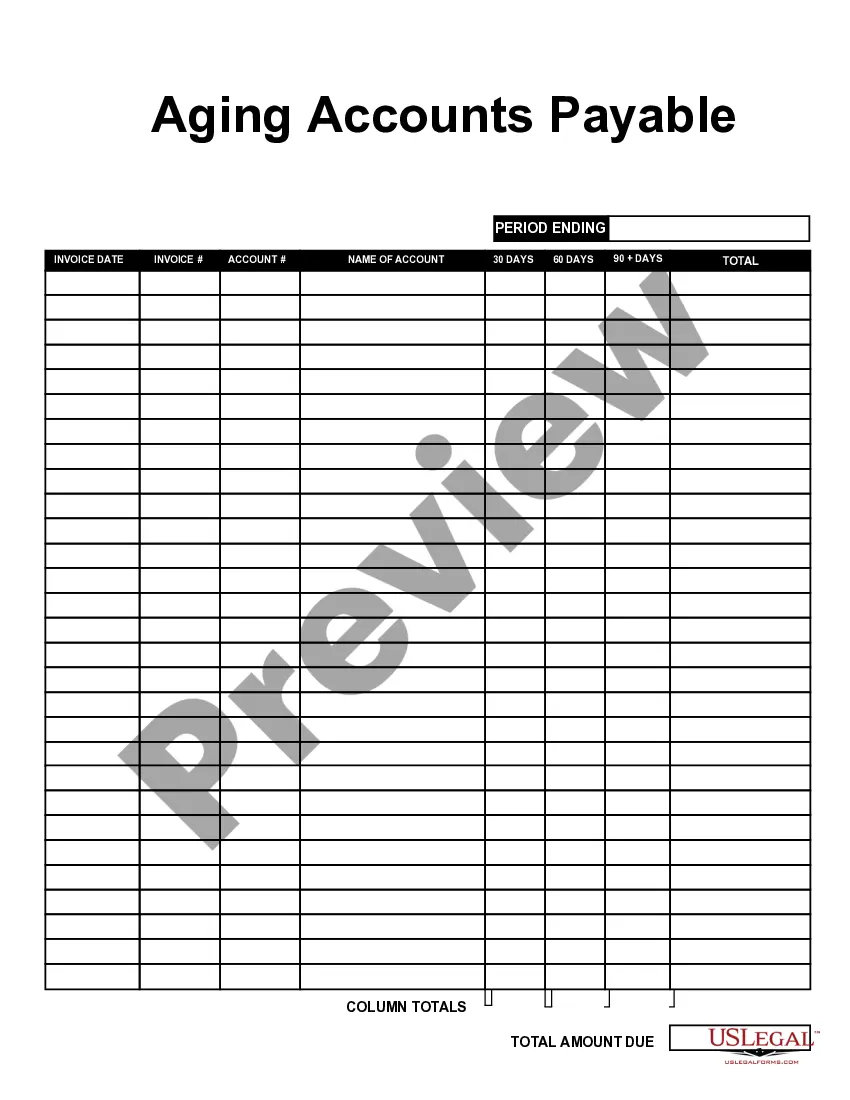
Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable
Description
How to fill out Aging Of Accounts Receivable?
Selecting the optimal legal document template may be a challenge.
Certainly, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how do you locate the legal form you need.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. This service offers a plethora of templates, including the Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable, suitable for both business and personal use.
If the form does not meet your needs, utilize the Search area to find the appropriate form.
- All templates are reviewed by experts and comply with federal and state standards.
- If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click the Download button to obtain the Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable.
- Use your account to browse through the legal documents you may have purchased previously.
- Navigate to the My documents section of your account and obtain another copy of the document you need.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are straightforward instructions you can follow.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/region. You can check the form using the Review button and read the form details to confirm it is suitable for you.
Form popularity
FAQ
To calculate the aging of accounts receivable, first list all outstanding invoices along with their due dates. Then, determine the number of days each invoice is late by subtracting the due date from the current date. By categorizing these amounts into chronological buckets, you create a clear picture of your Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable, empowering you to manage client payments effectively.
The aged receivables detail report displays specific information about outstanding invoices, including customer names, amounts due, and the aging period of each receivable. This report categorizes debts into buckets that represent time frames such as 0-30 days, 31-60 days, and so on. Monitoring your Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable through this detailed report helps prioritize collection efforts effectively.
To run an accounts receivable aging report, access your accounting software and locate the reports area. Select the accounts receivable option and choose 'Aging Report' for details. This report provides a quick snapshot of overdue invoices and is vital for monitoring your Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable efficiently.
Running an accounts receivable aging report in QuickBooks is straightforward. Go to the 'Reports' section and select 'Aging Receivables,' then customize it according to your needs. With just a few clicks, you will have a detailed view of your Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable, facilitating better tracking of overdue payments.
To get aging receivables, first compile a list of your outstanding invoices and categorize them based on the length of time they have been unpaid. This involves reviewing your accounts receivable ledger and using aging methods to group invoices effectively. By calculating your Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable, you gain insights into which accounts need immediate attention, ultimately improving your revenue collection process.
In QuickBooks Online, you can choose between the 'Summary' and 'Detail' aging methods for your aging reports. The Summary method provides an overview of your accounts receivable, categorizing amounts into buckets based on how long they have been outstanding. On the other hand, the Detail method breaks down each transaction, showing you the individual amounts owed. Utilizing these two Wyoming Aging of Accounts Receivable methods helps you monitor customer payment behavior.
To record aging accounts receivable, maintain a detailed log of all outstanding invoices, categorizing them based on the time they have been overdue. This practice enables timely follow-ups on collections and keeps your financial records updated. For a more efficient process, consider using platforms like US Legal Forms to manage your Wyoming aging of accounts receivable effectively.
In QuickBooks, you can generate an accounts receivable aging report by selecting the 'Reports' menu and choosing 'Accounts Receivable Aging'. Customize the report as needed to reflect different aging periods. This tool simplifies tracking overdue accounts, giving businesses in Wyoming better control over their aging of accounts receivable.
To write an accounts receivable aging report, begin by compiling a list of all customer invoices and their due dates. Organize the invoices by age group, providing total amounts for each category. This structured report enables businesses to assess collection efforts related to Wyoming aging of accounts receivable, making it easier to follow up with clients.
To prepare an aging schedule for accounts receivable, start by listing all outstanding invoices and the corresponding due dates. Next, categorize each invoice based on its age. This aging schedule helps stakeholders visualize overdue payments and prioritize collection efforts effectively in the context of Wyoming's aging of accounts receivable.