over the form`s information. Never overlook to see the explanation.
- Step 3. When you are not happy with the type, use the Lookup discipline towards the top of the display to locate other types of your legitimate type design.
- Step 4. Once you have found the shape you need, click the Acquire now switch. Pick the prices strategy you favor and put your references to register on an bank account.
- Step 5. Method the financial transaction. You can use your bank card or PayPal bank account to complete the financial transaction.
- Step 6. Select the formatting of your legitimate type and obtain it on the gadget.
- Step 7. Complete, modify and printing or signal the Wisconsin Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement.
Every single legitimate file design you buy is the one you have permanently. You may have acces to each type you delivered electronically with your acccount. Click on the My Forms section and choose a type to printing or obtain once again.
Compete and obtain, and printing the Wisconsin Model Electronic Data Interchange Trading Partner Agreement with US Legal Forms. There are millions of professional and state-certain types you can use to your enterprise or personal requires.
Form popularity
FAQ
To define business entities in an external trading partner company: Specify which trading partner company this business entity is a part of. ... Specify the customer ID or vendor ID for this business entity. ... Identify the internal trading partners who do business with this external business entity, and then save the page.
EDI Support Services (EDISS) assigns a Trading Partner ID, also known as a Submitter ID, when an entity registers for an electronic transaction in EDISS Connect. The Trading Partner ID is used to submit electronic transactions and to register for the Noridian Medicare Portal (NMP).
This could be a supplier, a manufacturer, a transporter, or a partner in wholesale for example. Most supply chain companies will have a large network of trading partners and primarily communicate and trade using EDI standards.
In order to perform intercompany transactions in SAP, you must also define a trading partner on every transaction. A trading partner represents the company code that is in transaction with your company code. Intercompany transactions can be done at either a general ledger account or a sub-ledger level.
Below, you have a left-right broad overview of the 6 common steps of the EDI onboarding process: EDI PARTNER CAMPAIGN. This outlines the project in its totality. ... EDI PARTNER QUESTIONNAIRE. ... EDI PROFILE CREATION. ... EDI PROVISIONING. ... EDI TESTING. ... DEPLOYMENT.
EDI Support Services (EDISS) assigns a Trading Partner ID, also known as a Submitter ID, when an entity registers for an electronic transaction in EDISS Connect. The Trading Partner ID is used to submit electronic transactions and to register for the Noridian Medicare Portal (NMP).
A region or country that another region or country buys goods from or sells goods to: The United States is Vietnam's largest trading partner. Exporters are struggling because Britain's trading partners are cutting back on orders.