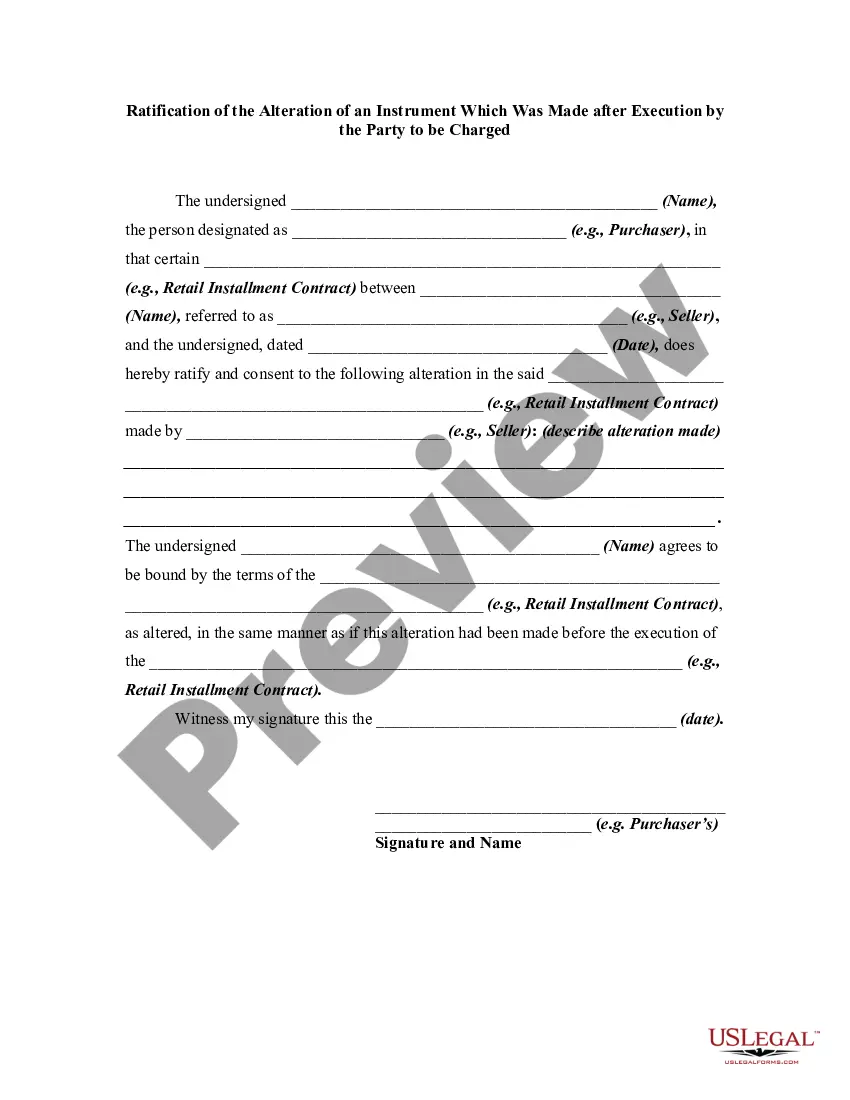
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought.
If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Fulton Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged In Fulton, Georgia, the ratification of the alteration of an instrument made after execution by the party to be charged refers to the legal process by which changes or modifications made to a legally binding document are authorized by the concerned party after the document has been executed or signed. This ratification is crucial to ensure the validity and enforceability of the altered instrument. Key elements and keywords related to Fulton Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged include: 1. Instrument Alteration: It refers to any changes, amendments, or modifications made to a legal instrument, such as a contract, deed, or promissory note, after it has been executed by the signing parties. 2. Ratification: It refers to the act of affirming, approving, or authorizing an action or decision after it has been taken. In this context, ratification applies to accepting and recognizing the alterations made to the instrument by the party to be charged. 3. Execution: Execution involves the formal signing and delivery of a legal instrument. Once executed, the document becomes legally binding, and any subsequent changes must go through the ratification process. Types of Fulton Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged: 1. Monetary Alteration Ratification: This type of ratification specifically relates to modifications made to monetary terms within a financial instrument, like a loan agreement or a promissory note. It ensures that changes to the amount, interest rates, payment schedules, or any other monetary provisions are properly authorized. 2. Contractual Alteration Ratification: This type of ratification applies when changes are made to contractual terms after execution. It covers alterations to clauses, obligations, responsibilities, timelines, or any other essential elements of a contract. The party to be charged must formally ratify these changes to uphold their legal validity. 3. Real Estate Alteration Ratification: This type of ratification pertains to changes made to real estate-related instruments, like deeds, contracts, or agreements. It ensures that modifications affecting property ownership, boundaries, easements, restrictions, or any other real estate-specific provisions are duly authorized. Overall, Fulton, Georgia, necessitates the ratification of any alterations made to instruments after execution by the party to be charged to maintain the legal enforceability of such modifications. Whether related to monetary matters, contractual terms, or real estate provisions, the ratification process plays a crucial role in validating and recognizing the changes made to legal instruments.
Fulton Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged In Fulton, Georgia, the ratification of the alteration of an instrument made after execution by the party to be charged refers to the legal process by which changes or modifications made to a legally binding document are authorized by the concerned party after the document has been executed or signed. This ratification is crucial to ensure the validity and enforceability of the altered instrument. Key elements and keywords related to Fulton Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged include: 1. Instrument Alteration: It refers to any changes, amendments, or modifications made to a legal instrument, such as a contract, deed, or promissory note, after it has been executed by the signing parties. 2. Ratification: It refers to the act of affirming, approving, or authorizing an action or decision after it has been taken. In this context, ratification applies to accepting and recognizing the alterations made to the instrument by the party to be charged. 3. Execution: Execution involves the formal signing and delivery of a legal instrument. Once executed, the document becomes legally binding, and any subsequent changes must go through the ratification process. Types of Fulton Georgia Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged: 1. Monetary Alteration Ratification: This type of ratification specifically relates to modifications made to monetary terms within a financial instrument, like a loan agreement or a promissory note. It ensures that changes to the amount, interest rates, payment schedules, or any other monetary provisions are properly authorized. 2. Contractual Alteration Ratification: This type of ratification applies when changes are made to contractual terms after execution. It covers alterations to clauses, obligations, responsibilities, timelines, or any other essential elements of a contract. The party to be charged must formally ratify these changes to uphold their legal validity. 3. Real Estate Alteration Ratification: This type of ratification pertains to changes made to real estate-related instruments, like deeds, contracts, or agreements. It ensures that modifications affecting property ownership, boundaries, easements, restrictions, or any other real estate-specific provisions are duly authorized. Overall, Fulton, Georgia, necessitates the ratification of any alterations made to instruments after execution by the party to be charged to maintain the legal enforceability of such modifications. Whether related to monetary matters, contractual terms, or real estate provisions, the ratification process plays a crucial role in validating and recognizing the changes made to legal instruments.