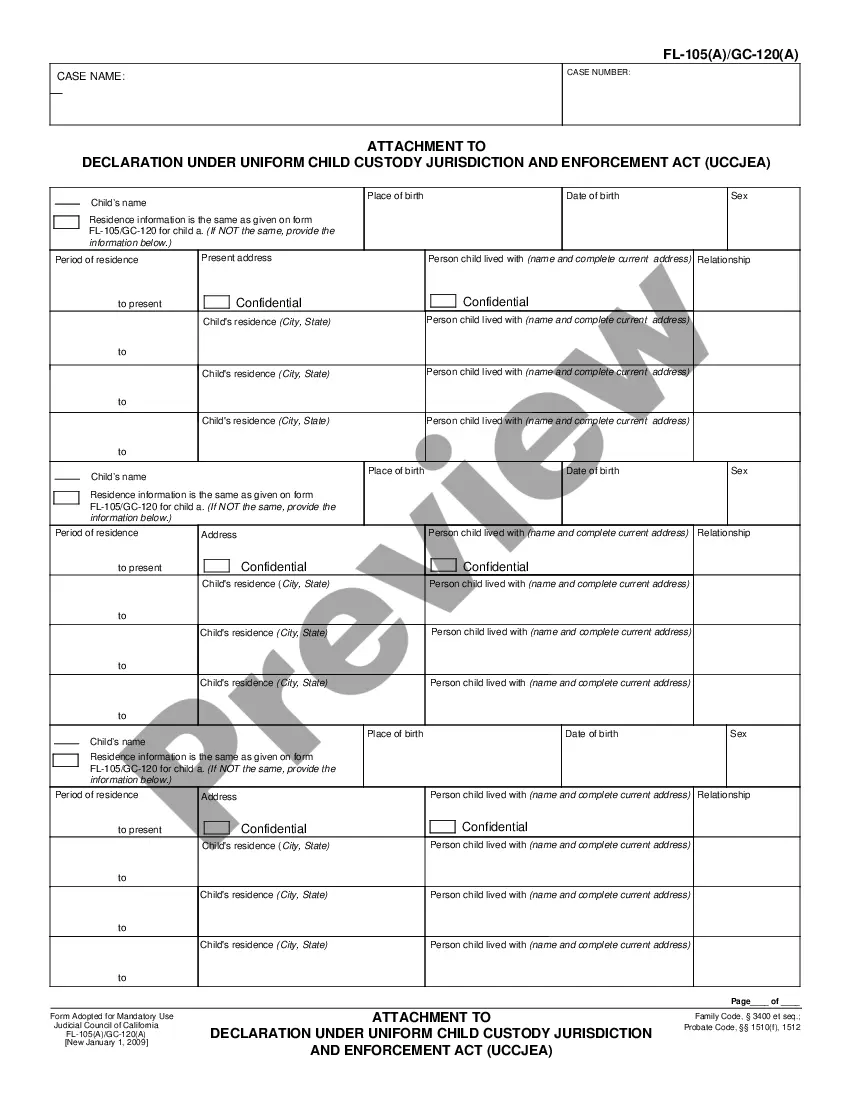
This is an official form from the California Judicial Council, which complies with all applicable laws and statutes. USLF amends and updates the forms as is required by California statutes and law.
The El Monte California Semiannual Report to the Judicial Council on the Use of Noncertified Interpreters provides a comprehensive overview of the utilization and effectiveness of noncertified interpreters within the judicial system. This report aims to assess the impact of noncertified interpreters on court proceedings and the overall access to justice for non-English speaking litigants. The examination of these reports provides valuable insights for policymakers, judges, and court administrators to make informed decisions and improvements in the realm of interpreter services. Key areas covered in the El Monte California Semiannual Report include: 1. Interpreter Utilization: This section focuses on the number of noncertified interpreters employed by the courts and their utilization across various legal proceedings. It examines the frequency of their usage, types of cases involved, and languages requested, highlighting areas of high demand. 2. Language Access: This report delves into the effectiveness and sufficiency of language access services provided by noncertified interpreters. Evaluating the quality and accuracy of interpretation in courtrooms, it identifies the challenges faced by noncertified interpreters and suggests strategies for improvement. 3. Interpreter Training and Certification: The El Monte California Semiannual Report acknowledges the influence of interpreter training programs and the role they play in enhancing the skills and professionalism of noncertified interpreters. It examines the impact of certifications, if any, on the quality of interpretation and discusses potential avenues for expanding training opportunities. 4. Rules and Regulations: This section explores the existing regulations and policies governing the use of noncertified interpreters in California courts. It assesses their effectiveness, identifies any gaps or inconsistencies, and proposes recommendations to ensure consistency and adherence to standards. 5. Stakeholder Feedback: The report includes feedback from judges, attorneys, litigants, and noncertified interpreters themselves, providing valuable perspectives on the strengths and weaknesses of the current system. It captures insights on interpreter competence, cultural sensitivity, and the impact of noncertified interpretation on overall courtroom proceedings. Additionally, specific types of El Monte California Semiannual Reports to the Judicial Council on the Use of Noncertified Interpreters may be categorized based on the specific language(s) involved, such as Spanish, Mandarin, Korean, Vietnamese, or other prevalent languages in the community. These language-specific reports may provide more focused insights and recommendations for improving language access services within each linguistic group.