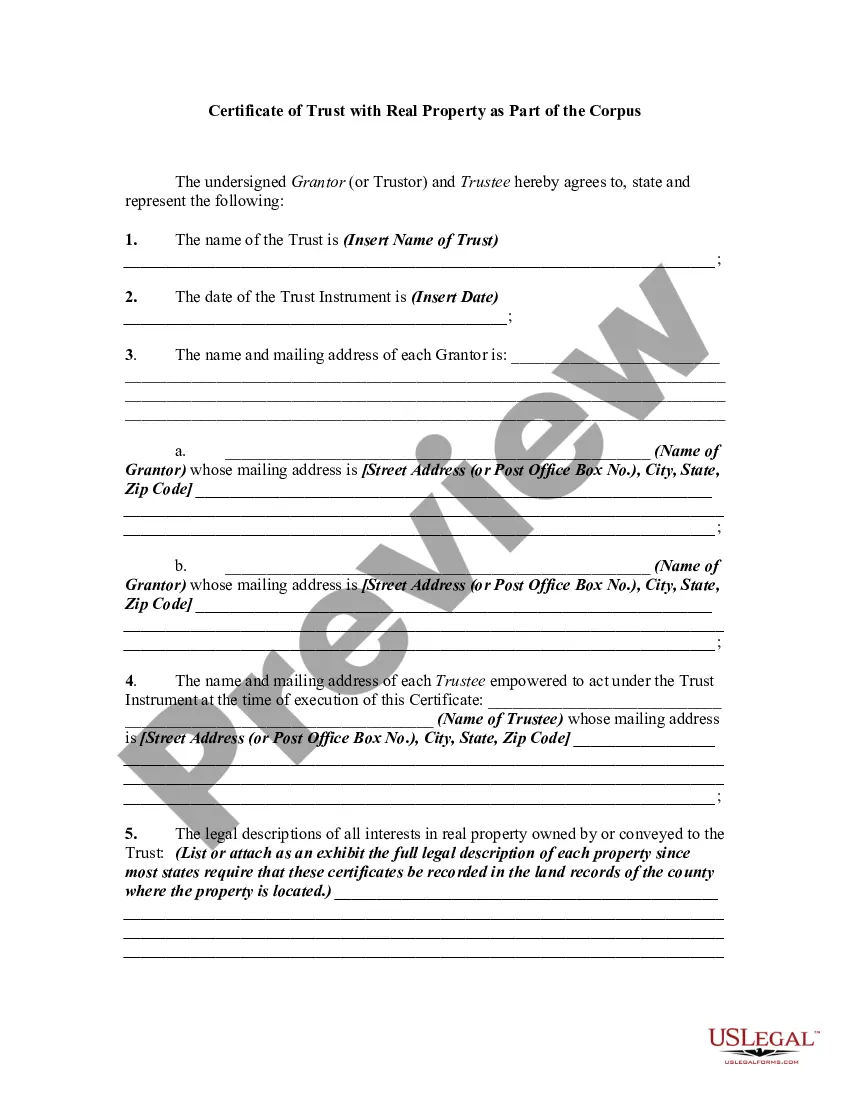
The Hennepin Minnesota Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee is a legal document that serves as a testamentary proof of the existence of a trust and designates the successor trustee who will take over the administration of the trust upon the original trustee's incapacity, resignation, or death. This certificate is vital in establishing the trust's validity and providing necessary information to financial institutions, third parties, and individuals involved in trust-related matters. The Hennepin Minnesota Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee typically includes essential details and keywords related to the trust arrangement. These may vary depending on the specific trust and the preferences of the settler (creator of the trust). Some common information and keywords found in the certificate are: 1. Trust Identification: The certificate usually begins with the identification of the trust, including its formal name, date of establishment, and identification number. This information ensures accurate identification of the trust, which is crucial for legal and administrative purposes. 2. Trustee Details: The certificate presents the name, address, and contact information of the current trustee, highlighting their authority to act on behalf of the trust during their tenure. This information helps in establishing the trustee's role and authority in trust-related matters. 3. Successor Trustee Appointment: The certificate specifies the name, address, and contact information of the designated successor trustee who will step in to manage the trust in the event of the current trustee's incapacity or incapability to continue with their duties. This appointment ensures a smooth transition of trust administration, avoiding potential uncertainties or disputes. 4. Powers and Responsibilities: The certificate may outline the powers and authorities granted to the successor trustee, providing details about their ability to manage and distribute trust assets, make investment decisions, and handle any legal or financial obligations of the trust. This section ensures that the successor trustee understands their fiduciary duties and responsibilities. 5. Execution and Notarization: The certificate is typically dated and signed by the current trustee, acknowledging the accuracy of the information provided. In some cases, it may require notarization or witnessing to validate its authenticity. It is worth noting that the Hennepin County, Minnesota jurisdiction may have specific requirements or additional elements that need to be included in the Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee. These requirements may be influenced by state laws or local regulations, so it is vital to consult with a legal professional or refer to official guidelines to ensure compliance. Overall, the Hennepin Minnesota Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee serves as a crucial document in the trust administration process, providing assurance to stakeholders and facilitating the seamless transfer of trustee responsibilities.
Hennepin Minnesota Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee
Description
How to fill out Hennepin Minnesota Certificate Of Trust For Successor Trustee?
If you need to get a reliable legal paperwork supplier to find the Hennepin Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee, look no further than US Legal Forms. No matter if you need to launch your LLC business or manage your asset distribution, we got you covered. You don't need to be knowledgeable about in law to find and download the appropriate form.
- You can browse from over 85,000 forms arranged by state/county and situation.
- The self-explanatory interface, variety of learning materials, and dedicated support team make it easy to find and complete different papers.
- US Legal Forms is a trusted service offering legal forms to millions of customers since 1997.
Simply type to look for or browse Hennepin Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee, either by a keyword or by the state/county the document is created for. After locating needed form, you can log in and download it or save it in the My Forms tab.
Don't have an account? It's easy to get started! Simply locate the Hennepin Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee template and take a look at the form's preview and short introductory information (if available). If you're confident about the template’s terminology, go ahead and hit Buy now. Create an account and select a subscription plan. The template will be instantly available for download as soon as the payment is completed. Now you can complete the form.
Taking care of your law-related matters doesn’t have to be expensive or time-consuming. US Legal Forms is here to demonstrate it. Our extensive variety of legal forms makes these tasks less expensive and more reasonably priced. Set up your first company, organize your advance care planning, draft a real estate contract, or complete the Hennepin Certificate of Trust for Successor Trustee - all from the comfort of your sofa.
Sign up for US Legal Forms now!