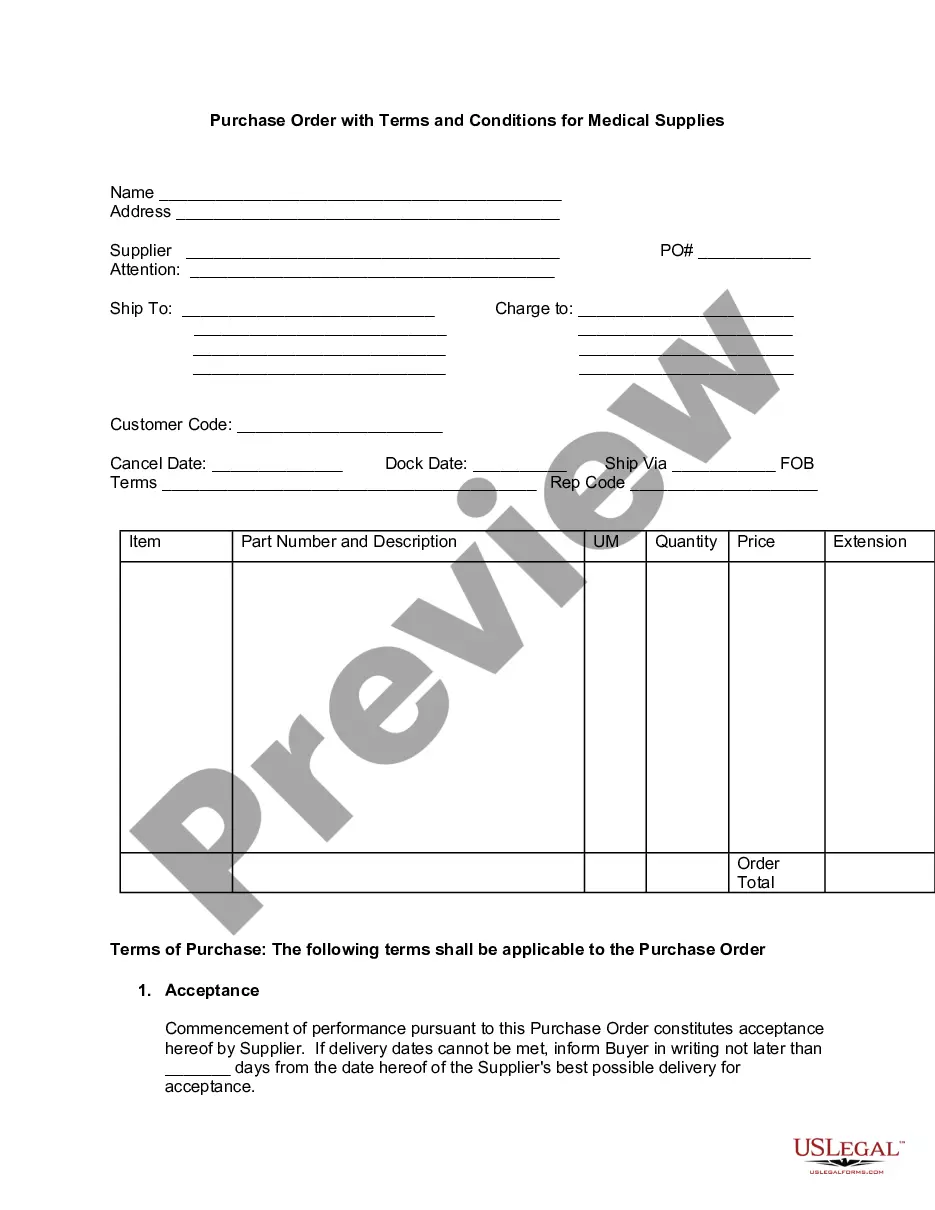
This office lease clause is an onerous approach to a default remedies clause. This clause is similar to those found in many New York City landlord office lease forms.
West Virginia Onerous Approach to Default Remedy Clause
Description
How to fill out Onerous Approach To Default Remedy Clause?
Are you currently in the placement where you need papers for either enterprise or personal functions just about every day? There are tons of lawful papers layouts available online, but finding types you can rely isn`t effortless. US Legal Forms offers a large number of develop layouts, like the West Virginia Onerous Approach to Default Remedy Clause, that are created to satisfy state and federal demands.
When you are already knowledgeable about US Legal Forms website and possess a free account, merely log in. Next, you can download the West Virginia Onerous Approach to Default Remedy Clause format.
Should you not provide an bank account and would like to begin using US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Find the develop you want and ensure it is for that appropriate area/county.
- Take advantage of the Review switch to review the shape.
- See the explanation to actually have chosen the correct develop.
- In the event the develop isn`t what you`re seeking, utilize the Search industry to discover the develop that suits you and demands.
- Once you discover the appropriate develop, just click Purchase now.
- Choose the prices strategy you would like, fill in the necessary details to produce your account, and purchase the transaction utilizing your PayPal or Visa or Mastercard.
- Pick a handy file format and download your backup.
Discover all the papers layouts you might have purchased in the My Forms menus. You can obtain a additional backup of West Virginia Onerous Approach to Default Remedy Clause whenever, if needed. Just select the required develop to download or print the papers format.
Use US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive variety of lawful forms, to save some time and steer clear of mistakes. The services offers appropriately produced lawful papers layouts that you can use for a variety of functions. Create a free account on US Legal Forms and start making your lifestyle a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
This provision specifies the remedies for an Event of Default and also outlines the order in which available funds will be disbursed to the lenders. all outstanding borrowings become immediately due and payable. all outstanding borrowings become immediately due and payable.
Other remedies that lenders can consider if an event of default exists under a loan agreement are: Refusing to make further loans or issue additional letters of credit. Accelerating the borrower's loan repayment obligations. Requiring the borrower to cash collateralize undrawn and unexpired letters of credit.
How can an event of default be cured? Agreements typically allow the defaulting party an opportunity to cure or remedy the default within a certain period before negative consequences apply. The grace period could be days, weeks, or longer, and some agreements allow for a maximum number of cures.
A ?default? is a failure to comply with a provision in the lease. ?Curing? or ?remedying? the default means correcting the failure or omission. A common example is a failure to pay the rent on time.