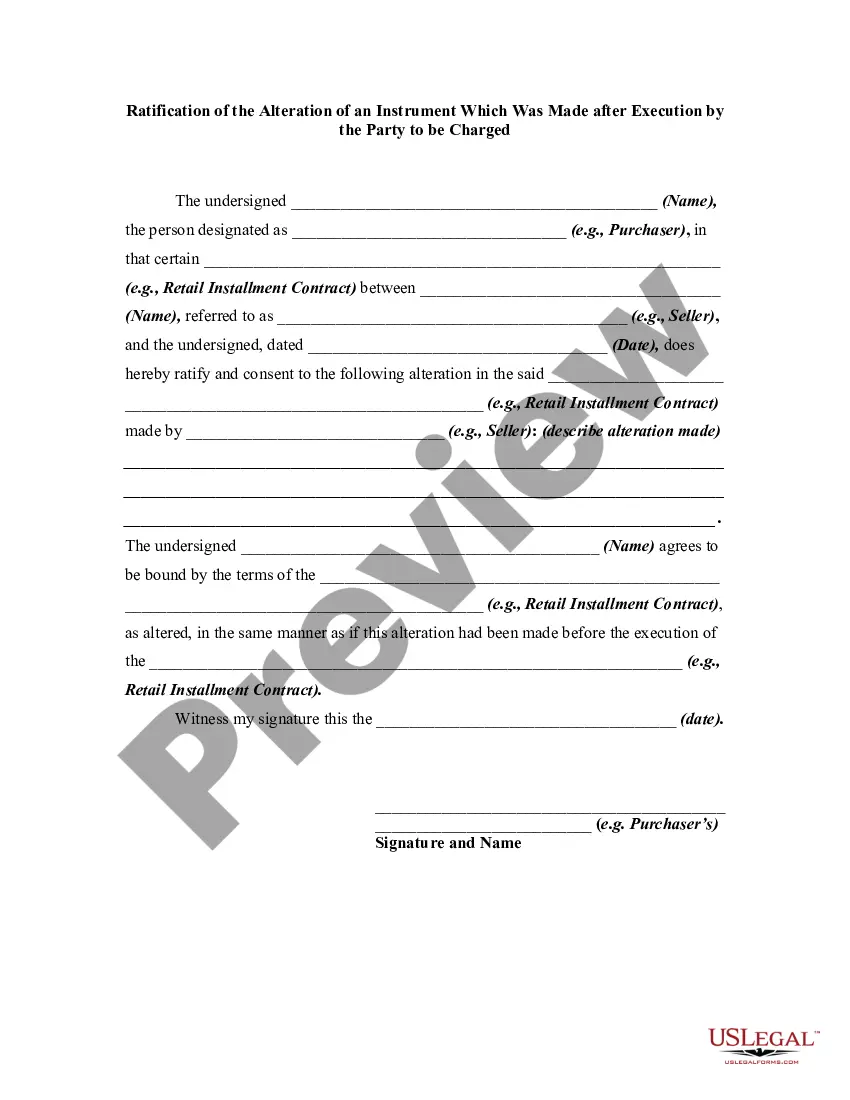
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought.
If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Collin Texas Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument: In Collin County, Texas, the ratification of an alteration of an instrument, which was made after execution by the party to be charged, refers to a legal process that validates changes made to a document or contract after it has been signed or agreed upon by the party involved. This ratification is essential to ensure the enforceability and legality of the modified instrument. When an alteration occurs on a document without the consent or knowledge of the party to be charged, it could potentially nullify or affect the terms agreed upon. However, if the party later acknowledges and accepts the modifications, they can ratify the altered instrument, granting it legal validity. This process safeguards the rights and intentions of all parties involved. Keywords: Collin Texas, ratification, alteration of an instrument, execution, party to be charged, legal process, document, contract, signed, agreed upon, enforceability, legality, modified instrument, alteration without consent, nullify, affect terms, acknowledge, accept, ratify, legal validity, rights, intentions. Different Types of Collin Texas Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged: 1. Express Ratification: When the party to be charged openly and explicitly declares their acceptance of the altered instrument, either through writing or verbal communication. 2. Implied Ratification: This type of ratification occurs when the party to be charged acts in a manner that implies their acceptance of the modified instrument. For example, if they continue to conduct business based on the altered terms or accept benefits from the changes made. 3. Partial Ratification: In some instances, the party to be charged may ratify some parts of the altered instrument but not others. This partial ratification makes only the accepted modifications valid while excluding the rest. 4. Conditional Ratification: This occurs when the party to be charged ratifies the altered instrument with certain conditions or limitations. The ratification is contingent upon specific criteria being met or fulfilled. 5. Subsequent Agreement: Rather than ratifying outright, the party to be charged and the party responsible for the alteration may enter into a subsequent agreement addressing the changes made and confirming their mutual consent. This is an alternative way to grant the modifications legal validity. By understanding the process of Collin Texas ratification of an alteration of an instrument after execution by the party to be charged, individuals can navigate the legal requirements necessary to validate modified documents or contracts effectively.