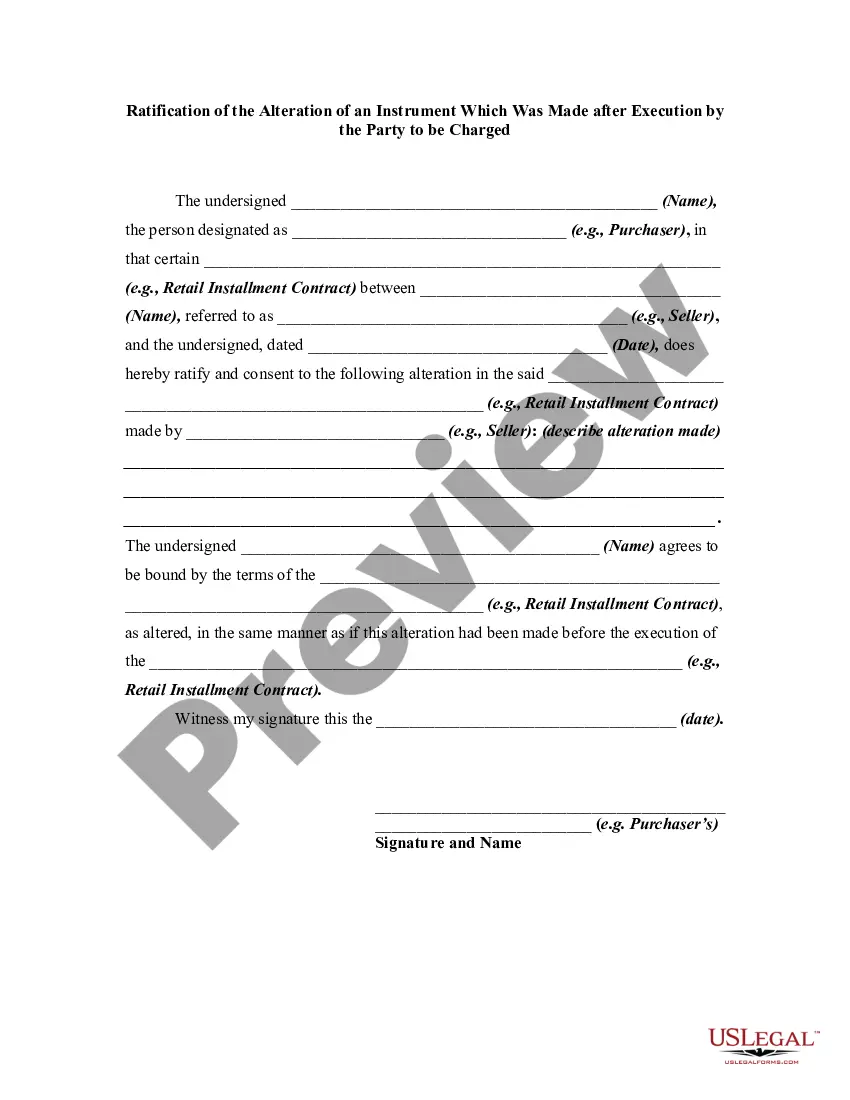
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought. If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
Phoenix Arizona Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a legal procedure that deals with validating any changes made to a legal document or instrument after it has been executed by the party involved. This process ensures that any modifications made to the original document are authorized and acknowledged by the party to be charged. In Phoenix, Arizona, the ratification of alterations in legal instruments is an important step in maintaining the integrity of contractual agreements or other legal documents. It involves the party who made the alterations formally recognizing and accepting responsibility for the changes made. This is done to prevent any potential disputes or misunderstandings that may arise due to unauthorized modifications. The ratification process may involve various types, depending on the nature of the altered instrument. These may include: 1. Ratification of an Altered Contract: This type of ratification is specific to contractual agreements that have been modified after execution. Parties involved in the contract must go through the ratification process to validate the changes and ensure mutual agreement on the altered terms. 2. Ratification of Altered Legal Documentation: This type of ratification refers to alterations made to legal documents such as wills, deeds, or powers of attorney. The party to be charged must confirm and acknowledge the changes made to these documents to maintain their legal validity. 3. Ratification of Altered Financial Instruments: In cases where financial instruments, such as promissory notes or bills of exchange, have been altered after execution, the ratification process is necessary to verify the amendments made by the party to be charged. In Phoenix, Arizona, the ratification of alterations is often facilitated through legal channels, such as involving an attorney or going through a formal court process. This ensures that the ratification holds legal weight and can be enforced if needed. To conclude, Phoenix Arizona Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a vital legal process to validate and authorize any modifications made to legal documents or instruments. It ensures clarity, prevents disputes, and upholds the legal validity of the revised agreements.Phoenix Arizona Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a legal procedure that deals with validating any changes made to a legal document or instrument after it has been executed by the party involved. This process ensures that any modifications made to the original document are authorized and acknowledged by the party to be charged. In Phoenix, Arizona, the ratification of alterations in legal instruments is an important step in maintaining the integrity of contractual agreements or other legal documents. It involves the party who made the alterations formally recognizing and accepting responsibility for the changes made. This is done to prevent any potential disputes or misunderstandings that may arise due to unauthorized modifications. The ratification process may involve various types, depending on the nature of the altered instrument. These may include: 1. Ratification of an Altered Contract: This type of ratification is specific to contractual agreements that have been modified after execution. Parties involved in the contract must go through the ratification process to validate the changes and ensure mutual agreement on the altered terms. 2. Ratification of Altered Legal Documentation: This type of ratification refers to alterations made to legal documents such as wills, deeds, or powers of attorney. The party to be charged must confirm and acknowledge the changes made to these documents to maintain their legal validity. 3. Ratification of Altered Financial Instruments: In cases where financial instruments, such as promissory notes or bills of exchange, have been altered after execution, the ratification process is necessary to verify the amendments made by the party to be charged. In Phoenix, Arizona, the ratification of alterations is often facilitated through legal channels, such as involving an attorney or going through a formal court process. This ensures that the ratification holds legal weight and can be enforced if needed. To conclude, Phoenix Arizona Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged is a vital legal process to validate and authorize any modifications made to legal documents or instruments. It ensures clarity, prevents disputes, and upholds the legal validity of the revised agreements.