West Virginia Addendums to Shopping Center Lease
Description
How to fill out Addendums To Shopping Center Lease?
US Legal Forms - among the most significant libraries of legitimate varieties in America - delivers a wide array of legitimate document web templates you may acquire or printing. Utilizing the internet site, you may get a large number of varieties for enterprise and specific uses, sorted by types, states, or search phrases.You will discover the most recent variations of varieties much like the West Virginia Addendums to Shopping Center Lease in seconds.
If you already have a registration, log in and acquire West Virginia Addendums to Shopping Center Lease through the US Legal Forms library. The Down load option will appear on each develop you view. You get access to all in the past saved varieties inside the My Forms tab of your respective account.
If you want to use US Legal Forms the very first time, listed below are easy recommendations to help you started off:
- Make sure you have selected the proper develop for your town/region. Go through the Review option to analyze the form`s articles. See the develop information to actually have chosen the proper develop.
- If the develop doesn`t suit your specifications, use the Lookup area at the top of the display screen to find the the one that does.
- When you are pleased with the form, verify your choice by clicking on the Get now option. Then, pick the pricing prepare you like and offer your accreditations to sign up for the account.
- Method the purchase. Use your Visa or Mastercard or PayPal account to perform the purchase.
- Choose the file format and acquire the form in your gadget.
- Make alterations. Fill up, revise and printing and signal the saved West Virginia Addendums to Shopping Center Lease.
Each and every design you put into your account lacks an expiration date which is your own forever. So, in order to acquire or printing one more duplicate, just proceed to the My Forms area and then click on the develop you need.
Get access to the West Virginia Addendums to Shopping Center Lease with US Legal Forms, probably the most comprehensive library of legitimate document web templates. Use a large number of specialist and state-certain web templates that fulfill your business or specific needs and specifications.
Form popularity
FAQ
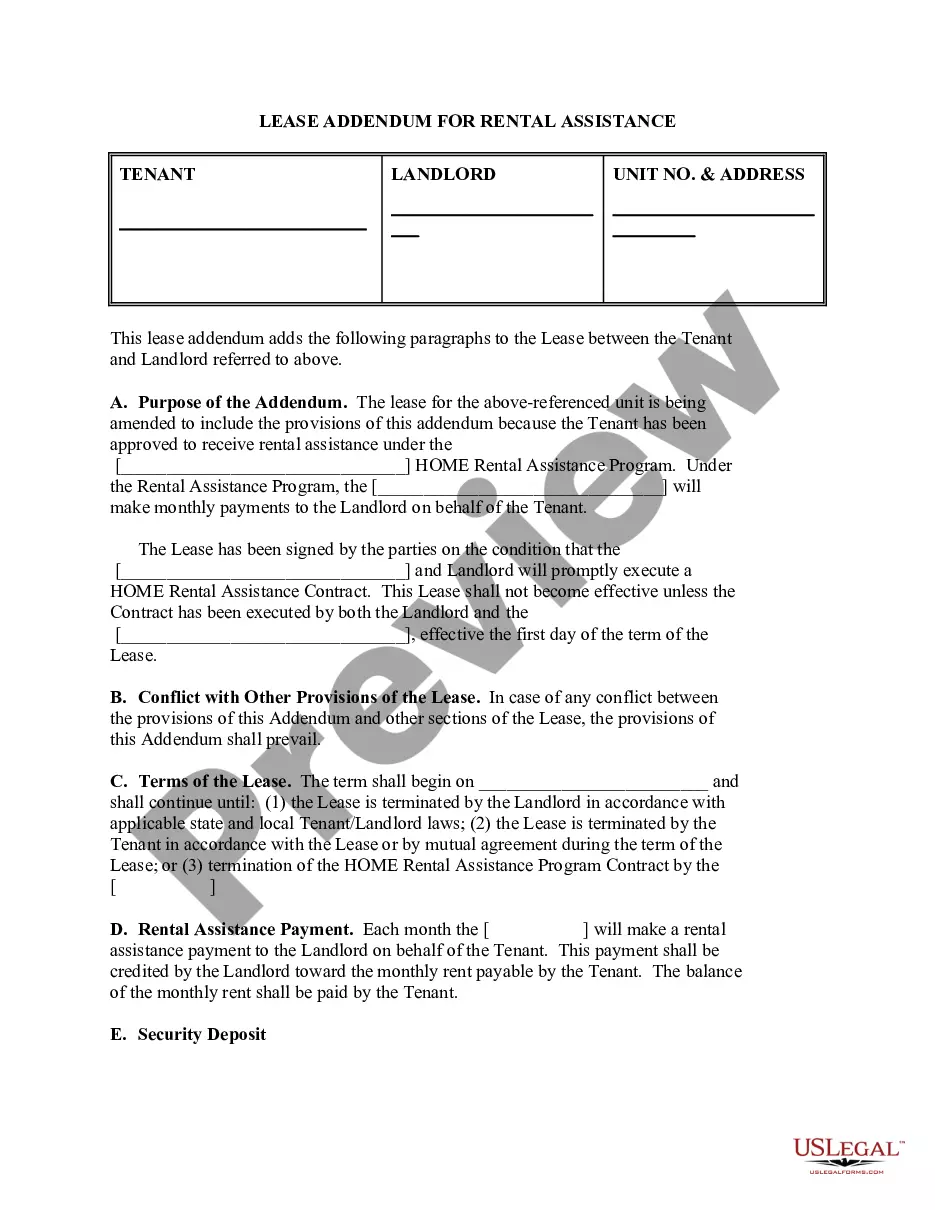
With a Lease Addendum, a landlord and tenant can add new or update existing lease terms without having to terminate their original agreement and create a new one. A Lease Addendum is also known as a: Tenancy addendum. Lease amendment.
An addendum may include any written item added to an existing piece of writing. The addition often applies to supplemental documentation that changes the initial agreement that forms the original contract.
Using Addenda in a Sentence When to use addenda: Addenda is the plural form of addendum, which means a thing which is added to another thing. For example, The lawyers introduced various addenda to the contract. New discoveries meant that the police had to attach several addenda to the crime report.
What is a Lease Addendum? Lease addenda are separate documents that landlords add to an original lease agreement. Landlords use them to provide additional information that the original lease doesn't cover.
Instead of changing the actual lease agreement, an addendum is a document added that outlines its modifications. Once both parties agree and sign, the addendum should be added to the original lease.
An addendum is additional information added to your pathology report after it was finalized by your pathologist. Most addendums are added to the bottom of the original report. The purpose of an addendum is to communicate additional information which supports the original diagnosis or interpretation.
File a copy of the signed lease agreement with the Office of the County Registrar (known as the County Recorder or Deed Registry in some states) in the county where the rental property resides. The office may charge a nominal filing fee for registration, which you must pay at the time of filing.
Tips for Writing an AddendumEnforceable. Before you write an addendum, you should have an attorney verify it is the correct solution.Formatting. Use the same formatting as the original contract.Language.Title of the Addendum.Date.Specific List of Changes.Concluding Paragraph.Signature Block.More items...?13 July 2020
A written lease agreement must contain:The names and addresses of both parties;The description of the property;The rental amount and reasonable escalation;The frequency of rental payments, i.e. monthly;The amount of the deposit;The lease period;The notice period for termination of contract;More items...
An example of an addendum being used would be if the parties wanted to add something to the original document. For instance, an individual who is purchasing a house may not want to purchase all of the furniture that is being left behind. However, after thinking about it further, he changes his mind.