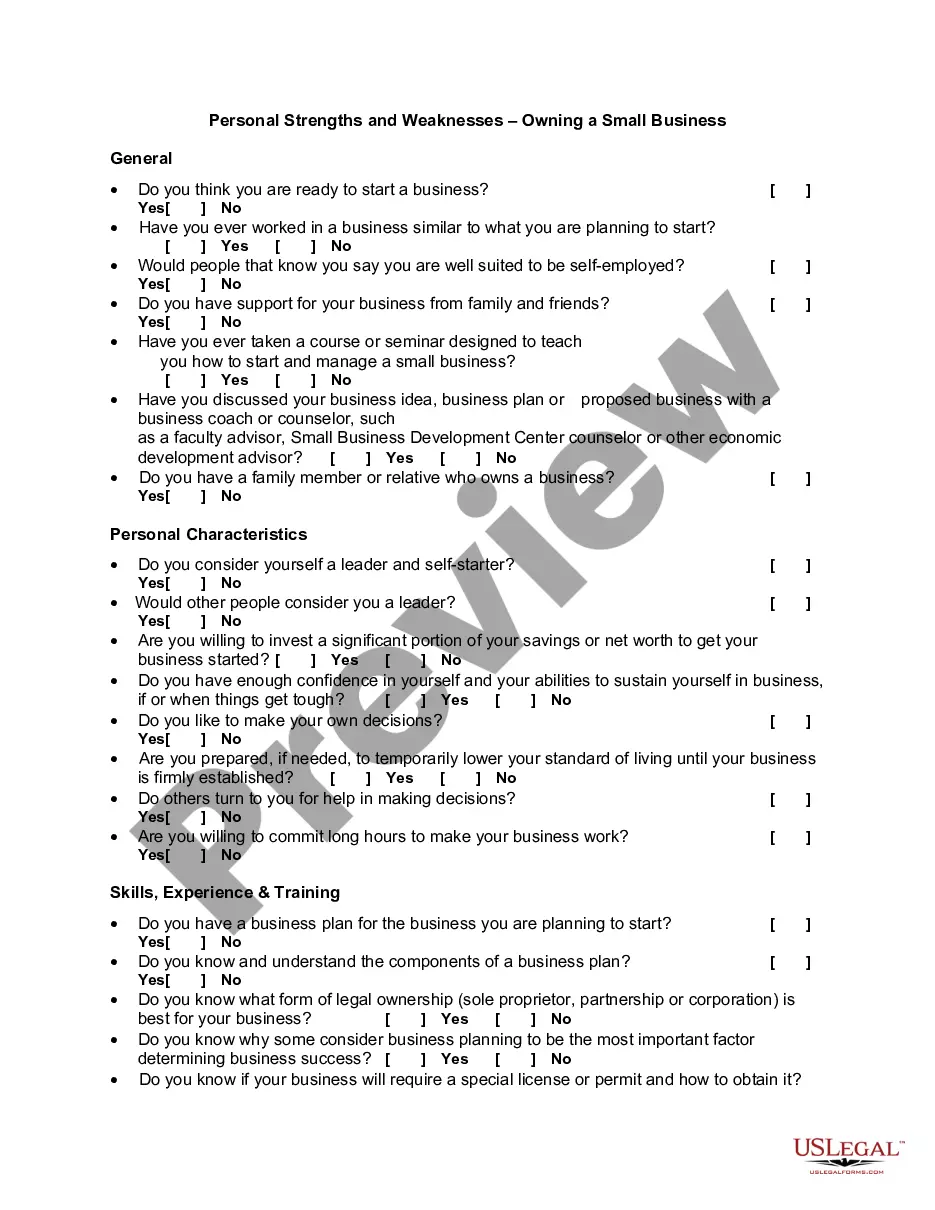
Full text and statutory guidelines for the Insurers Rehabilitation and Liquidation Model Act.
The Cuyahoga Ohio Insurers Rehabilitation and Liquidation Model Act (Cuyahoga Ohio Act) is a legal framework designed to address the rehabilitation and liquidation of insurance companies operating in the state of Ohio, United States. This act is an essential tool for regulating the insurance industry and protecting policyholders and claimants in case of insolvency or financial instability of insurance companies. The Cuyahoga Ohio Act provides a detailed set of procedures and guidelines that must be followed when an insurer faces financial difficulties or becomes insolvent. It aims to ensure the orderly and fair disposition of the insurer's assets, liabilities, and obligations, while protecting the interests of policyholders and claimants. The act offers a systematic approach to handle the rehabilitation and liquidation process efficiently, minimizing disruptions to policyholders, claimants, and the insurance market as a whole. Key features of the Cuyahoga Ohio Insurers Rehabilitation and Liquidation Model Act include: 1. Rehabilitation Process: The act outlines the steps to rehabilitate financially troubled insurers, ensuring they have an opportunity to restore their financial stability while protecting the interests of policyholders. This may involve a comprehensive assessment of the insurer's financial condition, the development of a rehabilitation plan, and the appointment of a rehabilitation receiver. 2. Liquidation Process: If rehabilitation is not feasible or in the best interest of policyholders and claimants, the Cuyahoga Ohio Act provides a well-defined liquidation process. This involves the appointment of a liquidation receiver who is responsible for managing and disposing of the insurer's assets in an orderly manner. 3. Claims Handling: The act establishes mechanisms for the fair and efficient handling of policyholders' and claimants' claims during the rehabilitation or liquidation process. It ensures that valid and unpaid claims are addressed, while fraudulent or excessive claims are appropriately investigated and denied. 4. Priority of Distribution: The act specifies the priority of distribution of the insurer's assets, ensuring that claims of policyholders, employees, administrative expenses, and other essential obligations are prioritized over other creditors. 5. Cooperation with Other States: The Cuyahoga Ohio Act promotes cooperation among insurance regulators in different states, facilitating the efficient handling of cross-border insurer insolvencies and ensuring consistency in the treatment of policyholders and claimants. It's important to note that the Cuyahoga Ohio Act is a model act, meaning that it serves as a template for individual states to adopt and tailor to their specific needs. Therefore, there may be variations of this act in different states, which are commonly known as "Insurance Rehabilitation and Liquidation Acts" or "Insurers Rehabilitation and Liquidation Model Acts." These acts generally share similar principles and objectives but may differ in certain provisions to conform to varying state laws and regulations.The Cuyahoga Ohio Insurers Rehabilitation and Liquidation Model Act (Cuyahoga Ohio Act) is a legal framework designed to address the rehabilitation and liquidation of insurance companies operating in the state of Ohio, United States. This act is an essential tool for regulating the insurance industry and protecting policyholders and claimants in case of insolvency or financial instability of insurance companies. The Cuyahoga Ohio Act provides a detailed set of procedures and guidelines that must be followed when an insurer faces financial difficulties or becomes insolvent. It aims to ensure the orderly and fair disposition of the insurer's assets, liabilities, and obligations, while protecting the interests of policyholders and claimants. The act offers a systematic approach to handle the rehabilitation and liquidation process efficiently, minimizing disruptions to policyholders, claimants, and the insurance market as a whole. Key features of the Cuyahoga Ohio Insurers Rehabilitation and Liquidation Model Act include: 1. Rehabilitation Process: The act outlines the steps to rehabilitate financially troubled insurers, ensuring they have an opportunity to restore their financial stability while protecting the interests of policyholders. This may involve a comprehensive assessment of the insurer's financial condition, the development of a rehabilitation plan, and the appointment of a rehabilitation receiver. 2. Liquidation Process: If rehabilitation is not feasible or in the best interest of policyholders and claimants, the Cuyahoga Ohio Act provides a well-defined liquidation process. This involves the appointment of a liquidation receiver who is responsible for managing and disposing of the insurer's assets in an orderly manner. 3. Claims Handling: The act establishes mechanisms for the fair and efficient handling of policyholders' and claimants' claims during the rehabilitation or liquidation process. It ensures that valid and unpaid claims are addressed, while fraudulent or excessive claims are appropriately investigated and denied. 4. Priority of Distribution: The act specifies the priority of distribution of the insurer's assets, ensuring that claims of policyholders, employees, administrative expenses, and other essential obligations are prioritized over other creditors. 5. Cooperation with Other States: The Cuyahoga Ohio Act promotes cooperation among insurance regulators in different states, facilitating the efficient handling of cross-border insurer insolvencies and ensuring consistency in the treatment of policyholders and claimants. It's important to note that the Cuyahoga Ohio Act is a model act, meaning that it serves as a template for individual states to adopt and tailor to their specific needs. Therefore, there may be variations of this act in different states, which are commonly known as "Insurance Rehabilitation and Liquidation Acts" or "Insurers Rehabilitation and Liquidation Model Acts." These acts generally share similar principles and objectives but may differ in certain provisions to conform to varying state laws and regulations.