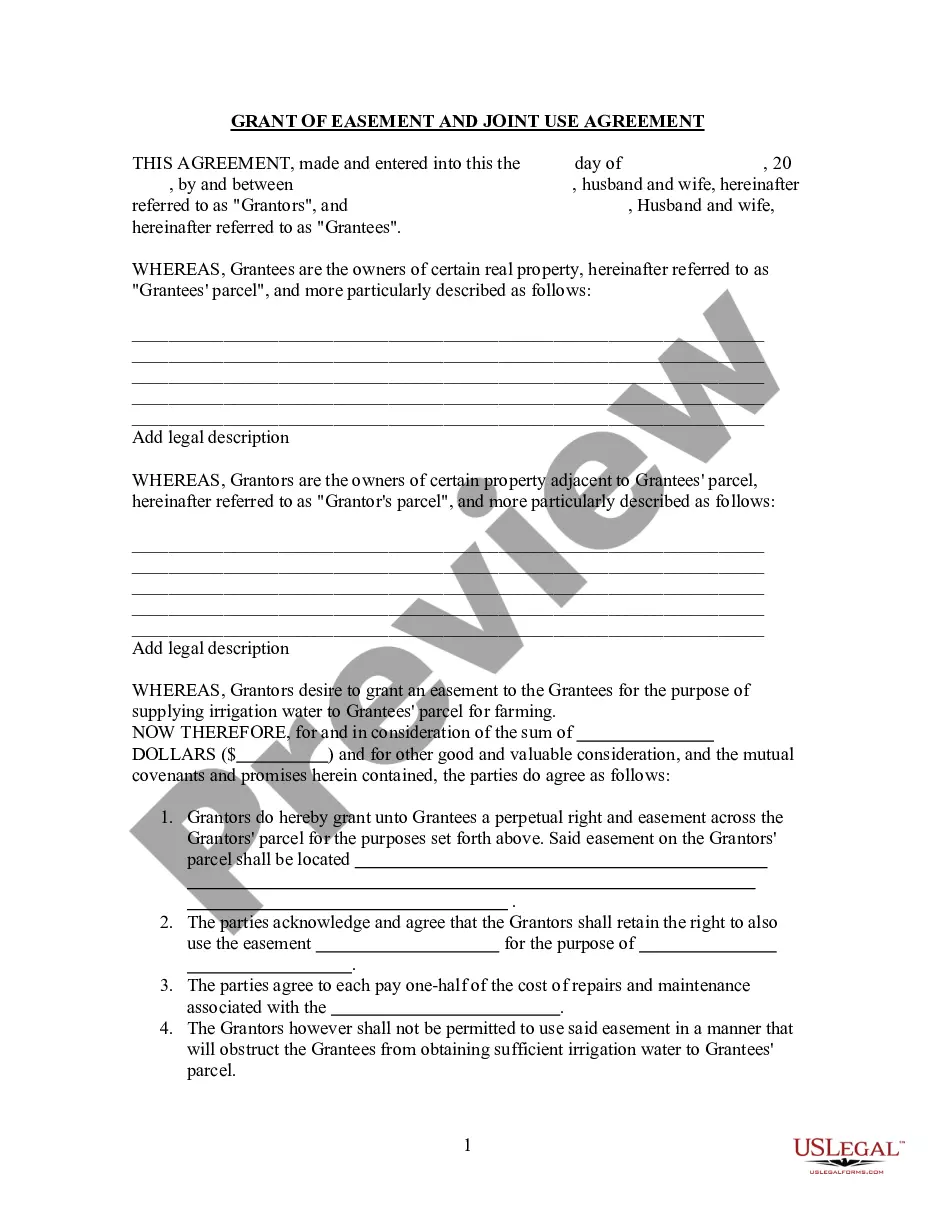
McAllen Texas Notice of Removal is a legal document filed by a defendant in a lawsuit to transfer the case from a state court to a federal court. This procedure is governed by 28 U.S.C. § 1441, which allows defendants to remove cases to a federal court when certain conditions are met. The Notice of Removal in McAllen Texas is typically filed when the defendant believes that the case involves federal questions or if the parties involved are from different states, and the amount in dispute exceeds a certain threshold set by federal law. By requesting removal, the defendant seeks to change the jurisdiction of the case from the state court where it was originally filed to a federal court. There are various types or grounds for filing a McAllen Texas Notice of Removal, including: 1. Federal Question Removal: When the case involves federal laws, regulations, or constitutional issues, the defendant can request removal to the federal court. 2. Diversity Jurisdiction Removal: If the lawsuit is between citizens of different states and the amount in controversy exceeds $75,000, the defendant can seek removal based on diversity jurisdiction. 3. Class Action Fairness Act (Café) RemovalUnderheatedA, class action lawsuits involving a minimum of 100 plaintiffs and an aggregate amount in controversy exceeding $5 million can be removed to federal court. 4. Removal based on Arbitration: If the dispute contains an enforceable arbitration agreement, the defendant can argue that the case should be removed to federal court based on the Federal Arbitration Act. It is important to note that filing a McAllen Texas Notice of Removal requires careful consideration of jurisdictional requirements and legal strategy. Therefore, it is advisable to seek legal counsel in order to accurately determine whether removal is appropriate and to navigate the complex process efficiently. In summary, McAllen Texas Notice of Removal is a legal filing allowing a defendant to transfer a lawsuit from a state court to a federal court. It can be pursued under different grounds such as federal questions, diversity jurisdiction, class action lawsuits, or based on arbitration agreements.
McAllen Texas Notice of Removal
Description
How to fill out McAllen Texas Notice Of Removal?
We consistently aim to reduce or prevent legal complications when navigating intricate legal or financial issues.
To achieve this, we seek attorney services that, typically, are quite expensive.
However, not every legal issue is as intricate as others, and many can be handled by ourselves.
US Legal Forms is an online repository of current DIY legal documents covering a range of needs from wills and powers of attorney to articles of incorporation and petitions for dissolution.
Just Log In to your account and click the Get button adjacent to it. If you misplace the form, you can always retrieve it again from the My documents section. The procedure is just as simple even if you are not familiar with the platform! You can set up your account in just a few minutes. Ensure that the McAllen Texas Notice of Removal complies with the rules and regulations applicable to your state and region. Additionally, it is essential to review the form’s description (if available), and if you notice any inconsistencies with what you initially required, look for a different form. Once you have confirmed that the McAllen Texas Notice of Removal is appropriate for your situation, you can select the subscription plan and proceed with the payment. Then, you can download the form in any available file format. We have assisted millions of individuals over our 24 years in providing ready-to-customize and current legal forms. Leverage US Legal Forms now to conserve time and resources!
- Our platform empowers you to manage your matters independently without the necessity of consulting an attorney.
- We offer access to legal document templates that may not always be widely available.
- Our templates are tailored to specific states and regions, greatly simplifying the search process.
- Utilize US Legal Forms whenever you require obtaining and downloading the McAllen Texas Notice of Removal or any other document conveniently and securely.
Form popularity
FAQ
To file a removal to federal court, you must prepare a notice of removal and submit it along with the required documents to the appropriate federal court. Ensure that you include a copy of all pleadings and process served to you. Filing a thorough McAllen Texas Notice of Removal can prevent delays and complications in your case. Services like US Legal Forms can help you navigate this process efficiently.
Yes, a local defendant can remove a case to federal court under specific conditions, such as diversity jurisdiction. However, it's important to note that if the case arises solely from events occurring in that defendant's state, removal might not be possible. Understanding the nuances of a McAllen Texas Notice of Removal will clarify your options. Legal services can provide support in determining the best course of action.
A notice of removal must be filed whenever a defendant believes the case is eligible for federal jurisdiction. This usually occurs within 30 days of receiving the complaint. It is essential to prepare a McAllen Texas Notice of Removal as soon as possible to avoid missing any deadlines. To ensure all requirements are met, consulting legal help or using platforms designed for legal forms can be very beneficial.
In general, you have 30 days from the date of service of the complaint to file a notice of removal to federal court. This timeline is critical and adhering to it is necessary to maintain your right to remove the case. Missing this deadline could jeopardize your ability to pursue a McAllen Texas Notice of Removal. Using resources like US Legal Forms can help you track deadlines and prepare your documents timely.
Removal jurisdiction allows a defendant to move a case from state court to federal court. The process involves filing a notice of removal promptly after being served with the initial complaint. Different rules may apply depending on your case, which is why understanding the McAllen Texas Notice of Removal is important. Seeking legal assistance can help ensure that all steps are followed correctly and efficiently.
To remove a case to federal court, you must file a notice of removal with the federal court. Make sure your case meets the criteria for federal jurisdiction, such as diversity of citizenship or a federal question. A properly filed McAllen Texas Notice of Removal is crucial to this process, ensuring you adhere to the necessary legal standards. Resources like US Legal Forms can guide you through the paperwork required.
Rule 355 in Texas pertains to the removal process in lawsuits. It allows defendants to remove cases from state court to federal court under certain circumstances. Understanding this rule is essential for anyone considering a McAllen Texas Notice of Removal, as it outlines specific criteria that must be met for removal. Utilizing professional resources or legal platforms can simplify navigating these requirements.
A removal notice is a formal document filed by a party seeking to transfer a case from state court to federal court. This notice outlines the grounds for removal, such as jurisdictional issues or federal questions. The McAllen Texas Notice of Removal includes specific details about the case and must comply with procedural rules. Using legal services, like those provided by uslegalforms, makes understanding and drafting this document much simpler.
In general, only defendants—both individuals and entities—have the right to file a notice of removal. This procedure allows defendants to transfer a case from state to federal court if specific conditions are met. It is vital to adhere to deadlines and procedural rules when completing the McAllen Texas Notice of Removal. Utilizing resources from platforms like uslegalforms can help guide you through this legal process.
For a case to be eligible for removal, it must meet specific jurisdictional criteria set by federal law. Most importantly, there must be diversity of citizenship or a federal question. The amount in controversy must also exceed a certain threshold, generally $75,000 for diversity cases. If you're considering a McAllen Texas Notice of Removal, be sure to understand these requirements thoroughly to avoid complications.