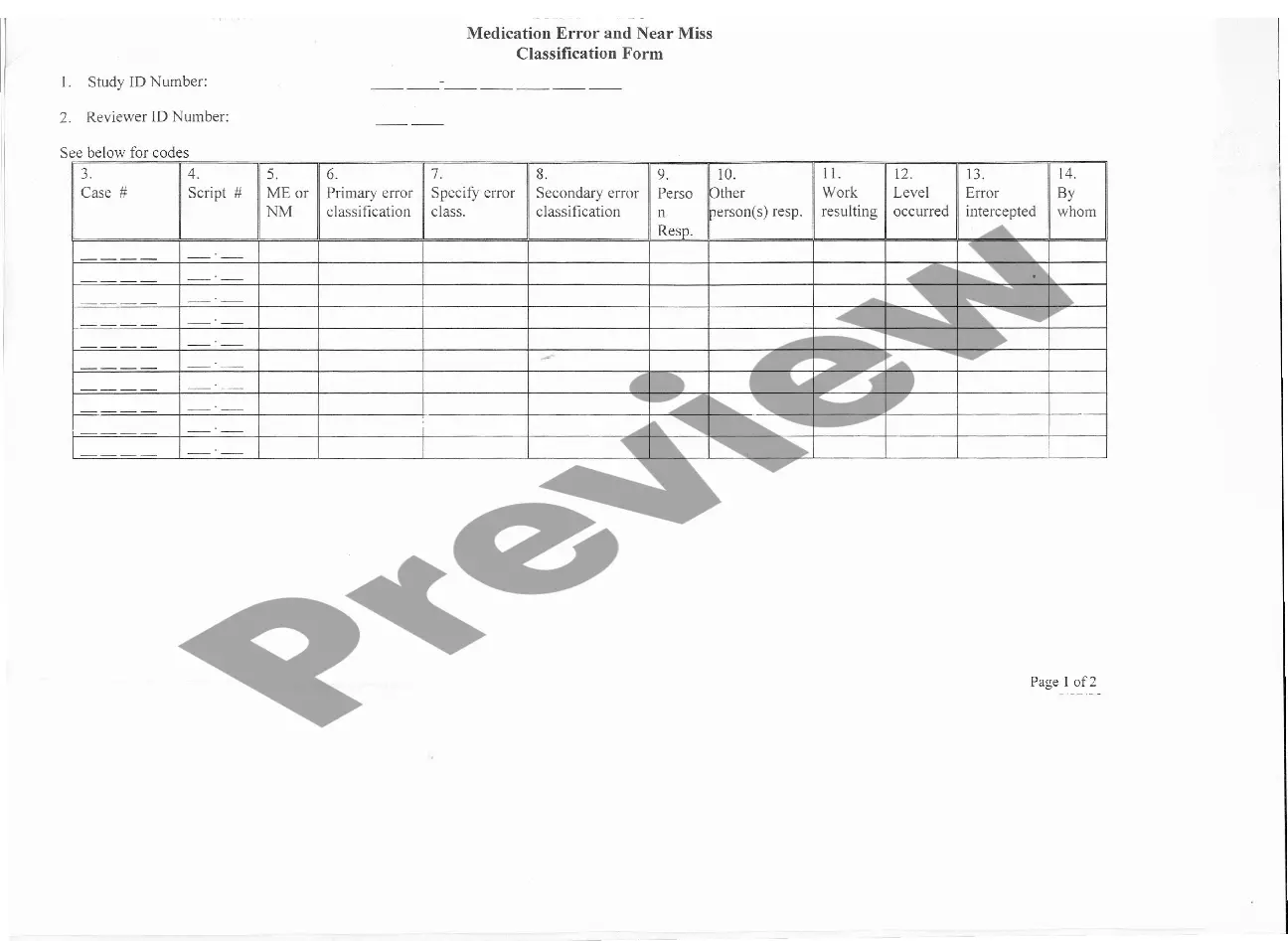
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.
Maricopa Arizona Medication Data Form — Medication Error and Near Miss Classification is a crucial tool used in healthcare settings to ensure patient safety and optimize medication management. It plays a vital role in documenting and analyzing medication errors and near misses, aiding in the development of strategies to prevent future incidents and improve patient care. Keywords: Maricopa Arizona Medication Data Form, medication error, near miss classification, patient safety, medication management, documenting, analyzing, strategies, prevent incidents, improve patient care. The Maricopa Arizona Medication Data Form — Medication Error and Near Miss Classification consists of various sections aimed at collecting comprehensive data regarding medication errors and near misses. Here are some potential types of sections/forms that may be included: 1. Incident Details Section: This section collects information about the incident, including the date and time it occurred, the individuals involved, the medication(s) involved, the location of the incident, and a brief description of what happened. 2. Error Classification Section: Here, specific error classification systems are utilized to categorize the type of medication error that occurred. Common classification systems include the National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention (NCC MERE) Index or the Medication Error Index (ME). 3. Contributing Factors Section: This section aims to identify factors that played a role in the medication error or near miss. It may include factors such as medication labeling issues, communication breakdowns, inadequate staff training, equipment malfunctions, or environmental factors. 4. Severity Assessment Section: In this section, the severity of the medication error or near miss is assessed. Severity levels can range from minor, requiring no medical intervention, to major, resulting in significant patient harm or even death. This assessment helps prioritize necessary corrective actions. 5. Root Cause Analysis Section: This part focuses on analyzing the underlying causes of the incident, going beyond immediate factors. It may involve investigating systemic issues, organizational culture, workflow processes, or human factors in order to create effective prevention measures. 6. Prevention Strategies Section: Based on the collected data, this section provides a platform to document proposed strategies, interventions, and recommendations aimed at preventing similar incidents in the future. These strategies may encompass improvements in medication procedures, staff training, technology implementation, or policy revisions. By utilizing the Maricopa Arizona Medication Data Form — Medication Error and Near Miss Classification, healthcare providers foster a culture of safety, transparency, and continuous improvement. The data collected through this form facilitates evidence-based decision-making and helps healthcare organizations enhance their medication practices, ultimately ensuring better patient outcomes.Maricopa Arizona Medication Data Form — Medication Error and Near Miss Classification is a crucial tool used in healthcare settings to ensure patient safety and optimize medication management. It plays a vital role in documenting and analyzing medication errors and near misses, aiding in the development of strategies to prevent future incidents and improve patient care. Keywords: Maricopa Arizona Medication Data Form, medication error, near miss classification, patient safety, medication management, documenting, analyzing, strategies, prevent incidents, improve patient care. The Maricopa Arizona Medication Data Form — Medication Error and Near Miss Classification consists of various sections aimed at collecting comprehensive data regarding medication errors and near misses. Here are some potential types of sections/forms that may be included: 1. Incident Details Section: This section collects information about the incident, including the date and time it occurred, the individuals involved, the medication(s) involved, the location of the incident, and a brief description of what happened. 2. Error Classification Section: Here, specific error classification systems are utilized to categorize the type of medication error that occurred. Common classification systems include the National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention (NCC MERE) Index or the Medication Error Index (ME). 3. Contributing Factors Section: This section aims to identify factors that played a role in the medication error or near miss. It may include factors such as medication labeling issues, communication breakdowns, inadequate staff training, equipment malfunctions, or environmental factors. 4. Severity Assessment Section: In this section, the severity of the medication error or near miss is assessed. Severity levels can range from minor, requiring no medical intervention, to major, resulting in significant patient harm or even death. This assessment helps prioritize necessary corrective actions. 5. Root Cause Analysis Section: This part focuses on analyzing the underlying causes of the incident, going beyond immediate factors. It may involve investigating systemic issues, organizational culture, workflow processes, or human factors in order to create effective prevention measures. 6. Prevention Strategies Section: Based on the collected data, this section provides a platform to document proposed strategies, interventions, and recommendations aimed at preventing similar incidents in the future. These strategies may encompass improvements in medication procedures, staff training, technology implementation, or policy revisions. By utilizing the Maricopa Arizona Medication Data Form — Medication Error and Near Miss Classification, healthcare providers foster a culture of safety, transparency, and continuous improvement. The data collected through this form facilitates evidence-based decision-making and helps healthcare organizations enhance their medication practices, ultimately ensuring better patient outcomes.