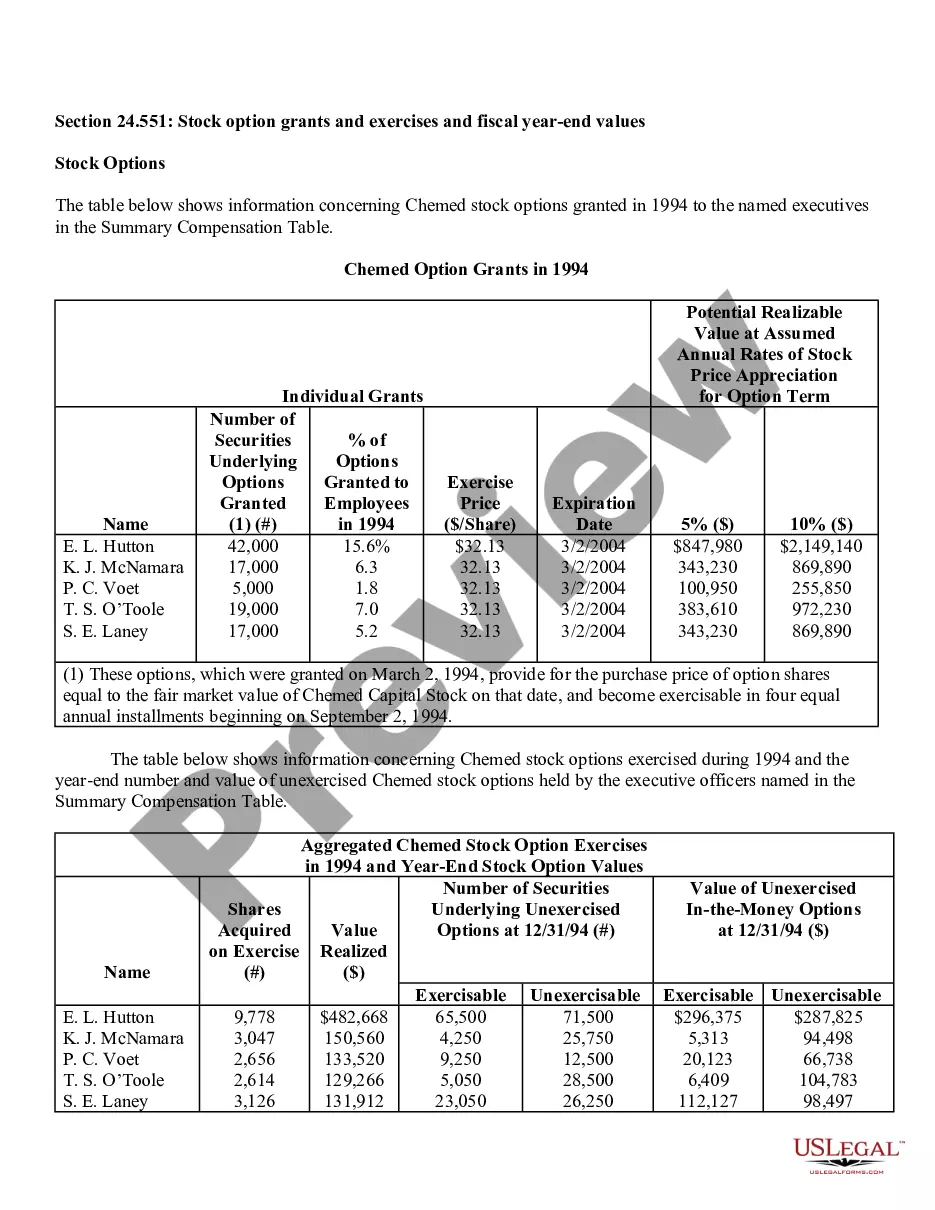
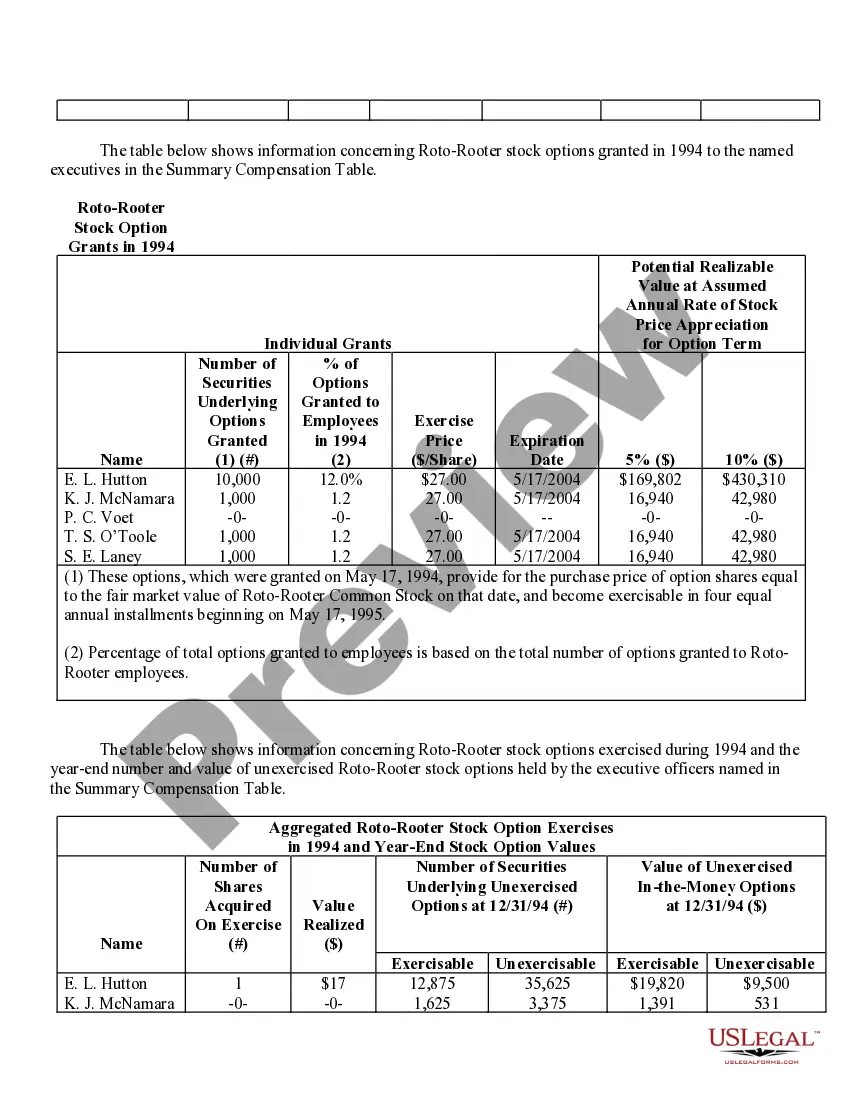
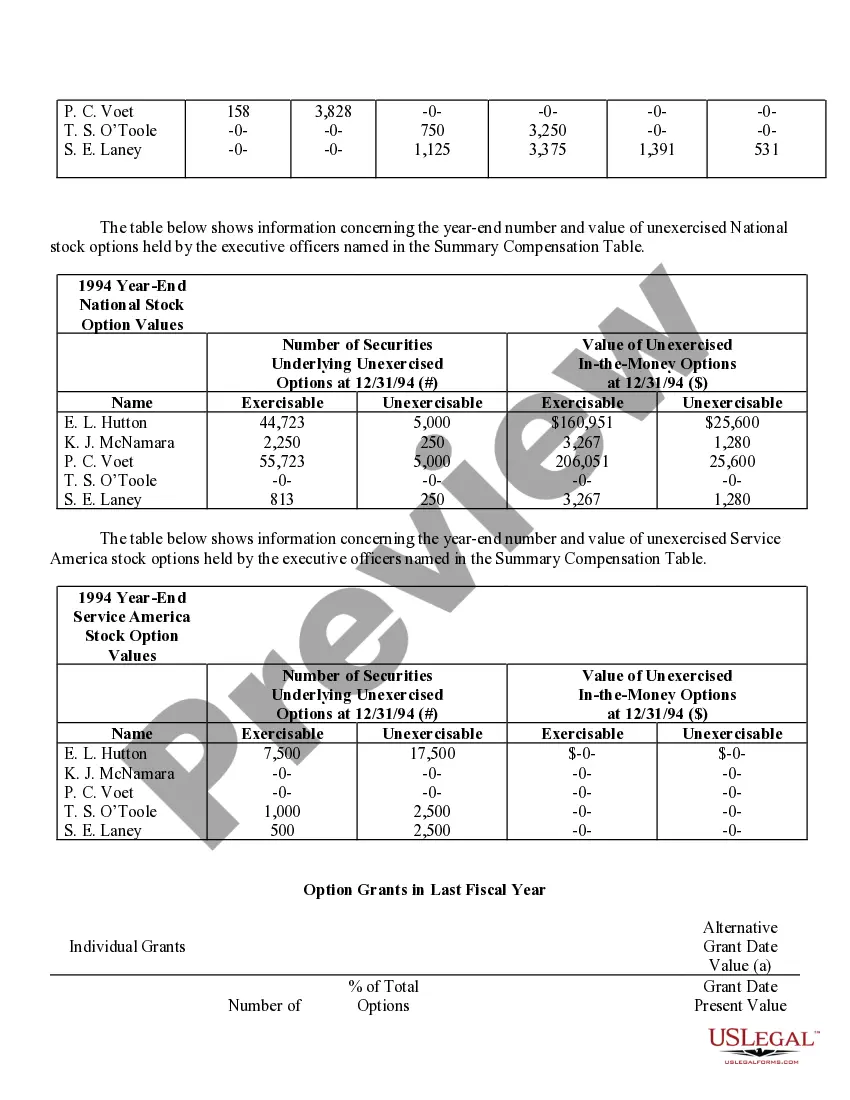
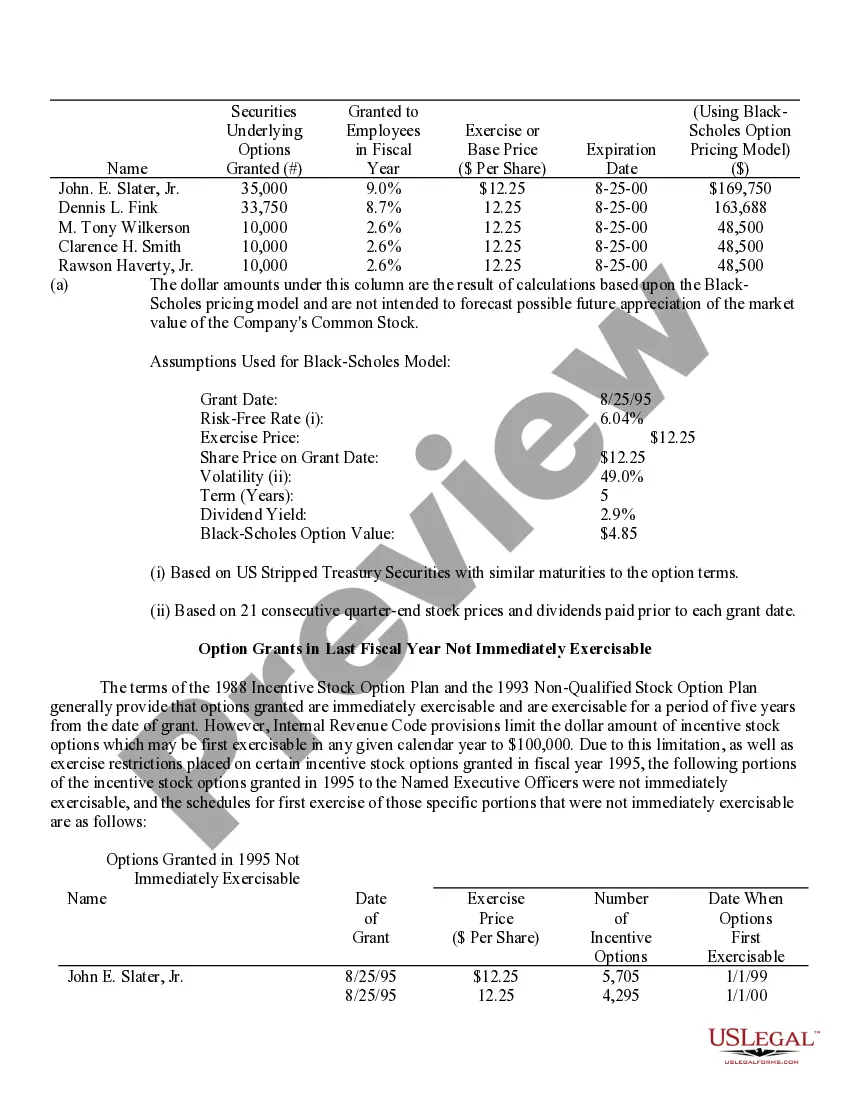
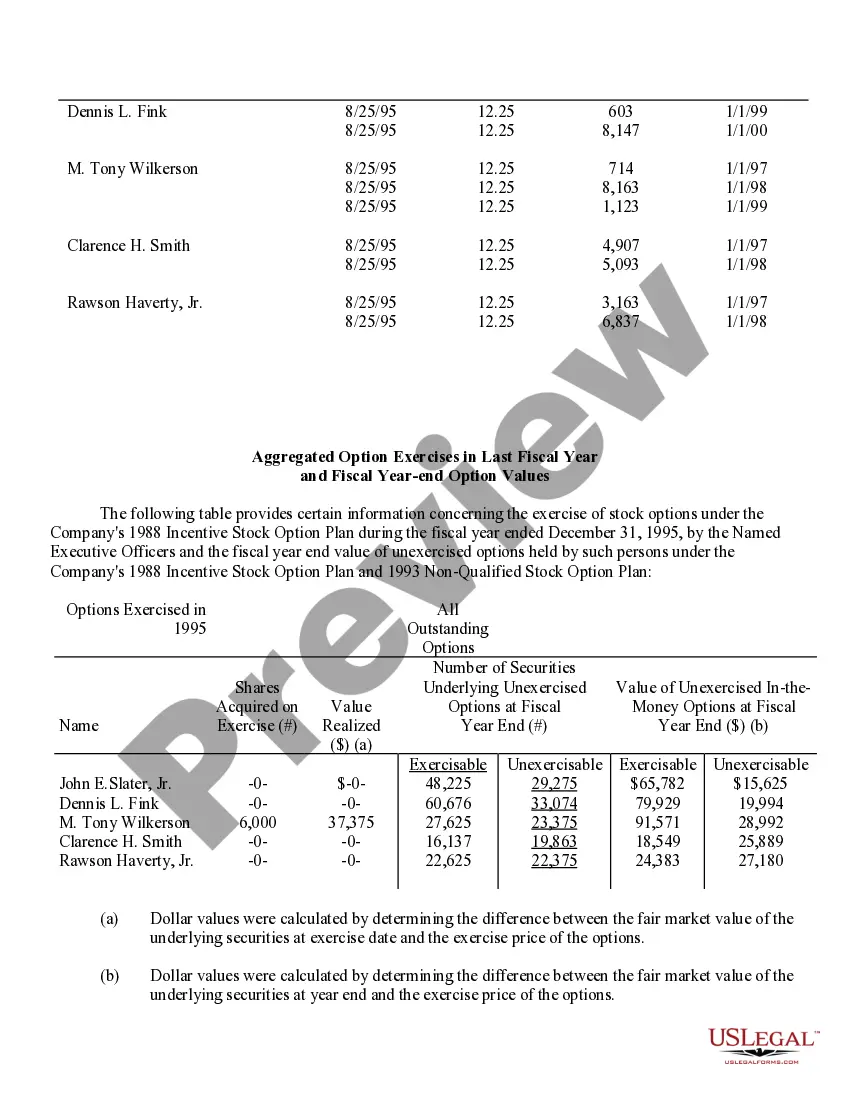
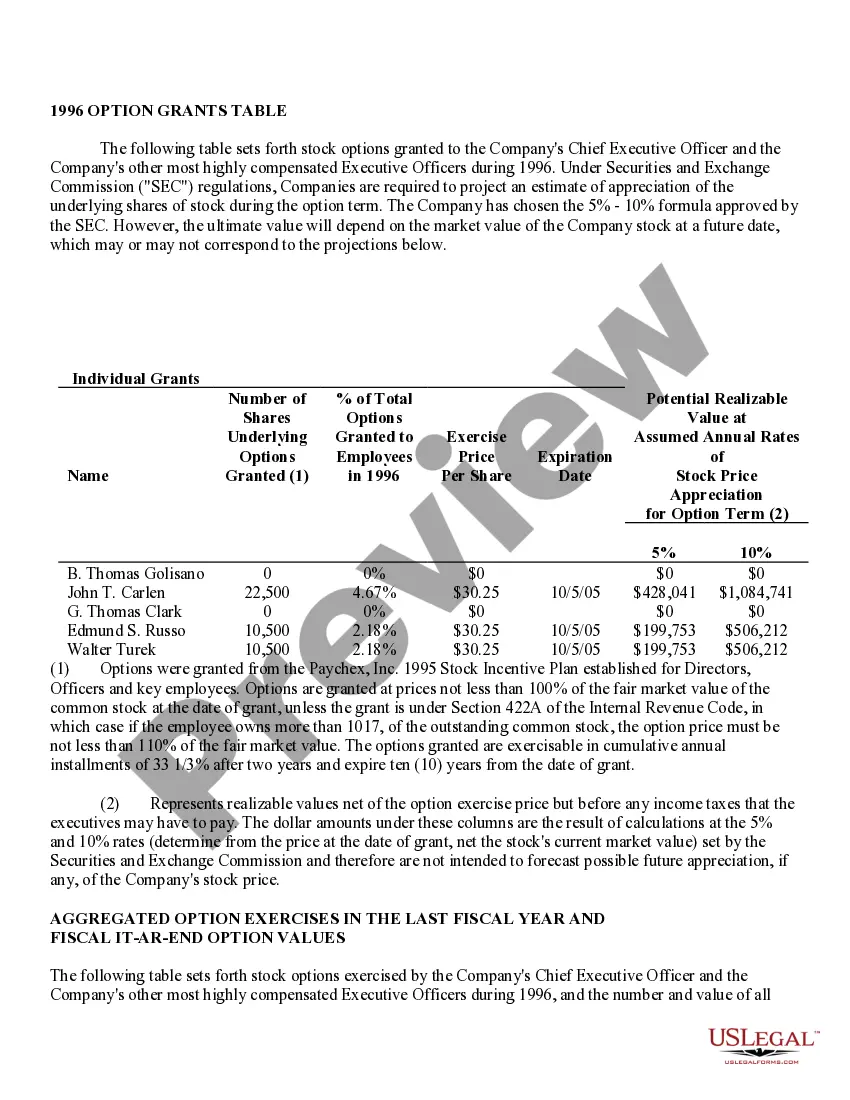
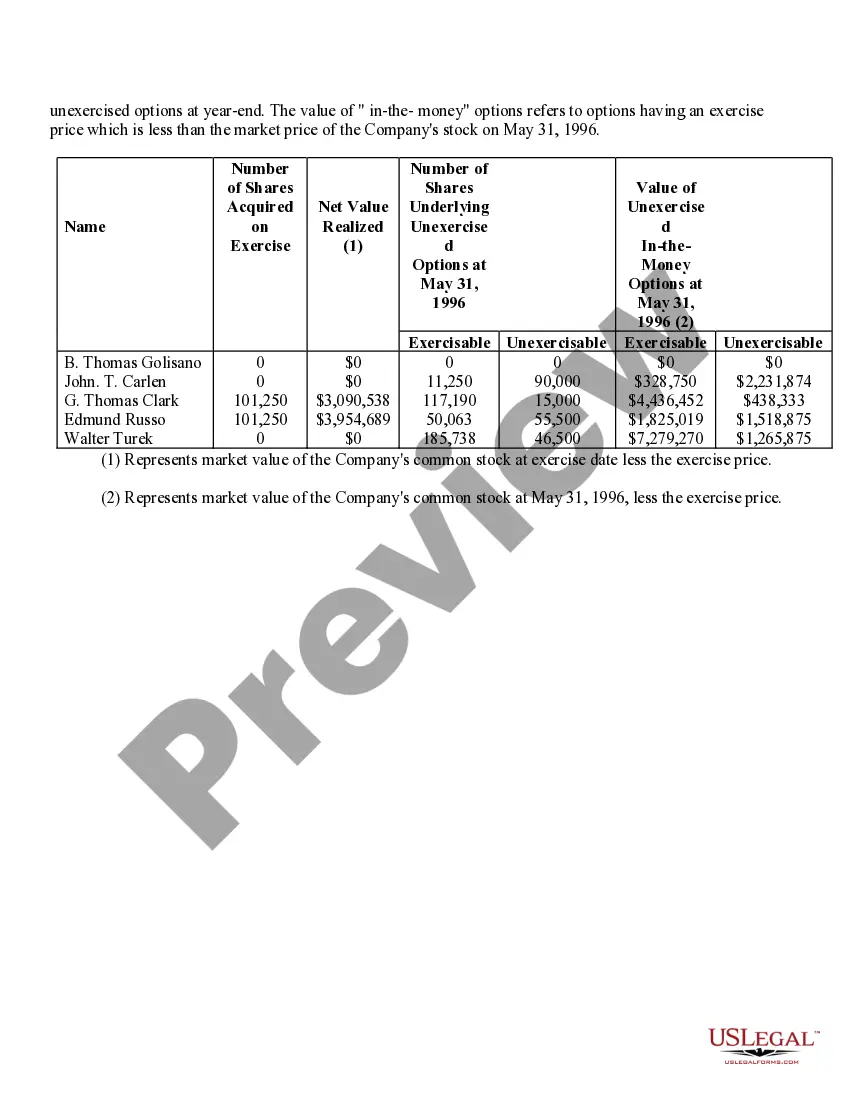
Phoenix Arizona Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values are important aspects of financial planning and employee compensation in the corporate world. Stock option grants refer to the process where employers provide employees with the opportunity to purchase company stock at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. In Phoenix, Arizona, stock option grants are commonly offered to attract, retain, and incentivize talented individuals in various industries. These grants can take different forms, such as Non-Qualified Stock Options (Nests) and Incentive Stock Options (SOS). Non-Qualified Stock Options (Nests) are commonly provided to employees as part of their compensation packages. These grants allow employees to purchase company stock at a predetermined exercise price, regardless of the market value at the time of exercise. Nests are typically subject to income tax upon exercise, and the gains or losses are treated as ordinary income or capital gains, respectively. On the other hand, Incentive Stock Options (SOS) are usually reserved for key employees and offer potential tax advantages. SOS allow employees to purchase company stock at a specified price, known as the strike price or exercise price. To benefit from advantageous tax treatment, SOS have specific rules regarding their granting, exercise, and sale. If employees hold SOS for a certain period and meet other requirements, they might qualify for favorable long-term capital gains tax rates upon the sale of the stock. Stock option exercises represent the act of executing the right to purchase company stock. Once an employee decides to exercise their stock options, they must pay the exercise price to acquire the shares. Depending on the type of option grant, tax implications and reporting requirements may arise at the time of exercise. Fiscal year-end values play a crucial role in assessing the financial impact of stock option grants for both employers and employees. At the end of each fiscal year, the fair value of the stock options is determined based on various factors such as the current stock price, exercise price, vesting schedule, expected risk, time until expiration, and market conditions. This valuation helps companies accurately account for stock options as an expense and provides employees with insight into the potential value of their grants. In conclusion, Phoenix Arizona Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values are essential components of employee compensation and financial planning in the region. By offering stock option grants, companies aim to attract and retain top talent, while employees can potentially benefit from future stock price appreciation and favorable tax treatment. Understanding the different types of stock options grants, exercise processes, and fiscal year-end values is crucial for both employers and employees to make informed financial decisions.
Phoenix Arizona Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values
Description
How to fill out Phoenix Arizona Stock Option Grants And Exercises And Fiscal Year-End Values?
How much time does it normally take you to create a legal document? Given that every state has its laws and regulations for every life situation, finding a Phoenix Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values suiting all local requirements can be exhausting, and ordering it from a professional lawyer is often pricey. Numerous online services offer the most popular state-specific documents for download, but using the US Legal Forms library is most advantegeous.
US Legal Forms is the most extensive online catalog of templates, collected by states and areas of use. Aside from the Phoenix Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values, here you can get any specific form to run your business or individual affairs, complying with your regional requirements. Specialists check all samples for their actuality, so you can be certain to prepare your documentation correctly.
Using the service is pretty easy. If you already have an account on the platform and your subscription is valid, you only need to log in, opt for the needed form, and download it. You can retain the document in your profile at any time later on. Otherwise, if you are new to the platform, there will be a few more steps to complete before you obtain your Phoenix Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values:
- Examine the content of the page you’re on.
- Read the description of the template or Preview it (if available).
- Search for another form utilizing the related option in the header.
- Click Buy Now once you’re certain in the selected document.
- Select the subscription plan that suits you most.
- Register for an account on the platform or log in to proceed to payment options.
- Pay via PalPal or with your credit card.
- Change the file format if necessary.
- Click Download to save the Phoenix Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values.
- Print the sample or use any preferred online editor to complete it electronically.
No matter how many times you need to use the acquired template, you can locate all the files you’ve ever downloaded in your profile by opening the My Forms tab. Give it a try!
Form popularity
FAQ
Employee stock options are offered by companies to their employees as equity compensation plans. These grants come in the form of regular call options and give an employee the right to buy the company's stock at a specified price for a finite period of time.
Assuming you stay employed at the company, you can exercise your options at any point in time upon vesting until the expiry date ? typically, this will span up to 10 years.
Statutory Stock Options You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option. You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss. However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income.
You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option. You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss. However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income.
Stock Options It appears on the W-2 with other income in: Box 1: Wages, tips, and other compensation. Box 3: Social Security wages (up to the income ceiling)
An employee stock option is a type of compensation that gives an employee the right to buy a number of shares of company stock at a specific price. This price is generally referred to as the ?strike price,? though other names for it include ?exercise price? and ?grant price.?
Exercising a stock option means purchasing the issuer's common stock at the price set by the option (grant price), regardless of the stock's price at the time you exercise the option. See About Stock Options for more information.
When you buy an open-market option, you're not responsible for reporting any information on your tax return. However, when you sell an option?or the stock you acquired by exercising the option?you must report the profit or loss on Schedule D of your Form 1040.
You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option. You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss. However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income.
Exercising a stock option means purchasing the issuer's common stock at the price set by the option (grant price), regardless of the stock's price at the time you exercise the option. See About Stock Options for more information.