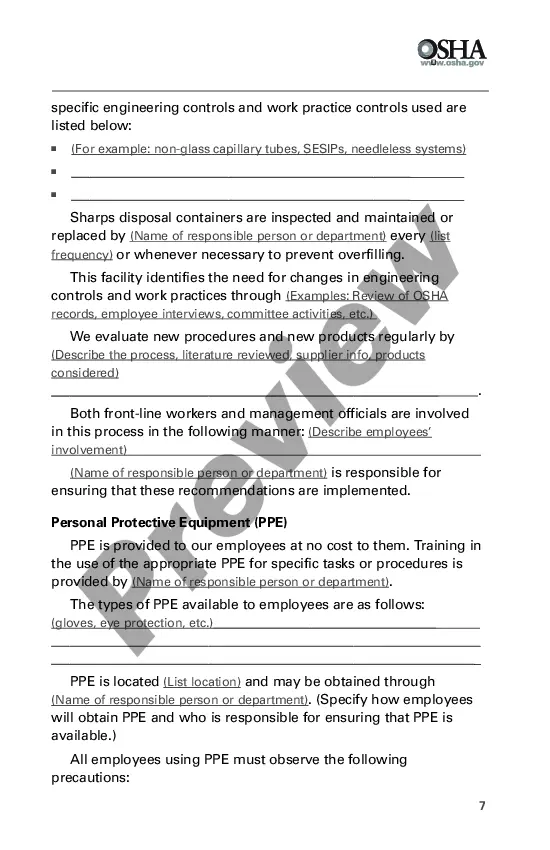
San Diego California Model Plans and Programs for the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens and Hazard Communications Standards
Description
How to fill out Model Plans And Programs For The OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens And Hazard Communications Standards?
Generating legal documents is essential in the modern era.
However, it is not always necessary to obtain expert assistance to create some of them from the ground up, such as the San Diego Model Plans and Programs for the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens and Hazard Communications Standards, utilizing a service like US Legal Forms.
US Legal Forms offers over 85,000 documents to choose from across various categories, including living wills, property agreements, and divorce filings.
Navigate to the My documents section to re-download the document.
If you are already a subscriber to US Legal Forms, locate the corresponding San Diego Model Plans and Programs for the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens and Hazard Communications Standards, Log In to your account, and obtain it. Naturally, our website cannot fully replace a lawyer. If you face an especially complex issue, we suggest seeking legal advice to review your form before signing and submitting it. With over 25 years in the industry, US Legal Forms has become a preferred resource for numerous legal documents for millions of clients. Join them today and effortlessly obtain your state-specific paperwork!
- Review the document's preview and outline (if available) to grasp a general understanding of what you can expect after acquiring the form.
- Confirm that the document you select is tailored to your state/county/region since local laws can influence the validity of certain records.
- Investigate related document templates or restart the search to locate the correct document.
- Click Buy now and set up your account. If you have an account already, opt to Log In.
- Select the method for payment and purchase the San Diego Model Plans and Programs for the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens and Hazard Communications Standards.
- Choose to save the form template in any available file format.
Form popularity
FAQ
The BBP standard requires the use of UP, and extends UP to protect workers against pathogens found in saliva during dental procedures and body fluids in situations where it is difficult or impossible to differentiate between body fluids (e.g., vomit mixed with blood).
What is the Bloodborne Pathogens Standard? OSHA's Bloodborne Pathogens Standard (29 CFR 1910.1030) as amended pursuant to the 2000 Needlestick Safety and Prevention Act, is a regulation that prescribes safeguards to protect workers against health hazards related to bloodborne pathogens.
Universal precautions shall be observed to prevent contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials. Under circumstances in which differentiation between body fluid types is difficult or impossible, all body fluids shall be considered potentially infectious materials.
The Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan is designed to minimize risks to the University community from exposure to human blood, blood products, and other potentially infectious materials, and to meet regulatory expectations mandated by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
The Bloodborne Pathogens standard (29 CFR 1910.1030) and CDC's recommended standard precautions both include personal protective equipment, such as gloves, gowns, masks, eye protection (e.g., goggles), and face shields, to protect workers from exposure to infectious diseases.
There are many bloodborne pathogens that could put employees at risk of infection in the workplace. This course highlights three of the bloodborne pathogens of most concern that could be encountered. These are the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Hepatitis B Virus (HBV), and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV).
Contact the Office of Risk Management for questions. Step 1: Required Personal Protective Equipment.Step 2: Equipment.Step 3: Decontamination Procedures.Step 4: Disposal.Step 5: Decontaminate Re-useable Equipment.Step 6: Wash Your Hands.
Medical records for employees with occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens include the employee's name, social security number, and hepatitis B vaccination status, including dates of hepatitis B vaccination and any medical records relative to the employee's ability to receive the vaccination.
Exposure control plan - A written plan outlining processes and procedures to prevent and correct exposure of potential infectious diseases and provide employee training.
An exposure control plan addresses the worksite hazards; everything from your chemical inventory, processes, maintenance activities, as well as physical hazards that may pose an exposure risk.