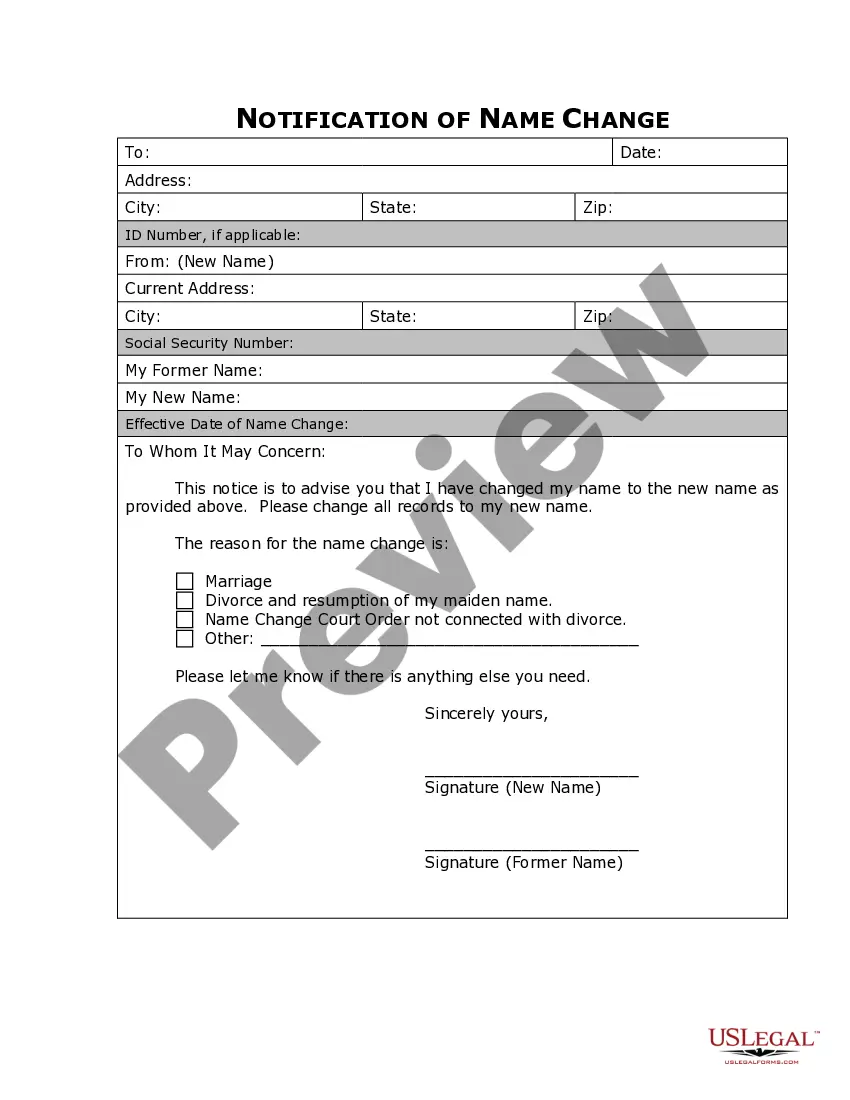
This form brings together several boilerplate contract clauses that work together to establish a confidentiality obligation from the parties and outline what that confidentiality agreement will apply to under the terms contract agreement. Also incorporated are clauses regarding indemnity in the event of unauthorized disclosures of confidential information.
Wisconsin Confidentiality - Long-Form Provision
Description
How to fill out Confidentiality - Long-Form Provision?
US Legal Forms - one of the most significant libraries of lawful varieties in the United States - provides a variety of lawful document web templates you are able to acquire or print. While using web site, you will get 1000s of varieties for organization and personal uses, sorted by groups, states, or search phrases.You can find the most recent variations of varieties just like the Wisconsin Confidentiality - Long-Form Provision in seconds.
If you already possess a subscription, log in and acquire Wisconsin Confidentiality - Long-Form Provision from your US Legal Forms local library. The Acquire option will show up on each and every form you look at. You get access to all previously saved varieties in the My Forms tab of your profile.
If you wish to use US Legal Forms for the first time, listed below are easy instructions to help you started:
- Be sure to have picked out the proper form to your metropolis/county. Click on the Preview option to review the form`s articles. Look at the form outline to actually have selected the appropriate form.
- If the form doesn`t fit your specifications, use the Research area at the top of the display to find the the one that does.
- Should you be satisfied with the shape, confirm your choice by clicking on the Purchase now option. Then, select the costs strategy you want and supply your qualifications to register for the profile.
- Process the transaction. Make use of your credit card or PayPal profile to finish the transaction.
- Select the structure and acquire the shape on your product.
- Make modifications. Load, modify and print and sign the saved Wisconsin Confidentiality - Long-Form Provision.
Every web template you included with your money does not have an expiry particular date and is yours forever. So, if you would like acquire or print yet another duplicate, just go to the My Forms area and then click about the form you want.
Gain access to the Wisconsin Confidentiality - Long-Form Provision with US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive local library of lawful document web templates. Use 1000s of specialist and state-certain web templates that satisfy your small business or personal requires and specifications.
Form popularity
FAQ
I agree that I owe the Company and such third parties, during the term of my employment and thereafter, a duty to hold all such confidential or proprietary information in the strictest confidence and not to disclose it to any person, firm or corporation (except as necessary in carrying out my work for the Company ... Form of Statement of Confidentiality, Non-Disclosure and Non ... - SEC.gov sec.gov ? Archives ? edgar ? data ? dex104 sec.gov ? Archives ? edgar ? data ? dex104
I agree that I will not disclose, disseminate, or publicize, or cause or permit to be disclosed, disseminated, or publicized, any of the terms of this Release or the fact that I have entered into this Release, to any person, corporation, association, government agency, or other entity, other than my spouse, legal ...
A Confidential Disclosure Agreement [(CDA), also referred to as non-disclosure agreement (NDA) or secrecy agreement, is a legal agreement between a minimum of two parties which outlines information the parties wish to share with one another for certain evaluation purposes, but wish to restrict from wider use and ... Confidential Disclosure Agreements (CDAs)/NDAs pitt.edu ? osp-teams ? negotiations ? co... pitt.edu ? osp-teams ? negotiations ? co...
A confidentiality agreement should include a clear definition of the confidential information, scope of the agreement, obligations of the receiving party, the duration of the contract, any exceptions to confidentiality, and the consequences of a breach of the contract.
Here is a common example: CONFIDENTIALITY NOTICE: This message and any accompanying documents contain information belonging to the sender which may be confidential and legally privileged. This information is only for the use of the individual or entity to which it was intended.
Here are some examples of confidential information: Name, date of birth, age, sex, and address. Current contact details of family. Bank information. Medical history or records. Personal care issues. Service records and file progress notes. Personal goals. Assessments or reports. Confidential Information | Definition, Types & Examples - Study.com study.com ? academy ? lesson ? confidential-infor... study.com ? academy ? lesson ? confidential-infor...
A typical confidentiality clause might say, "The phrases and circumstances of this Agreement are completely confidential between the parties and shall not be disclosed to anybody else. Any disclosure in violation shall be deemed a breach of this Agreement."
A confidentiality clause within a business contract can keep confidential information safe by limiting what an employee, contractor, or business partner can say or do with your confidential business information. The Confidentiality Clause: Essential Guidelines - Ironclad Ironclad ? Contracts and clauses Ironclad ? Contracts and clauses