An easement gives one party the right to go onto another party's property. That property may be owned by a private person, a business entity, or a group of owners. Utilities often get easements that allow them to run pipes or phone lines beneath private property. Easements may be obtained for access to another property, called "access and egress", use of spring water, entry to make repairs on a fence or slide area, drive cattle across and other uses. The easement is a real property interest, but separate from the legal title of the owner of the underlying land.
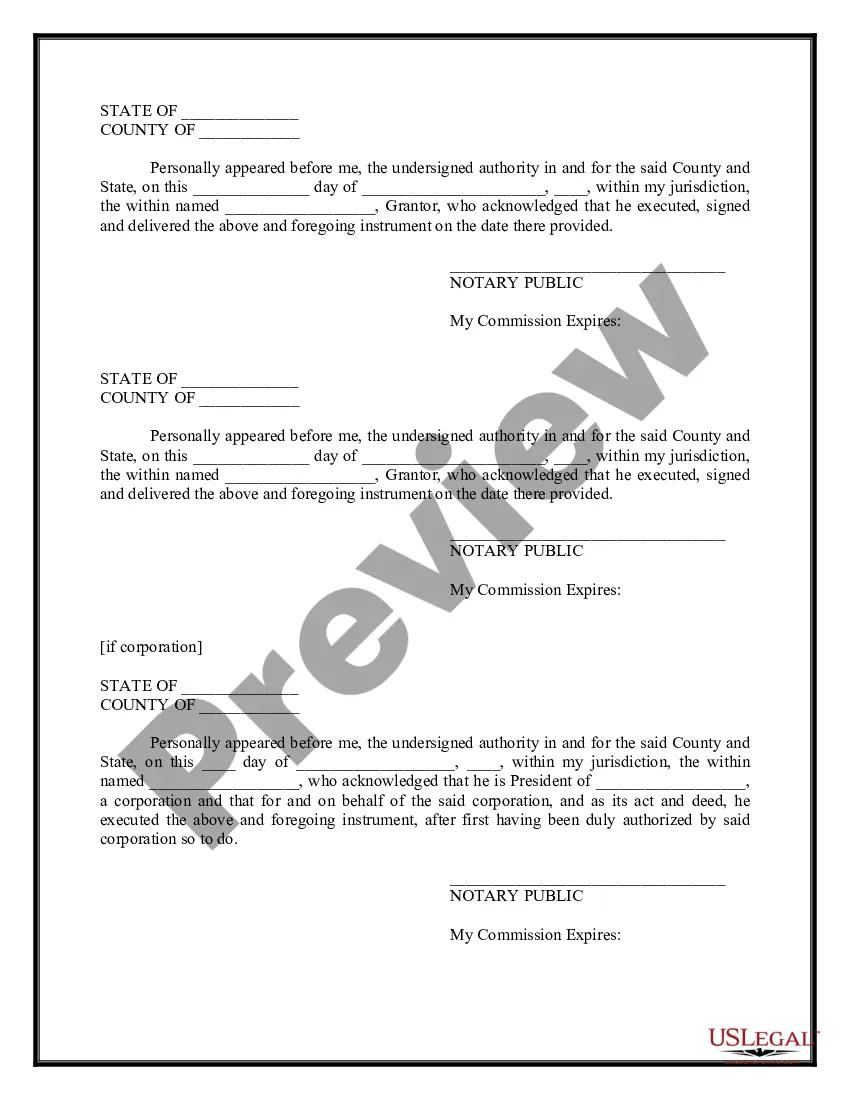
The Oakland Michigan General Right-of-Way Instrument is a legal document that outlines the rights and conditions of land use for public infrastructure projects within Oakland County, Michigan. It serves as a contractual agreement between the local government, typically the county or municipality, and the affected property owner. The purpose of the General Right-of-Way Instrument is to establish and define the legal framework for allowing the public to access and utilize specific portions of private property for the construction, operation, and maintenance of essential public services and facilities. These may include roads, sidewalks, utilities (such as water, sewer, and gas lines), drainage systems, telecommunications, and other public improvements. The General Right-of-Way Instrument specifies the terms and conditions of the right-of-way, as well as the obligations and responsibilities of both parties involved. It generally emphasizes the following key aspects: 1. Identification and description of the property boundaries: The document provides a detailed description of the land being granted for public use. This includes accurate surveys, legal descriptions, and maps to delineate the exact boundaries of the right-of-way. 2. Scope and purpose: The instrument defines the specific purpose for which the right-of-way is being granted, such as the construction of a new road or the installation of utilities. It outlines the intended use, dimensions, and restrictions associated with the right-of-way. 3. Easements and encroachments: The General Right-of-Way Instrument addresses any necessary easements or encroachments required for the installation, maintenance, and repair of public utilities. This ensures that necessary access is granted, while also protecting the property rights of the landowner. 4. Compensation and damages: In cases where land is taken for public use, the instrument outlines the compensation and damages payable to the property owner. This includes regulations pertaining to appraisal processes and fair market value assessments. 5. Construction and maintenance requirements: The document specifies the standards and regulations to be followed during the construction and maintenance of public infrastructure within the right-of-way. This ensures that the work is performed safely, efficiently, and without causing excessive inconvenience to property owners. 6. Termination and abandonment: The General Right-of-Way Instrument establishes the conditions under which the right-of-way can be terminated or abandoned. This may include situations such as the discontinuation of public services or changes in land use regulations. Different types of Oakland Michigan General Right-of-Way Instruments may exist depending on the specific purpose and characteristics of the public project. Some examples include Road Right-of-Way Instruments, Utility Right-of-Way Instruments, and Sidewalk Right-of-Way Instruments. Each type caters to a particular aspect of public infrastructure development and has unique requirements and specifications. Overall, the Oakland Michigan General Right-of-Way Instrument plays a crucial role in facilitating the efficient and lawful establishment of public infrastructure projects while ensuring that the rights of property owners are appropriately protected.