Cook Illinois Checklist for Protecting Trade Secret Information is a comprehensive guide that emphasizes the importance of safeguarding confidential business information to maintain a competitive edge. This checklist offers a systematic approach to identify, categorize, and protect trade secrets from unauthorized use, disclosure, or theft. By following the Cook Illinois Checklist, organizations can mitigate the risk of losing valuable intellectual property. The main types of Cook Illinois Checklists for Protecting Trade Secret Information are as follows: 1. Identification Checklist: This checklist assists businesses in recognizing and delineating what constitutes a trade secret within their organization. It helps identify proprietary information, such as formulas, algorithms, customer lists, business strategies, or technical specifications, that holds significant commercial value. 2. Classification Checklist: This checklist focuses on evaluating and categorizing trade secrets based on their level of importance and sensitivity. It aids in prioritizing resources for safeguarding trade secrets and allows businesses to implement appropriate protective measures based on the value associated with each trade secret. 3. Security Checklist: This checklist outlines a range of security measures to protect trade secrets. It includes physical security measures like access controls, secure storage, visitor policies, and video surveillance. Additionally, it covers digital security aspects like encryption, firewalls, secure networks, strong passwords, and user access restrictions. 4. Employee Training Checklist: This checklist addresses the need for training employees to understand the value of trade secrets and their role in protecting them. It covers best practices for maintaining secrecy, emphasizing the use of confidentiality agreements, and ensuring employees are aware of their obligations to protect trade secrets. 5. Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) Checklist: This checklist involves the creation and implementation of robust non-disclosure agreements. It provides comprehensive guidance on drafting legally binding NDAs that protect trade secrets during collaborations, partnerships, or other business relationships. It covers critical clauses, confidentiality obligations, dispute resolutions, and penalties for non-compliance. 6. Incident Response Checklist: This checklist assists organizations in creating an effective incident response plan to address potential trade secret breaches. It includes steps to follow in the event of a suspected or confirmed breach, like conducting internal investigations, notifying appropriate authorities, engaging legal counsel, and taking corrective actions to prevent further damage. By meticulously following the Cook Illinois Checklist for Protecting Trade Secret Information, businesses can instill a culture of secrecy, reduce the risk of trade secret misappropriation, and safeguard their intellectual property, ensuring long-term success in the competitive business landscape.
Cook Illinois Checklist for Protecting Trade Secret Information
Description
How to fill out Cook Illinois Checklist For Protecting Trade Secret Information?
Preparing legal documentation can be burdensome. In addition, if you decide to ask an attorney to draft a commercial contract, papers for proprietorship transfer, pre-marital agreement, divorce paperwork, or the Cook Checklist for Protecting Trade Secret Information, it may cost you a fortune. So what is the best way to save time and money and draw up legitimate documents in total compliance with your state and local regulations? US Legal Forms is a great solution, whether you're searching for templates for your personal or business needs.
US Legal Forms is biggest online library of state-specific legal documents, providing users with the up-to-date and professionally verified templates for any scenario gathered all in one place. Consequently, if you need the latest version of the Cook Checklist for Protecting Trade Secret Information, you can easily locate it on our platform. Obtaining the papers requires a minimum of time. Those who already have an account should check their subscription to be valid, log in, and pick the sample by clicking on the Download button. If you haven't subscribed yet, here's how you can get the Cook Checklist for Protecting Trade Secret Information:
- Look through the page and verify there is a sample for your area.
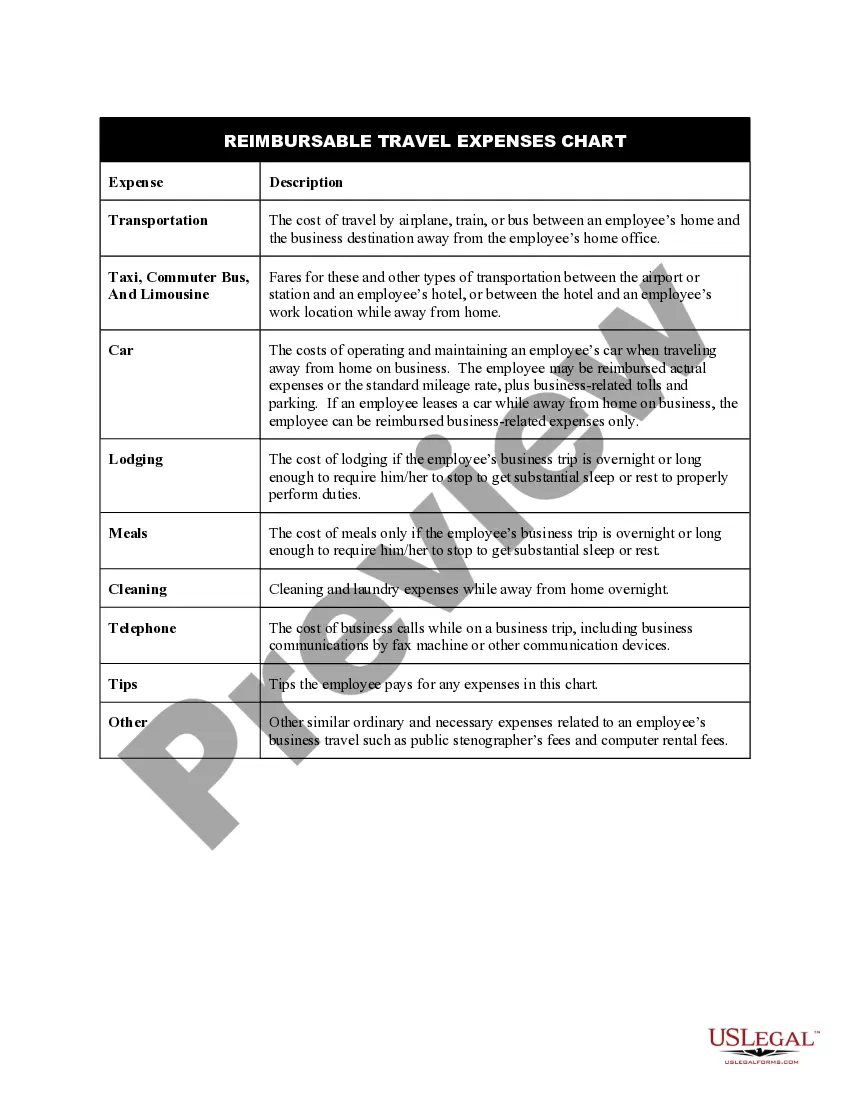
- Check the form description and use the Preview option, if available, to ensure it's the template you need.
- Don't worry if the form doesn't suit your requirements - look for the correct one in the header.
- Click Buy Now once you find the required sample and pick the best suitable subscription.
- Log in or sign up for an account to pay for your subscription.
- Make a payment with a credit card or through PayPal.
- Opt for the file format for your Cook Checklist for Protecting Trade Secret Information and download it.
When done, you can print it out and complete it on paper or import the samples to an online editor for a faster and more convenient fill-out. US Legal Forms enables you to use all the documents ever purchased multiple times - you can find your templates in the My Forms tab in your profile. Give it a try now!
Form popularity
FAQ
Even in this new environment, companies should still implement basic steps to protect trade secrets: (1) restrict access to specific information to those who need to know; (2) employ nondisclosure agreements (NDAs) with workers and business partners; (3) advise and train new hires that the company does not want and
The most common and most effective way to protect trade secrets is through use of nondisclosure agreements (NDAs). Courts have repeatedly reiterated that the use of nondisclosure agreements is the most important way to maintain the secrecy of confidential information.
Below we discuss the three elements of a trade secret, listed above. (1) The information is secret.(2) The information confers a competitive advantage.(3) The information is subject to reasonable efforts to keep it secret.
Popular examples of trade secrets include the recipe for Coca-Cola and the formula for WD-40. Trade secrets may also include items that an individual or company has not chosen to patent yet, such as a new plant hybrid or mechanical invention.
Trade secrets are intellectual property (IP) rights on confidential information which may be sold or licensed. In general, to qualify as a trade secret, the information must be: commercially valuable because it is secret, be known only to a limited group of persons, and.
To be legally considered a trade secret in the United States, a company must make a reasonable effort in concealing the information from the public; the secret must intrinsically have economic value, and the trade secret must contain information.
To qualify as a trade secret, the information in question must meet two essential criteria. First, the information must attain its value from the fact that it is not generally known. Second, the owner of that information must take reasonable efforts to maintain its secrecy.
Information that can be kept as a trade secret includes formulas, patterns, compilations, programs, devices, methods, techniques, or processes. Some examples of trade secrets include customer lists and manufacturing processes. The economic value of the information can be actual or potential.
The following tips are for businesses that wish to protect their trade secrets: Identify What Needs Protection.Label Documents That Contain Protected Information.Monitor Where Information is Stored.Secure Computers.Maintain Secrecy With Outside Vendors.Provide Adequate Security.Limit Public Access to the Company.