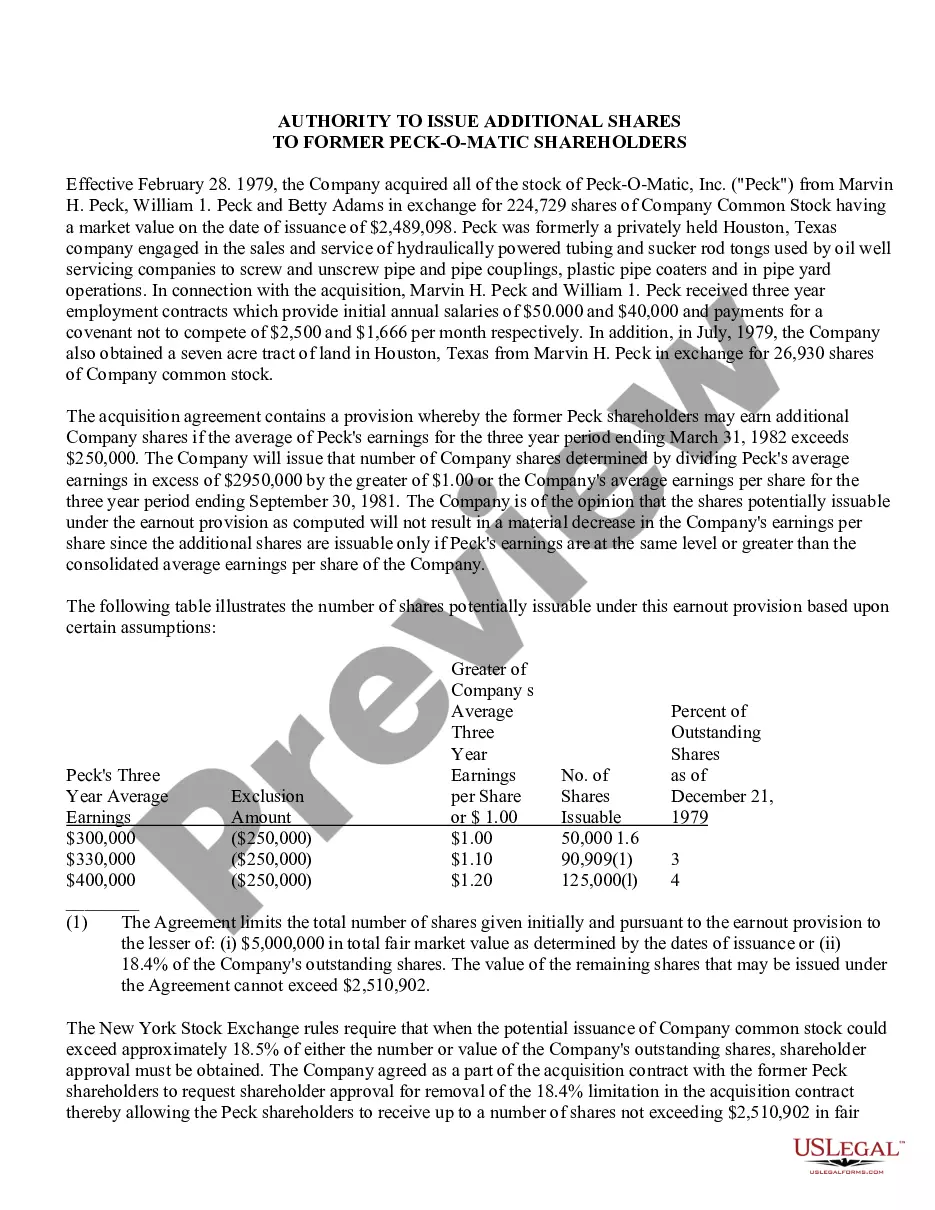
In Maricopa, Arizona, the security ownership of directors, nominees, and officers plays a crucial role in understanding the corporate structure and decision-making processes of various companies. This detailed description aims to shed light on the different types of security ownership, including sole and shared ownership, held by these key individuals. Sole Ownership: Sole ownership refers to instances where a single director, nominee, or officer possesses exclusive control and ownership over a particular security. This means that they are the sole shareholder and have full authority over the security without any shared rights or responsibilities. In Maricopa, Arizona, several directors, nominees, and officers may hold sole ownership of securities in different companies within various industries. Shared Ownership: Shared ownership, on the other hand, denotes a scenario where multiple directors, nominees, or officers collectively own a specific security. This type of ownership can be divided into different categories: 1. Joint Ownership: Joint ownership suggests that multiple individuals hold equal shares of ownership in a security. Each individual possesses an undivided interest in the security, and decisions regarding the security must be made jointly by all individuals involved. 2. Tenancy in Common: In Maricopa, Arizona, another form of shared ownership is tenancy in common. This type of ownership allows multiple directors, nominees, or officers to hold varying percentages or proportions of ownership in a particular security. Unlike joint ownership, each individual's share is distinct, and they have the autonomy to transfer, sell, or gift their portion of the ownership. 3. Community Property: Community property ownership is particularly relevant in Maricopa, Arizona, as the state follows community property laws. If a director, nominee, or officer acquires a security during their marriage or registered domestic partnership, it may be considered community property. This implies that both spouses or partners share equal ownership and control over the security, ensuring their joint decision-making authority. It is important to note that the extent of security ownership, whether sole or shared, can significantly impact corporate decision-making processes, voting rights, and overall governance within a company. Understanding the different types of ownership held by directors, nominees, and officers in Maricopa, Arizona, allows for a comprehensive understanding of the power dynamics within corporate structures in the region.
Maricopa Arizona Security ownership of directors, nominees and officers showing sole and shared ownership
Description
How to fill out Maricopa Arizona Security Ownership Of Directors, Nominees And Officers Showing Sole And Shared Ownership?
Whether you plan to start your company, enter into a deal, apply for your ID renewal, or resolve family-related legal concerns, you must prepare certain documentation meeting your local laws and regulations. Finding the correct papers may take a lot of time and effort unless you use the US Legal Forms library.
The service provides users with more than 85,000 professionally drafted and checked legal templates for any personal or business occurrence. All files are collected by state and area of use, so opting for a copy like Maricopa Security ownership of directors, nominees and officers showing sole and shared ownership is quick and simple.
The US Legal Forms website users only need to log in to their account and click the Download button next to the required template. If you are new to the service, it will take you several more steps to get the Maricopa Security ownership of directors, nominees and officers showing sole and shared ownership. Adhere to the guide below:
- Make certain the sample fulfills your personal needs and state law regulations.
- Look through the form description and check the Preview if available on the page.
- Make use of the search tab providing your state above to locate another template.
- Click Buy Now to get the sample when you find the proper one.
- Choose the subscription plan that suits you most to continue.
- Log in to your account and pay the service with a credit card or PayPal.
- Download the Maricopa Security ownership of directors, nominees and officers showing sole and shared ownership in the file format you require.
- Print the copy or complete it and sign it electronically via an online editor to save time.
Documents provided by our website are multi-usable. Having an active subscription, you are able to access all of your previously purchased paperwork at any time in the My Forms tab of your profile. Stop wasting time on a constant search for up-to-date formal documentation. Join the US Legal Forms platform and keep your paperwork in order with the most comprehensive online form collection!
Form popularity
FAQ
A registered owner or record holder holds shares directly with the company. A beneficial owner holds shares indirectly, through a bank or broker-dealer.
Registered Securityholder means a holder of Securities whose name appears in the register of holders of Common Shares or Warrants, as applicable, maintained by or on behalf of the Company as of the Record Date.
2. What is Beneficial Ownership? By way of a preliminary definition, a beneficial owner is usually defined as the natural person who has power to exercise controlling influence over the voting rights attached to shares.
For example, when shares of a mutual fund are held by a custodian bank or when securities are held by a broker in street name, the true owner is the beneficial owner, even though, for safety and convenience, the bank or broker holds the title.
A registered owner is the depository who holds the securities in his name. 2. A beneficial owner is the person whose name is recorded as such with the depository.
Beneficial owner refers to the natural person(s) who ultimately own(s) or control(s) a customer and/or the natural person on whose behalf a transaction is being conducted. It also includes those persons who exercise ultimate effective control over a legal person or arrangement.
The owner of shares in the company is a shareholder (or stockholder) of the corporation. A share is an indivisible unit of capital, expressing the ownership relationship between the company and the shareholder.
A holder of record is the person who is the registered owner of a security and who has the rights, benefits, and responsibilities of ownership. For a stock, the holder of record typically has shareholder voting rights and receives dividend payouts, if there are any.
The beneficial owner of a security generally includes any person who, directly or indirectly, through any contract, arrangement, understanding, relationship or otherwise has or shares one or both of the following: Voting power, which refers to the power to vote or direct someone else to vote the security.
More info
The City Of Chandler Board of Supervisors, pursuant to the powers vested in them by City Ordinance, adopted an Election Code and Ordinance that is now effective, which was submitted for the approval of the Mayor and the Board of Supervisors. Ordinance C.4.2017 is hereby adopted by the City of Chandler, Arizona, on January 11, 2016, and is applicable to all official actions of the City. The Elections Code and Ordinance C.4.
Disclaimer
The materials in this section are taken from public sources. We disclaim all representations or any warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, authenticity, reliability, accessibility, adequacy, or completeness of any data in this paragraph. Nevertheless, we make every effort to cite public sources deemed reliable and trustworthy.