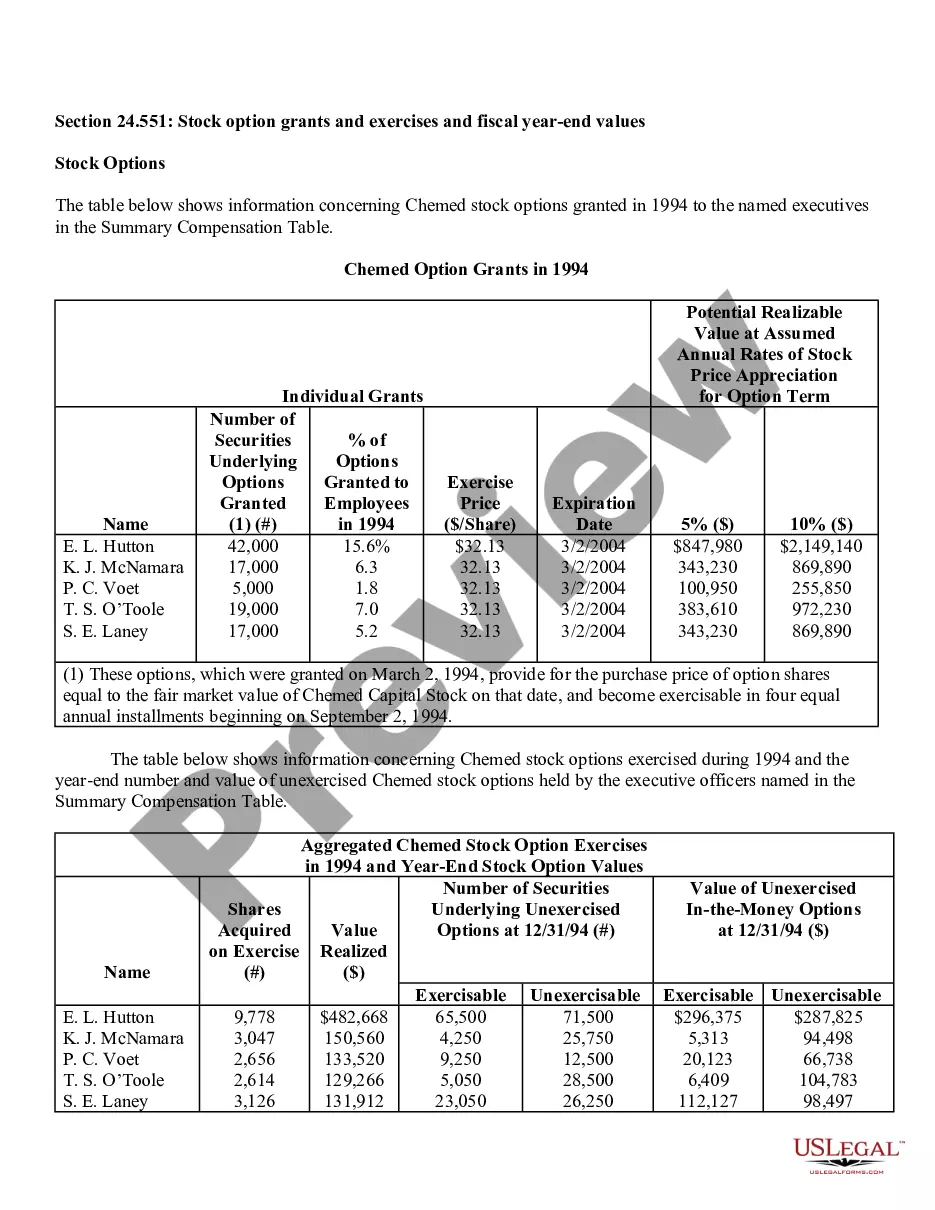
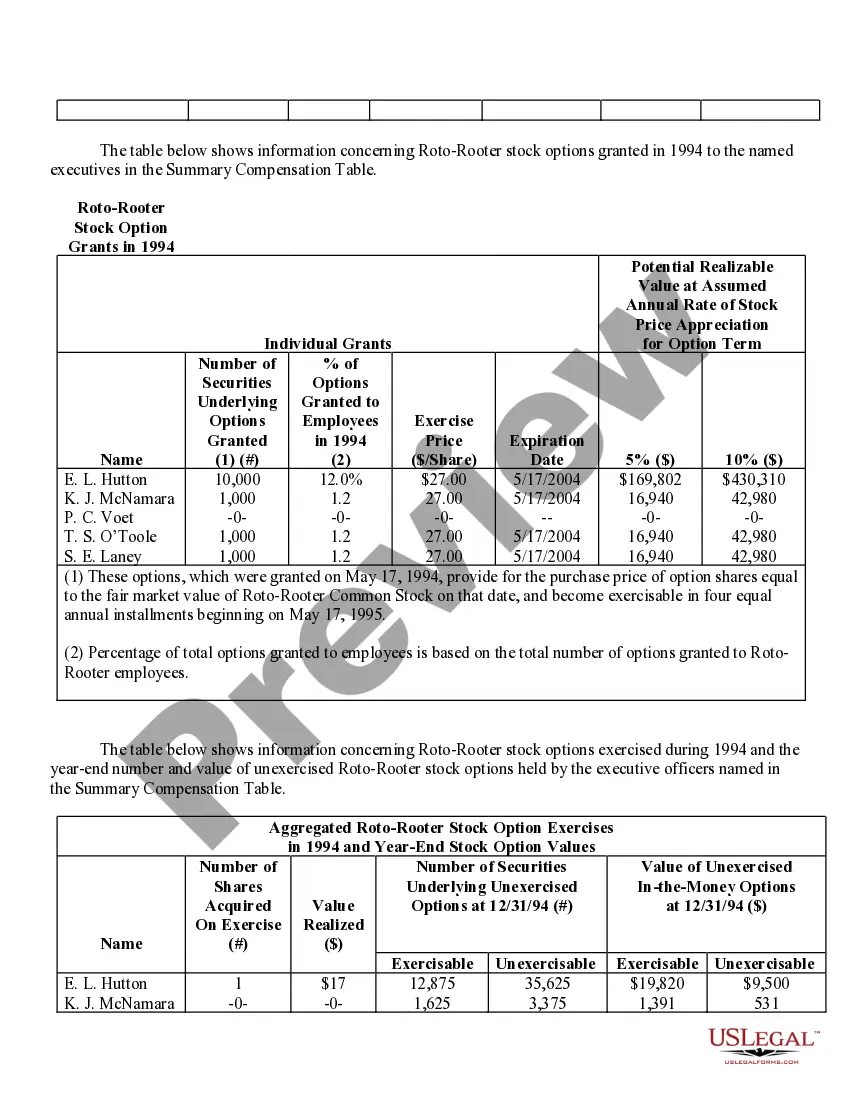
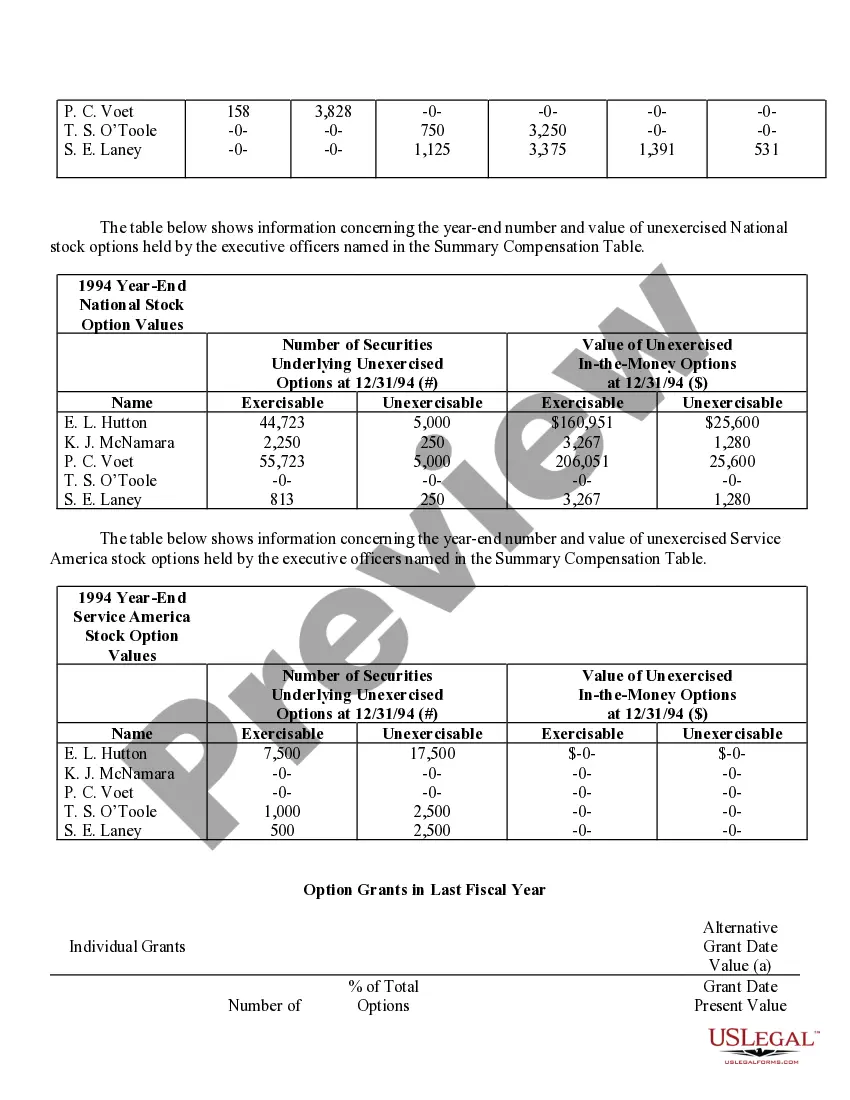
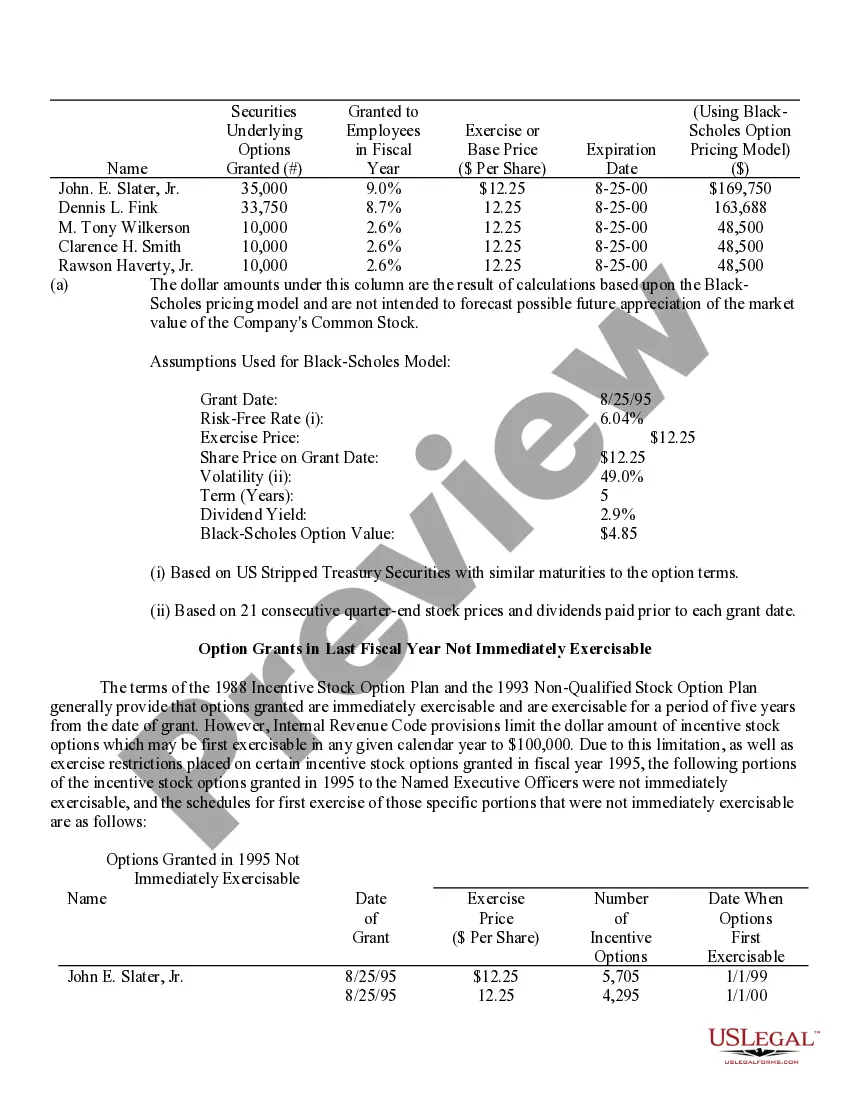
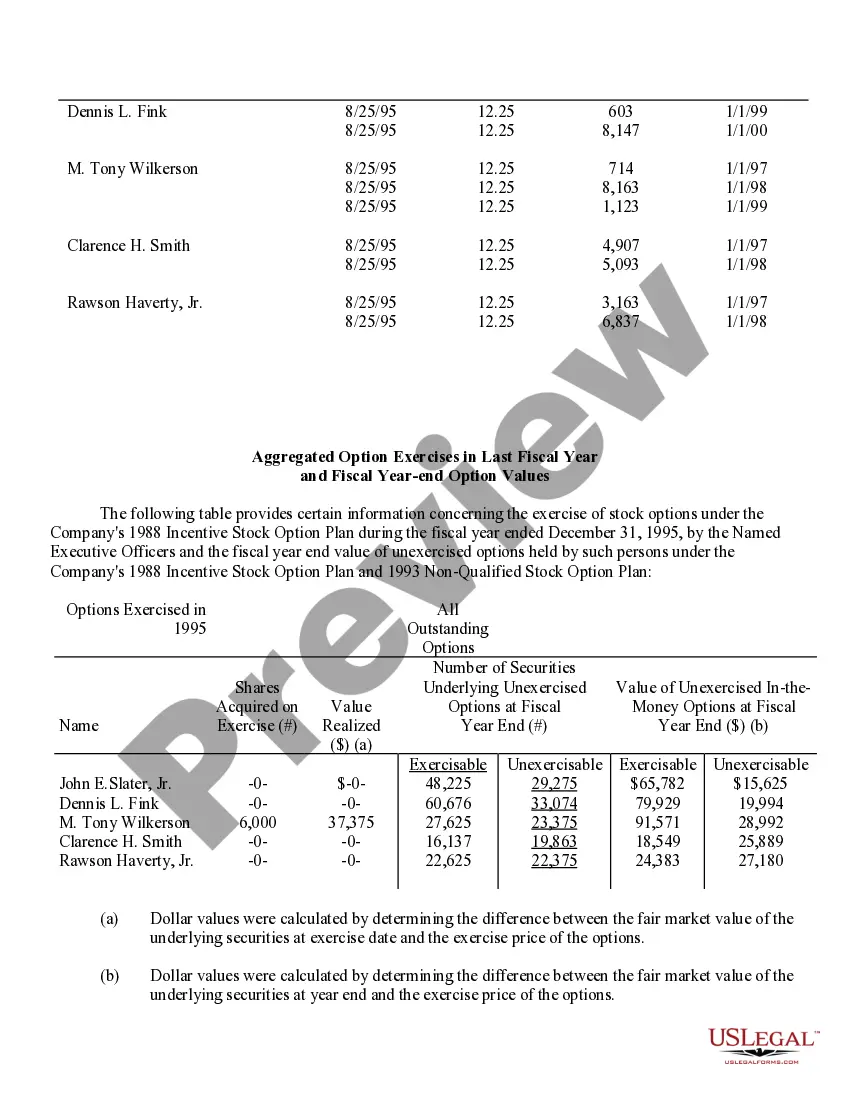
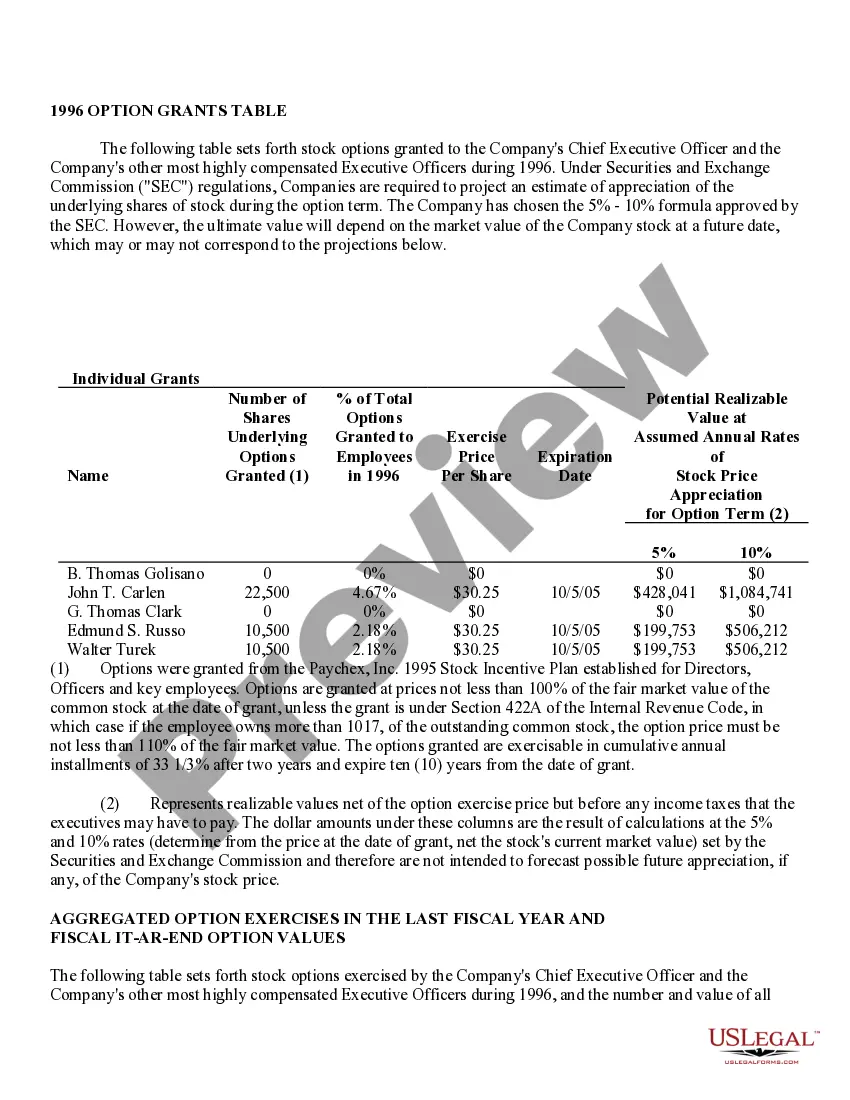
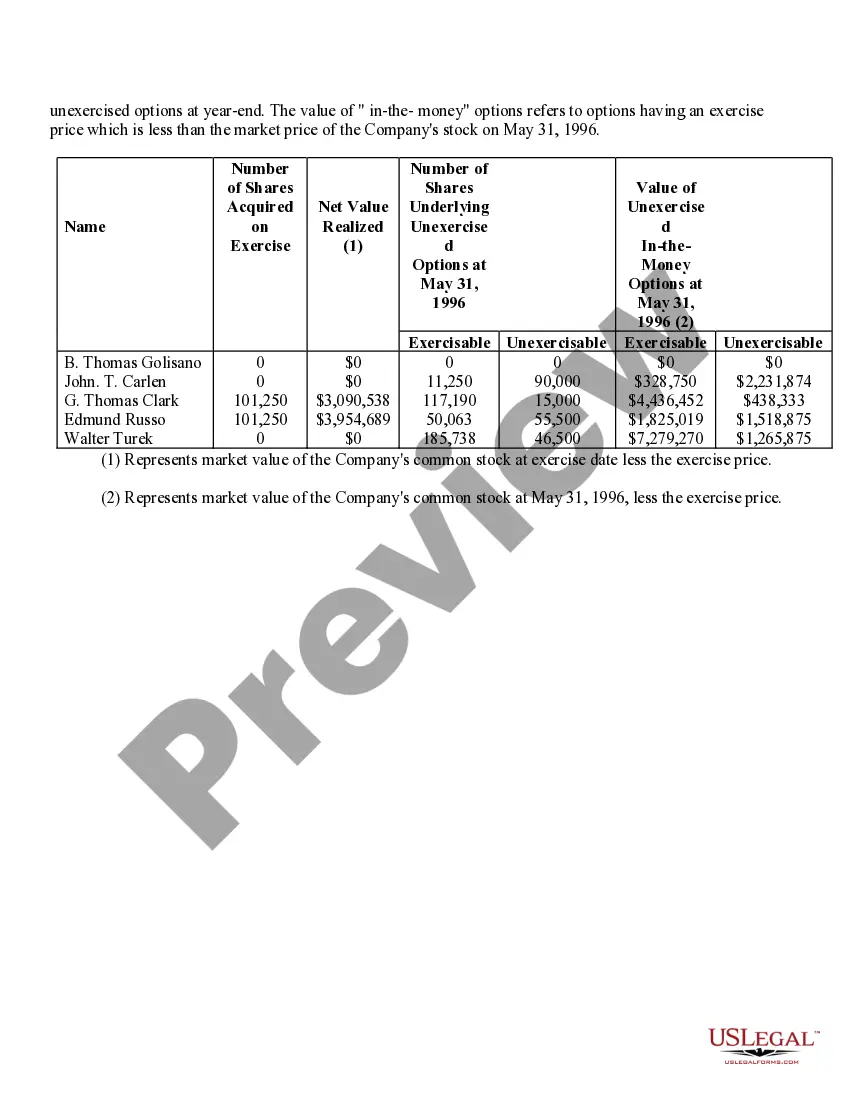
Fairfax Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values play a significant role in the compensation plans and financial reporting of companies in the area. This comprehensive system enables employees and executives to receive stock options as part of their compensation packages, subsequently allowing them to purchase company shares at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. Stock Option Grants: 1. Employee Stock Options: Employee stock options are one of the most common types of grants offered to employees by their companies as a form of incentive or reward. These grants typically come with specific terms and vesting schedules, where employees gradually earn the right to exercise the options over a set period. 2. Executive Stock Options: Executive stock options are typically granted to high-level executives, such as CEOs, CFOs, or other key personnel. These options often have different terms, vesting periods, and exercise prices compared to employee stock options, reflecting the executive's level of responsibility and contribution to the organization. Stock Option Exercises: 1. Cashless Exercise: Cashless exercise allows employees or executives to exercise their stock options without spending their own money. In this process, the individual borrows funds from a brokerage firm to purchase the shares, immediately sells a portion of those shares, and uses the proceeds to repay the loan. This method eliminates the need for personal funds and often provides immediate liquidity. 2. Direct Purchase: Direct purchase refers to exercising stock options by using personal funds to buy the shares at the predetermined exercise price. This method is suitable for individuals who have sufficient available funds or wish to hold the shares for potential long-term appreciation. 3. Stock Swap: Stock swap involves exercising stock options by exchanging existing company shares for the newly acquired shares. This method allows the individual to avoid using personal funds and can be useful in managing tax implications. Fiscal Year-End Values: 1. Fair Market Value (FMV): Fair market value is the estimated value of a company's shares at a particular time, typically used to determine the exercise price of stock options. FMV is crucial for accurate financial reporting, tax calculations, and ensuring that options are issued at a fair and reasonable price. 2. Option Value: Option value represents the current worth of an exercised stock option grant. It considers factors such as the current stock price, exercise price, and remaining time until expiration to calculate the potential value of the options. 3. Total Stock Option Expense: Total stock option expense refers to the cumulative value of all stock option grants given to employees or executives during a fiscal year. This figure is crucial for financial reporting purposes and determining the impact of stock option compensation on a company's financial statements. In summary, Fairfax Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values encompass various types of grants, exercise methods, and valuation metrics. These mechanisms serve to attract and retain talent, align employee interests with company growth, and accurately report the financial impact of stock-based compensation for businesses in the area.
Fairfax Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values play a significant role in the compensation plans and financial reporting of companies in the area. This comprehensive system enables employees and executives to receive stock options as part of their compensation packages, subsequently allowing them to purchase company shares at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. Stock Option Grants: 1. Employee Stock Options: Employee stock options are one of the most common types of grants offered to employees by their companies as a form of incentive or reward. These grants typically come with specific terms and vesting schedules, where employees gradually earn the right to exercise the options over a set period. 2. Executive Stock Options: Executive stock options are typically granted to high-level executives, such as CEOs, CFOs, or other key personnel. These options often have different terms, vesting periods, and exercise prices compared to employee stock options, reflecting the executive's level of responsibility and contribution to the organization. Stock Option Exercises: 1. Cashless Exercise: Cashless exercise allows employees or executives to exercise their stock options without spending their own money. In this process, the individual borrows funds from a brokerage firm to purchase the shares, immediately sells a portion of those shares, and uses the proceeds to repay the loan. This method eliminates the need for personal funds and often provides immediate liquidity. 2. Direct Purchase: Direct purchase refers to exercising stock options by using personal funds to buy the shares at the predetermined exercise price. This method is suitable for individuals who have sufficient available funds or wish to hold the shares for potential long-term appreciation. 3. Stock Swap: Stock swap involves exercising stock options by exchanging existing company shares for the newly acquired shares. This method allows the individual to avoid using personal funds and can be useful in managing tax implications. Fiscal Year-End Values: 1. Fair Market Value (FMV): Fair market value is the estimated value of a company's shares at a particular time, typically used to determine the exercise price of stock options. FMV is crucial for accurate financial reporting, tax calculations, and ensuring that options are issued at a fair and reasonable price. 2. Option Value: Option value represents the current worth of an exercised stock option grant. It considers factors such as the current stock price, exercise price, and remaining time until expiration to calculate the potential value of the options. 3. Total Stock Option Expense: Total stock option expense refers to the cumulative value of all stock option grants given to employees or executives during a fiscal year. This figure is crucial for financial reporting purposes and determining the impact of stock option compensation on a company's financial statements. In summary, Fairfax Virginia Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values encompass various types of grants, exercise methods, and valuation metrics. These mechanisms serve to attract and retain talent, align employee interests with company growth, and accurately report the financial impact of stock-based compensation for businesses in the area.