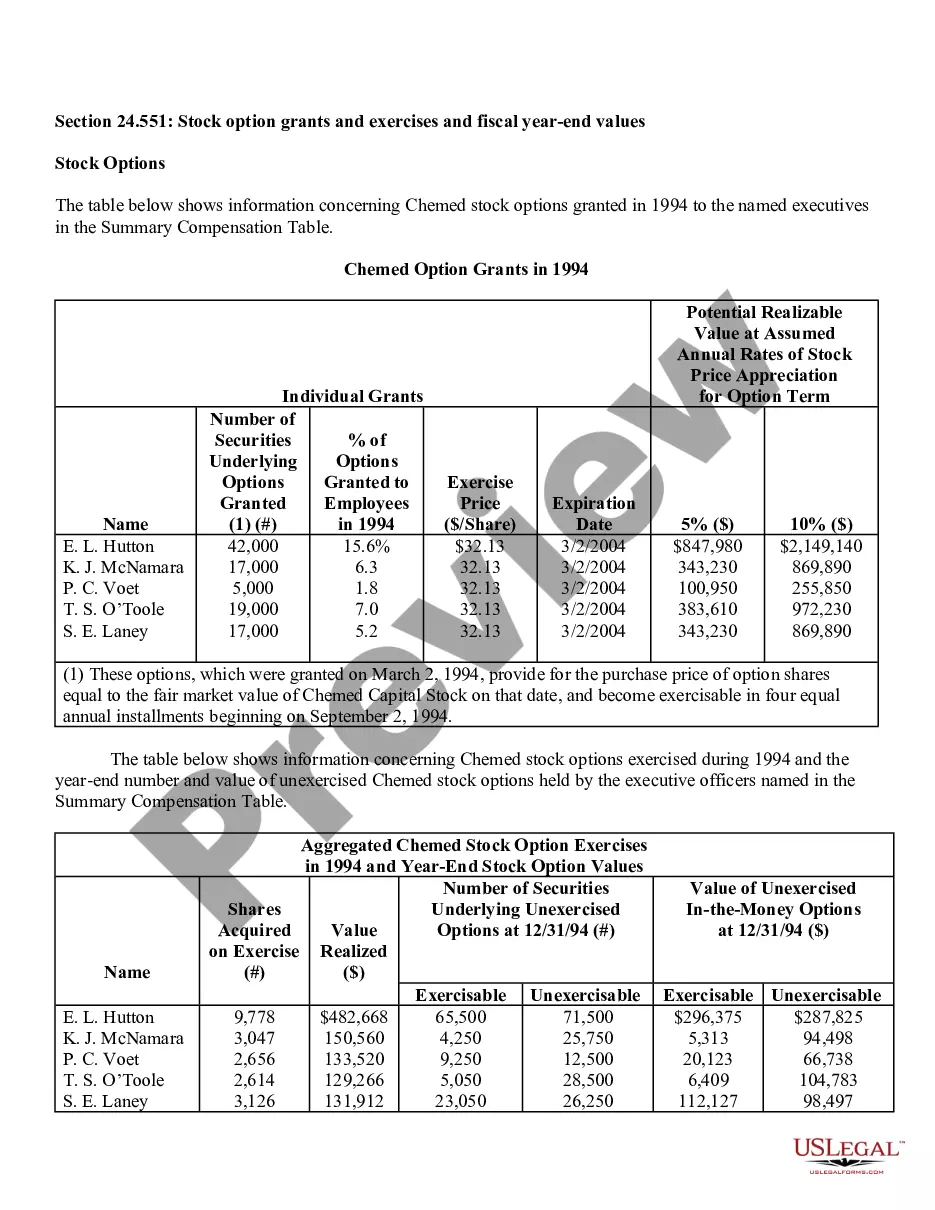
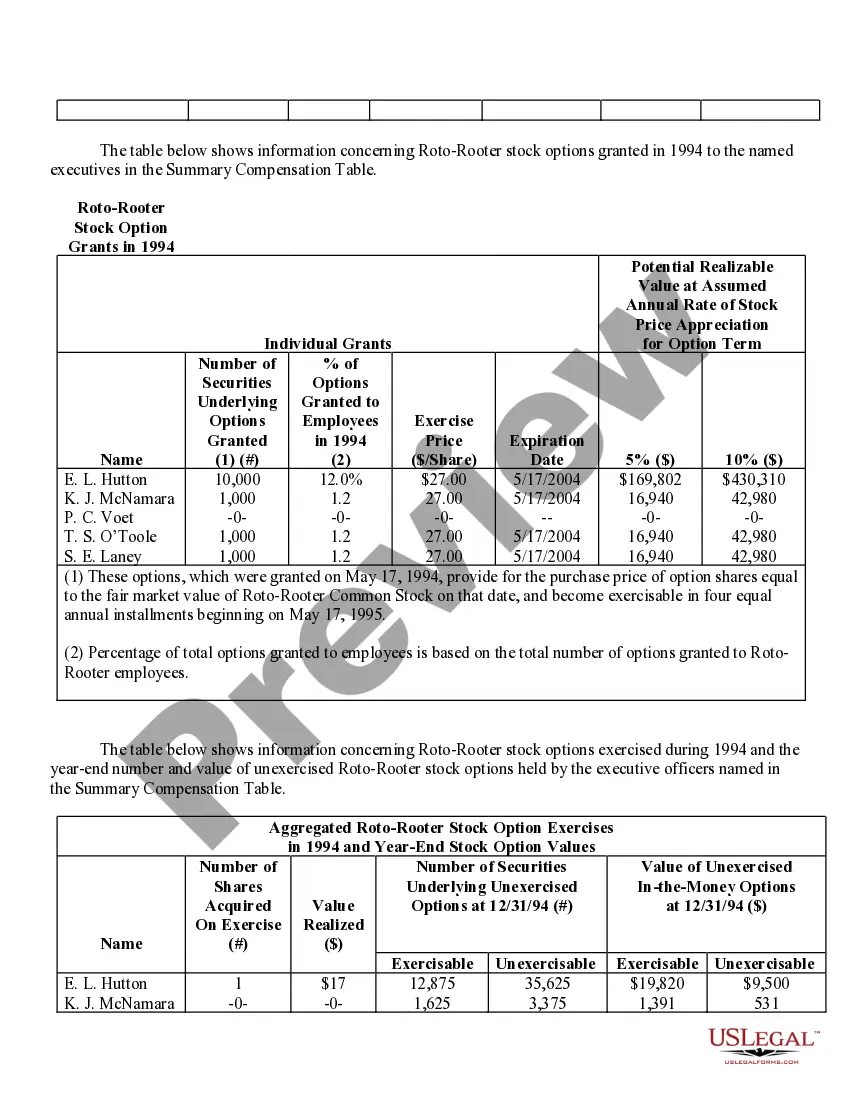
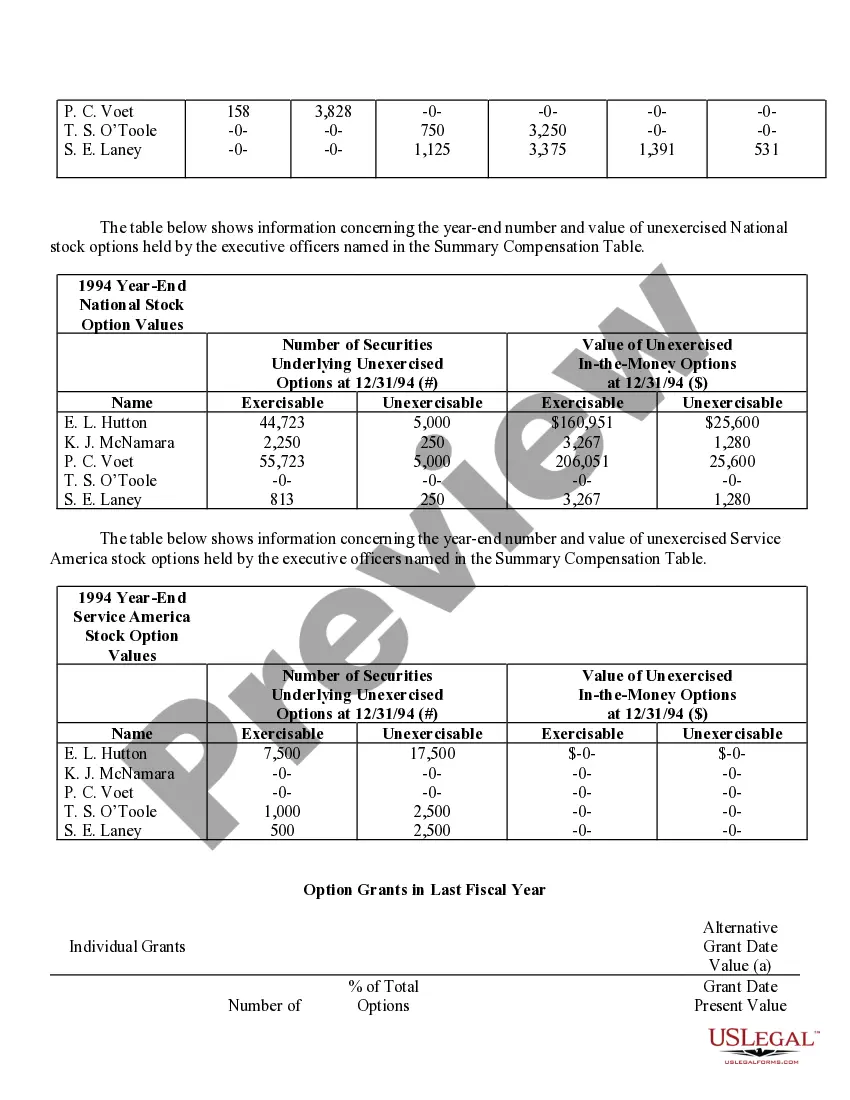
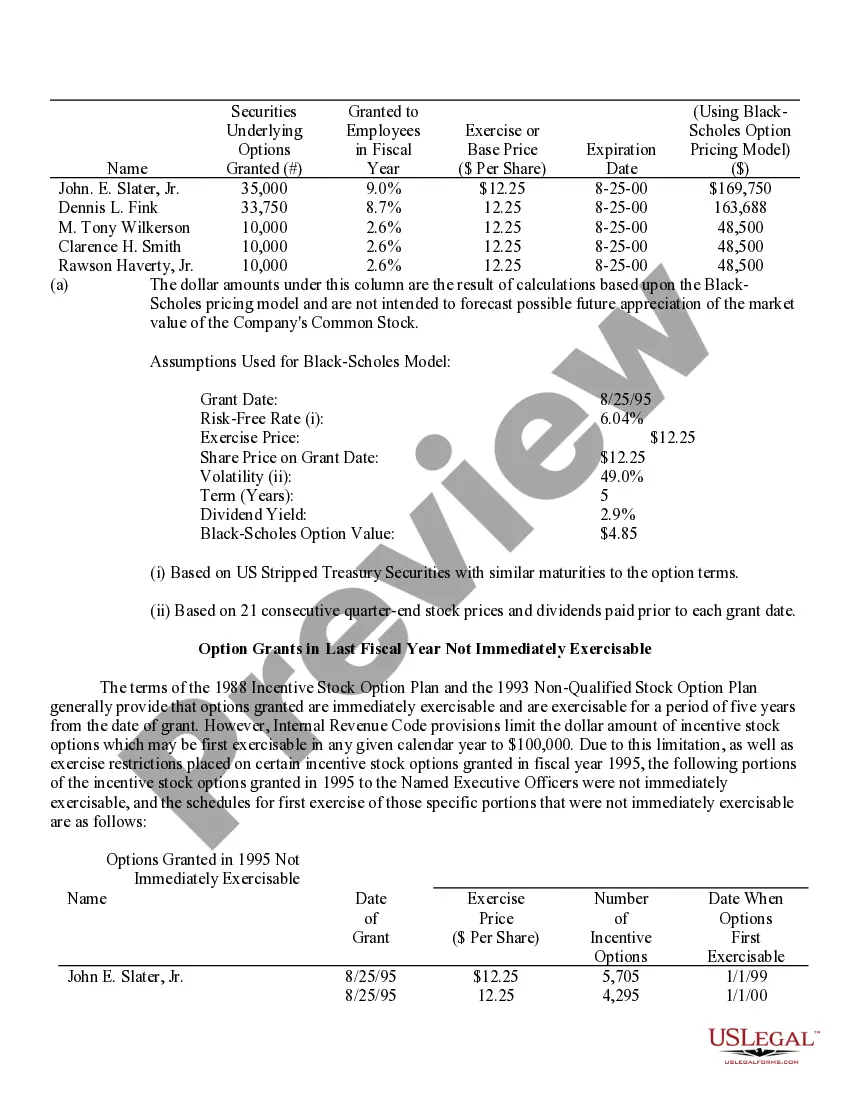
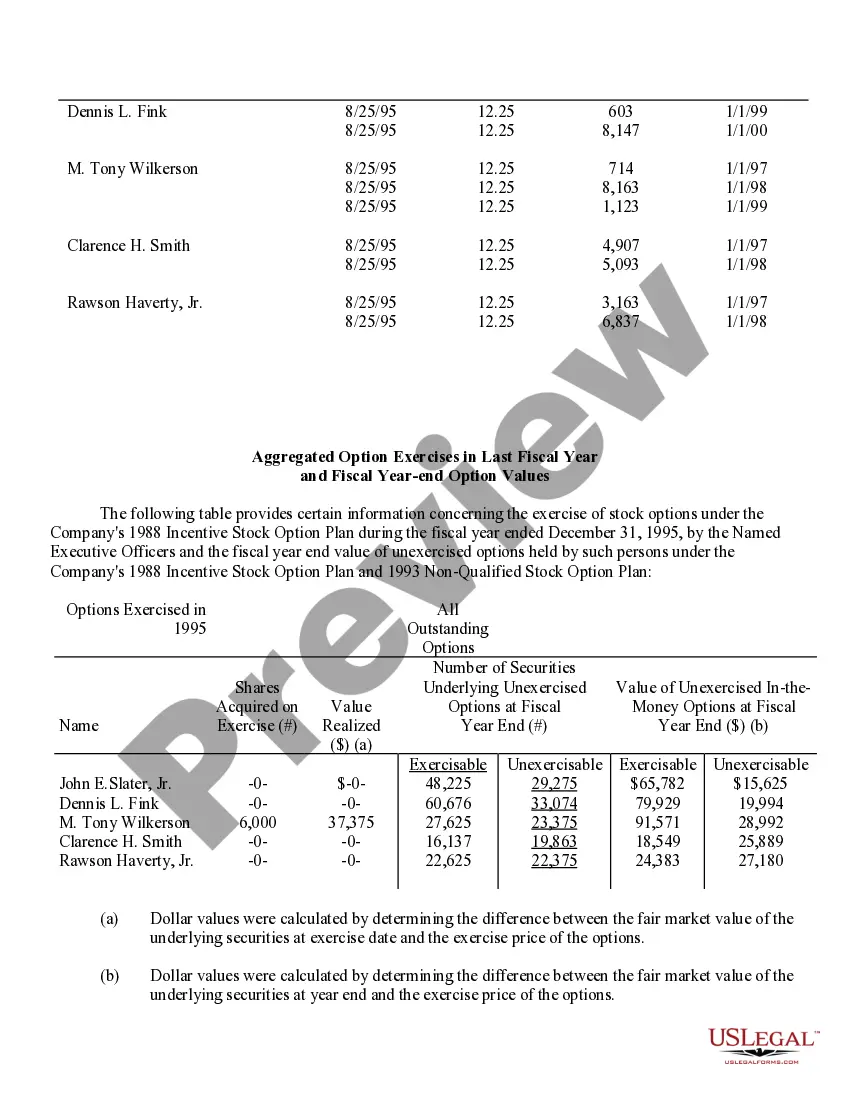
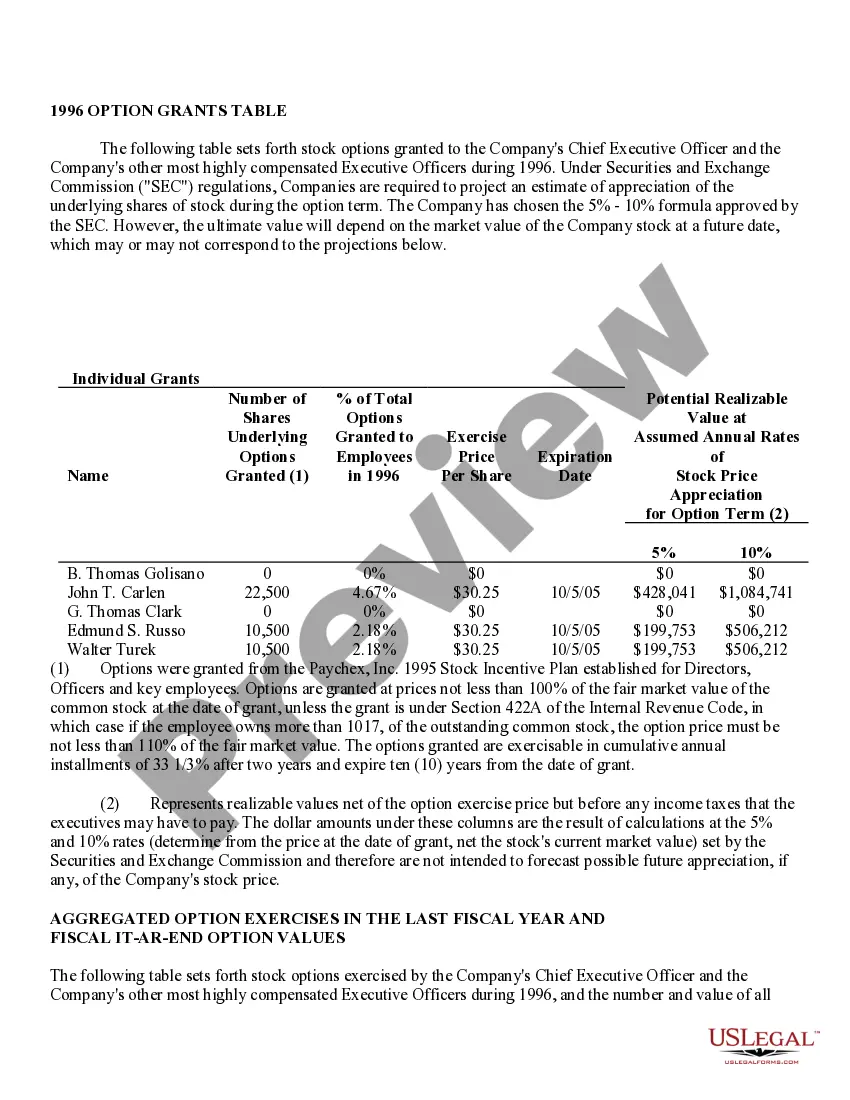
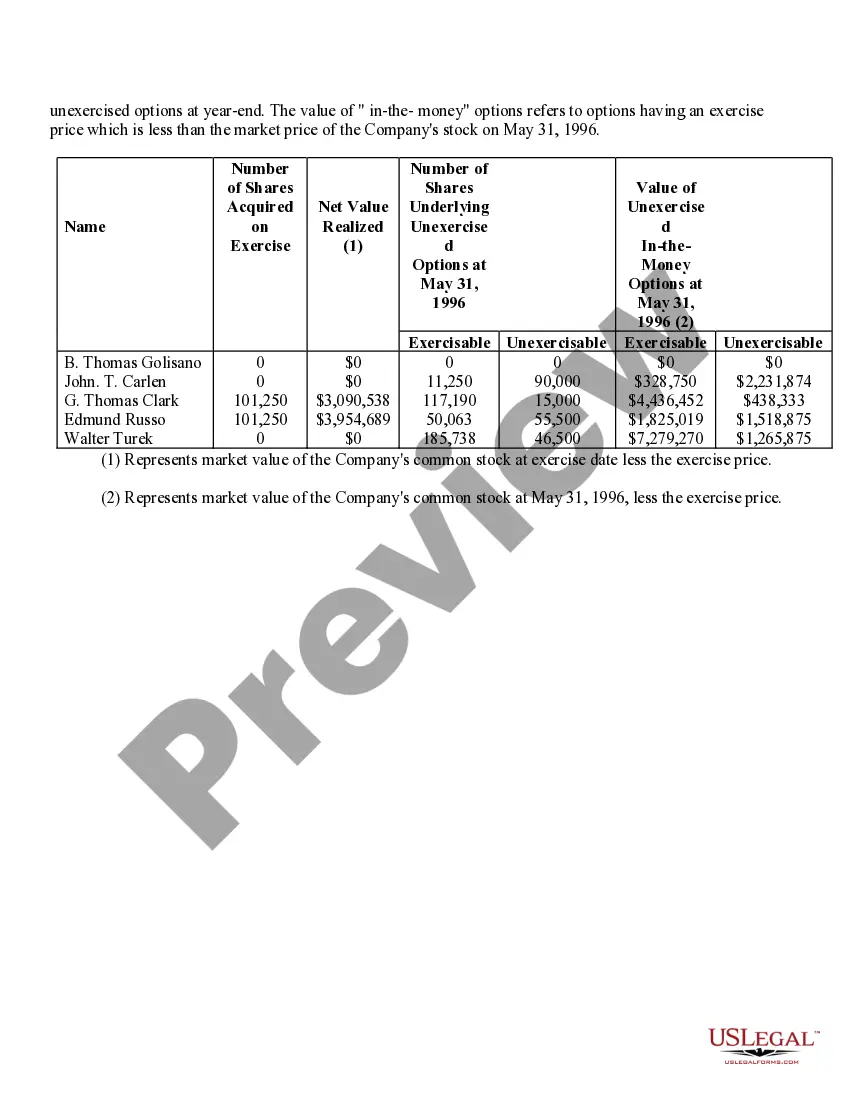
Houston Texas Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values play a crucial role in the financial landscape of companies in Houston, Texas. In the realm of employee compensation and retention strategies, stock options are a popular incentive offered to employees, giving them the opportunity to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, known as the exercise price or strike price. This description will delve into the various types of stock option grants and exercises available in Houston, Texas, and shed light on how fiscal year-end values impact these programs. 1. Incentive Stock Options (SOS): In Houston, Texas, companies often offer SOS to key employees as part of their compensation package. SOS confer tax advantages because the employees are not required to pay tax upon exercise. However, to qualify for these tax benefits, specific guidelines set by the IRS must be met. 2. Non-Qualified Stock Options (Nests): Unlike SOS, Nests do not conform to the IRS guidelines and do not enjoy the same tax advantages. These options are more flexible in terms of eligibility criteria, allowing companies to offer them more broadly to employees at different levels of the organization. 3. Restricted Stock Units (RSS): RSS represent an agreement between the company and the employee, promising the delivery of company stock at a future date or upon achieving certain performance milestones. RSS are often granted to employees as a reward for excellent performance or as a long-term incentive. They are not traditional stock options, but their value can be tied to the company's stock. When it comes to exercising stock options, employees in Houston must make a crucial decision. They can either exercise their options by purchasing the company stock at the agreed-upon exercise price or hold on to the options and wait for a more opportune moment to exercise. The timing of exercise is critical, as it determines the potential gains or losses associated with the stock options. Fiscal year-end values are of utmost importance in assessing the performance and valuation of the granted options. The fiscal year-end value refers to the price of the company's stock at the end of its fiscal year. This value directly impacts the financial outcome of exercising stock options. Employees who exercise their options when the stock price is higher than the exercise price benefit from a favorable price difference and potential capital gains. Conversely, if the fiscal year-end value is lower than the exercise price, employees may experience losses if they choose to exercise the options. Companies in Houston, Texas, carefully evaluate their stock option programs and fiscal year-end values to attract and retain top talent, align employee interests with company performance, and provide long-term incentives. By offering various types of stock options grants and exercises and monitoring fiscal year-end values, companies can strike a balance between employee motivation, tax advantages, and overall financial performance.
Houston Texas Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values play a crucial role in the financial landscape of companies in Houston, Texas. In the realm of employee compensation and retention strategies, stock options are a popular incentive offered to employees, giving them the opportunity to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, known as the exercise price or strike price. This description will delve into the various types of stock option grants and exercises available in Houston, Texas, and shed light on how fiscal year-end values impact these programs. 1. Incentive Stock Options (SOS): In Houston, Texas, companies often offer SOS to key employees as part of their compensation package. SOS confer tax advantages because the employees are not required to pay tax upon exercise. However, to qualify for these tax benefits, specific guidelines set by the IRS must be met. 2. Non-Qualified Stock Options (Nests): Unlike SOS, Nests do not conform to the IRS guidelines and do not enjoy the same tax advantages. These options are more flexible in terms of eligibility criteria, allowing companies to offer them more broadly to employees at different levels of the organization. 3. Restricted Stock Units (RSS): RSS represent an agreement between the company and the employee, promising the delivery of company stock at a future date or upon achieving certain performance milestones. RSS are often granted to employees as a reward for excellent performance or as a long-term incentive. They are not traditional stock options, but their value can be tied to the company's stock. When it comes to exercising stock options, employees in Houston must make a crucial decision. They can either exercise their options by purchasing the company stock at the agreed-upon exercise price or hold on to the options and wait for a more opportune moment to exercise. The timing of exercise is critical, as it determines the potential gains or losses associated with the stock options. Fiscal year-end values are of utmost importance in assessing the performance and valuation of the granted options. The fiscal year-end value refers to the price of the company's stock at the end of its fiscal year. This value directly impacts the financial outcome of exercising stock options. Employees who exercise their options when the stock price is higher than the exercise price benefit from a favorable price difference and potential capital gains. Conversely, if the fiscal year-end value is lower than the exercise price, employees may experience losses if they choose to exercise the options. Companies in Houston, Texas, carefully evaluate their stock option programs and fiscal year-end values to attract and retain top talent, align employee interests with company performance, and provide long-term incentives. By offering various types of stock options grants and exercises and monitoring fiscal year-end values, companies can strike a balance between employee motivation, tax advantages, and overall financial performance.