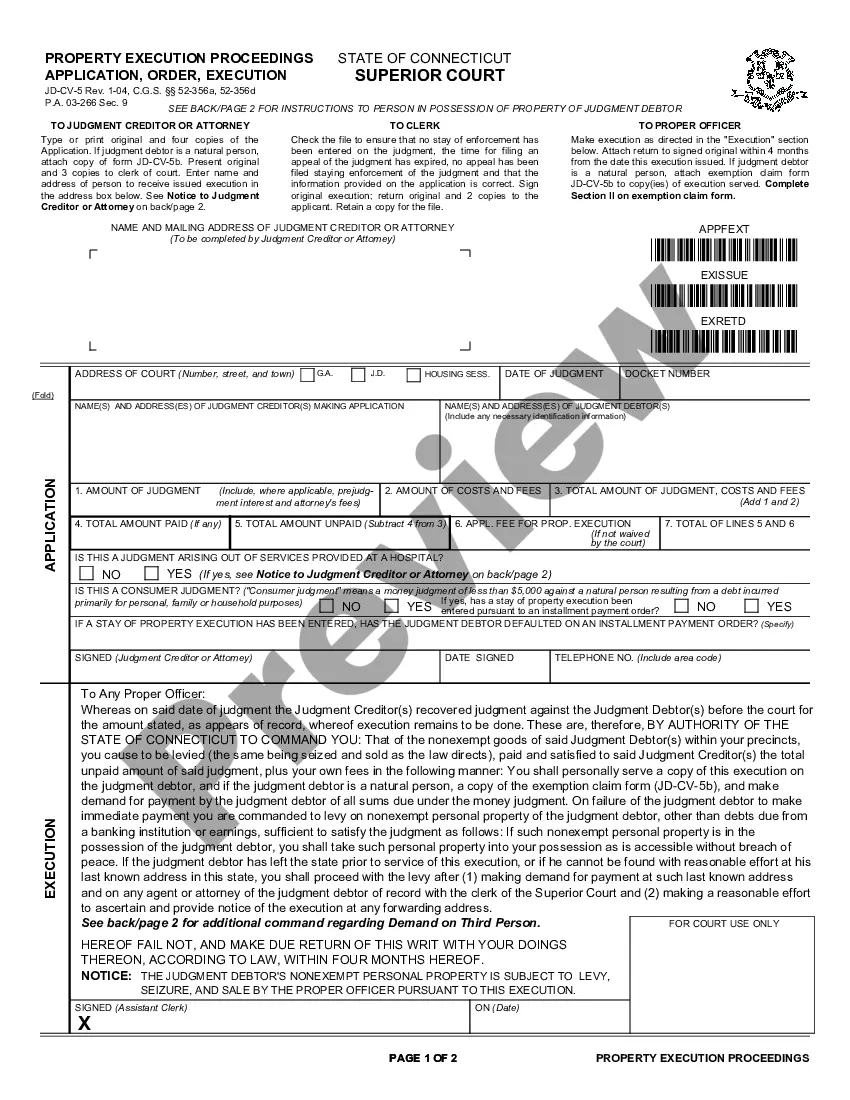
Title: Understanding Gresham Oregon Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion Introduction: In Gresham, Oregon, a Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion refers to the legal response submitted by the defendant in a lawsuit to counter the plaintiff's request for a summary judgment. This opposition aims to challenge the plaintiff's claims and present evidence supporting the defendant's position. Take a closer look at the different types and key elements involved in Gresham Oregon Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion. 1. Detailed analysis of the claims: In a Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion, defendants meticulously dissect the plaintiff's claims, highlighting any factual discrepancies, ambiguities, or misinterpretations. By undertaking an in-depth analysis, defendants aim to demonstrate that the plaintiff has failed to provide sufficient evidence to warrant a summary judgment. 2. Counterarguments and legal defenses: Defendants craft persuasive counterarguments to undermine the plaintiff's assertion that no material facts are genuinely in dispute. They introduce legal defenses relevant to their specific case, such as lack of evidence, statute of limitations, contributory negligence, or presenting alternative interpretations of the facts. 3. Evidence presentation: To refute the plaintiff's claims, defendants include relevant documentation, witness testimonies, expert opinions, and any other admissible evidence. This evidence should be compelling and directly contradict or weaken the plaintiff's case, supporting the defendant's opposition to the summary judgment motion. 4. Supporting case law and precedents: Defendants may bolster their arguments by citing relevant case law and precedents that demonstrate similar legal situations where a summary judgment was denied. By doing so, defendants seek to convince the court that their case should receive the same consideration, highlighting inconsistencies in the plaintiff's legal arguments. 5. Affidavits and expert opinions: Defendants often submit sworn affidavits from relevant parties, including themselves, experts, or witnesses, attesting to specific facts or presenting alternative interpretations. Expert opinions can be introduced to challenge the plaintiff's claims about complex issues in the case, offering further support to the defendant's opposition. 6. Summary of genuine disputes: Within the opposition, defendants provide a clear and concise summary of the genuine disputes of material facts in contention. These summaries outline specific points where the parties disagree, illustrating the existence of legitimate controversies that should be resolved by a trial rather than a summary judgment. In summary, a Gresham Oregon Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion involves a detailed legal argument that challenges the plaintiff's claims while presenting evidence, counterarguments, and legal defenses. By carefully constructing this opposition, defendants aim to convince the court that there are genuine disputes of material facts, warranting further judicial examination through a trial.
Gresham Oregon Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion
Description
How to fill out Gresham Oregon Defendant's Opposition To Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion?
Do you need a reliable and affordable legal forms provider to buy the Gresham Oregon Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion? US Legal Forms is your go-to option.
Whether you require a basic arrangement to set regulations for cohabitating with your partner or a set of forms to move your separation or divorce through the court, we got you covered. Our platform offers more than 85,000 up-to-date legal document templates for personal and company use. All templates that we offer aren’t universal and frameworked based on the requirements of separate state and county.
To download the form, you need to log in account, find the required form, and click the Download button next to it. Please remember that you can download your previously purchased form templates anytime in the My Forms tab.
Is the first time you visit our website? No worries. You can set up an account with swift ease, but before that, make sure to do the following:
- Check if the Gresham Oregon Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion conforms to the laws of your state and local area.
- Go through the form’s description (if available) to find out who and what the form is intended for.
- Start the search over if the form isn’t good for your specific situation.
Now you can create your account. Then select the subscription option and proceed to payment. Once the payment is done, download the Gresham Oregon Defendant's Opposition to Plaintiff's Summary Judgment Motion in any available format. You can get back to the website at any time and redownload the form free of charge.
Getting up-to-date legal forms has never been easier. Give US Legal Forms a go now, and forget about spending hours researching legal papers online for good.
Form popularity
FAQ
21 A defendant wishing to oppose summary judgment has to invoke the procedure set out in Rule 32 (3) which provides it with the following steps to follow, namely; that: (a) he must provide to the plaintiff security to the satisfaction of the Registrar, for any judgment including costs which may be given2 or (b) he
You can defeat the grant of summary judgment by presenting a multi-pronged attack. Don't rely on just lack of discovery (evidence), lack of particularity, or failure to strike affirmative defenses. If you can, point to other weaknesses in your opponent's motion.
If one party to a case has filed a motion with the court, the other side can file an ?opposition.? An ?opposition? is a written statement explaining to the judge why the other side is not entitled to whatever he is asking for in his motion. It is your opportunity to oppose the other side's request.
Any affidavit intended to be used in opposition to the petition shall be filed not less than 5 days before the date fixed for the hearing of the petition, and a copy of the affidavit shall be served on the petitioner or his advocate forthwith.
Any party contemplating a motion for summary judgment must always consider the possibility of a court granting ?reverse summary judgment,? i.e. granting judgment in favor of the responding / opposing party.
A Response or Reply to the Opposing Party's Pleadings is your answer to the opposing party's document filed with the Court. A Response is the initial answering document to a motion while a Reply is the Response filed to a Response.
You must include a summary of the legal basis for your opposition, explain the reason you are opposing the motion, and state what you would like the judge to order.
Is a Summary Judgment A Good Thing? Either a defendant or a plaintiff can request a summary judgment. Although a summary judgment is a favorable result for the motioning party, it can be detrimental for the opponent.
You should draft your own affidavit or affirmation in opposition to the motion. 1 . An affirmation is a statement which is made under penalty of perjury. An affidavit is sworn to before a licensed notary public of the state.